This document discusses chemical kinetics and reaction rates. It defines kinetics as the study of reaction rates and mechanisms. Reaction rates describe how quickly reactions occur, while thermodynamics determines whether reactions can occur. The rate of a reaction is the change in concentration of reactants or products over time. Reaction mechanisms involve the molecular steps of reactions. Rate laws are determined experimentally and describe the dependence of reaction rates on reactant concentrations. Integrated rate laws relate concentration to time for reactions and can be used to determine amounts of reactants or products over time. First-order reactions follow integrated rate laws of ln[A] = -kt or [A] = [A]0e-kt, where k is the rate constant and t is time.
![Definitions/Terminology
Kinetics is the study of rates of chemical
reactions and the mechanisms (pathways) by
which they occur.
3
• The rate is the increase in concentration of a
product per unit time or decrease in concentration of
a reactant per unit time.
• Rates have units of +/-[conc/time] (e.g., Molar/sec).
• A mechanism is the series of molecular steps by
which a reaction occurs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-2-320.jpg)
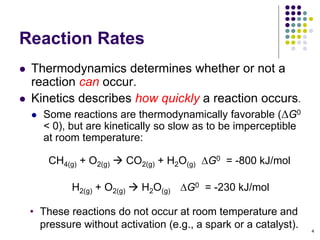
![Reaction Rates
5
• Rates define the velocity at which reactants
disappear or products appear
• Rates have units of [concentration/time].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-4-320.jpg)
![Reaction Rates
6
• in many reactions, the coefficients of reactants and products in
the balanced equation are not all the same, for example:
H2 (g) + I2 (g) 2 HI(g)
For every 1 mole of H2 consumed, 1 mole of I2 will also be
consumed, and 2 moles of HI will be produced.
The rate of disappearance of [H2] and [I2] will, therefore, be
½ the rate of appearance of [HI].
• The rate of the overall reaction is, thus, the change in the
concentration of each substance multiplied by
1/[coefficient in the balanced equation]:
Rate = -
D[H2 ]
Dt
= -
D[I2 ]
Dt
= +
1
2
æ
è
ç
ö
ø
÷
D[HI]
Dt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-5-320.jpg)
![Reaction Rates
7
For [H2], the
instantaneous
rate at 50 s is:
For [HI], the
instantaneous
rate at 50 s is:
s
M0.0070Rate
s40
M28.0Rate
s
M0.0070Rate
s40
M56.0
2
1Rate
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-6-320.jpg)
![Reaction Rates
Mathematically, the rate of a generic reaction:
aA + bB --> cC + dD can be written as:
For X = A, B, C or D, [X] = [X]t - [X]0, where
[X]t is concentration at time, t after the start of the reaction, and [X]0 is
the initial concentration at the beginning of the reaction, t = 0.
Minus sign indicates that the reactants concentrations decrease with
time.
8
• For example, for a reaction 2A B:
Rate = -(1/2)[A]/t = [B]/t
• Rates are often approximated as instantaneous
rates, and the notation of calculus is used:
Rate = -1/2d[A]/dt = d[B]/dt
The rate equation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-7-320.jpg)
![Reaction Rates
The rate of a simple one-reactant, one-step reaction
is directly proportional to the concentration of the
reacting substance:
Rate has units of conc/unit time (e.g., Ms-1)
[A] is the concentration of A, e.g., in molarity (M).
The proportionality constant, k is called the rate constant.
For this simple expression, k must have units of inverse
time (e.g., s-1).
Rate constants are always positive numerical quantities. 9
A B + C
rate [A] or rate = k[A] the rate law expression
(different from the rate eqn!)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-8-320.jpg)
![Reaction Rates
For the simple expression, rate = k[A]:
If the initial concentration of A is doubled, the
initial rate of the reaction is doubled.
If the initial concentration of A is halved, the
initial rate of reaction is cut in half.
The initial rate is, thus, directly proportional to
the initial [A].
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-9-320.jpg)
![Reaction Rates
If more than one reactant molecule appears in
the chemical equation for a one-step reaction:
2A B + C
The experimentally determined rate law is:
rate = k[A]2
11
• This relationship means that, If [A] is doubled,
the rate increases by a factor of 4 (= 22).
• If initial [A] is halved, the initial rate decreases
by a factor of 4 (=(1/2)2).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-10-320.jpg)
![Reaction Rates
Rate = k[X] or rate = k[X]2 are examples of a rate
law.
12
Rate laws can only be determined experimentally.
The rate law cannot be determined from the balanced
chemical equation because:
most chemical reactions are not one-step reactions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-11-320.jpg)
![Reaction Rates
The order of a reaction expresses:
the dependence on the concentrations of each reactant in the rate
law (= the exponent for each concentration).
the sum of the orders for each reactant.
13
• For the reaction:
N2O5(g) 2NO2(g) + 1/2O2(g)
The experimentally determined rate law is:
rate = k[N2O5]
• The reaction is said to be first order in N2O5 and first
order overall.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-12-320.jpg)
![Reaction Rates
First order reactions are dependent on the
concentration of only a single reactant.
First order reactions are common for many
chemical reactions and all simple radioactive
decays.
14
Two examples of first order reactions:
2N2O5(g) 2 N2O4(g) + O2(g)
238U 234Th + 4He
Rate = k[N2O5]
Rate = k[238U]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-13-320.jpg)
![Reaction Rates
15
• For the reaction:
2NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g)
• The experimentally determined rate law is:
rate = k[NO]2[O2]
• This reaction is second order in NO, first
order in O2 and third order overall.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-14-320.jpg)
![Reaction Rates
16
• For the reaction:
(CH3)3CBr(aq) + OH-
(aq) (CH3)3COH(aq) + Br -
(aq)
The experimentally determined rate law is:
rate = k[(CH3)3CBr]
• This reaction is first order in (CH3)3CBr and
zero order in OH- and first order overall.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-15-320.jpg)
![Concentrations of Reactants:
The Rate-Law Expression
Example 1: The following rate data were obtained at 25oC for
the reaction: 2A(g) + B(g) 3C(g)
What are the rate law and rate constant for this reaction?
Experiment
Number
Initial [A]
(M)
Initial [B]
(M)
Initial rate
(M/s)
1 0.10 0.10 2.0 x 10-4
2 0.20 0.10 4.0 x 10-4
3 0.10 0.20 2.0 x 10-4
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-16-320.jpg)
![Concentrations of Reactants:
The Rate-Law Expression
23
• Compare experiments 1 and 3.
• When [A] is held constant and [B] is doubled, the
rate does not change.
• The reaction is zeroth order in [B].
• The rate law can be written generically as:
Rate = k[A]x[B]y
• The rate law requires experimental
determination of the exponents, x and y.
• Therefore, y = 0 and the rate law reduces to:
Rate = k[A]x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-17-320.jpg)
![Concentrations of Reactants:
The Rate-Law Expression
24
• Next compare experiments 1 and 2.
• If [A] is doubled, the rate increases by a
factor of 2.
• Therefore, (2)x = 2 and x = 1.
• The rate law reduces to:
rate = k[A]
• The reaction is first order in [A] and first
order overall.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-18-320.jpg)
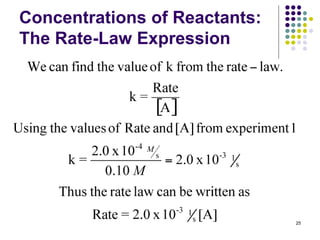
![Concentrations of Reactants:
The Rate-Law Expression
Example 2: The following data were obtained for the
reaction:
2 A(g) + B(g) + 2 C(g) 3 D(g) + 2 E(g)
Experiment
Initial [A]
(M)
Initial [B]
(M)
Initial [C]
(M)
Initial rate
(M/s)
1 0.20 0.10 0.10 2.0 x 10-4
2 0.20 0.30 0.20 6.0 x 10-4
3 0.20 0.10 0.30 2.0 x 10-4
4 0.60 0.30 0.40 1.8 x 10-3
26
From these initial rate data we can determine the rate-
law expression and the rate constant for this reaction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-20-320.jpg)
![Concentrations of Reactants:
The Rate-Law Expression
27
• Comparing experiments 1 and 3:
• [A] and [B] are held constant, but [C] is
increased by 3-times.
• The rate does not change.
• Therefore, the exponent, z = 0, and the rate
law simplifies to:
Rate = k[A]x[B]y
Rate = k[A]x[B]y[C]z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-21-320.jpg)
![Concentrations of Reactants:
The Rate-Law Expression
28
• Comparing experiments 1 and 2:
• [A] is held constant, but [B] is increased by 3-
times.
• The rate also increases by 3-times.
• Therefore, y = 1, and the rate law further
simplifies to:
Rate = k[A]x[B]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-22-320.jpg)
![Concentrations of Reactants:
The Rate-Law Expression
29
• Comparing experiments 2 and 4:
• [B] is held constant, but [A] is increased by 3-
times.
• The rate also increases by 3-times.
• The reaction is, thus, first order in A, first
order in B and second order overall.
• Therefore, x = 1, and the rate law further
simplifies to:
Rate = k[A][B]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-23-320.jpg)
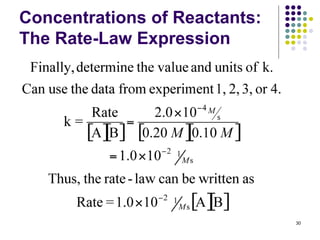
![Concentrations of Reactants:
The Rate-Law Expression
Example 3: A reaction between compounds A
and B is determined to be first order in A, first
order in B, and second order overall. From the
information given below, fill in the blanks.
Experiment
Initial Rate
(M/s)
Initial [A]
(M)
Initial [B]
(M)
1 4.0 x 10-3 0.20 0.050
2 1.6 x 10-2 ? 0.050
3 3.2 x 10-2 0.40 ? 31
Rate = k[A][B]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-25-320.jpg)

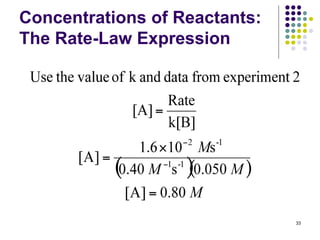
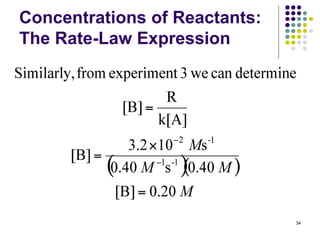
![Concentration vs. Time:
Integrated Rate Laws
The integrated rate equation relates time and
concentration for chemical reactions.
The integrated rate equation can be used to predict the
amount of product that is produced in a given amount of
time.
Provides an alternative to the initial rate method for
obtaining rate constants.
Initially we will look at the integrated rate equation
for first order reactions.
These reactions are 1st order in one reactant and 1st order
overall.
For a generic first order reaction with one reactant:
A products, rate = k[A]
35
or -d[A]/dt = k[A]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-29-320.jpg)
![Concentration vs. Time:
Integrated Rate Laws
where:
t = time elapsed since beginning of reaction.
[A]0= mol/L of A at t = 0 (sometimes called initial conc., [A]i)
[A] = mol/L of A at time t ([A] sometimes written as [A]t)
k = rate constant
Take the integral of this rate law from the beginning (t =
0, [A]0) to [A] at any later reaction time, t.
The integrated rate equation for a 1st order reaction:
36
ln([A]/[A]0) = -kt,
MEMORIZE and be able to
interconvert these equations!
or
[A] = [A]0e-kt
ln([A]0/[A]) = kt,
y = mx + bor ln[A] = -kt + ln[A]0
or ln[A]0 - ln[A] = kt,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-30-320.jpg)
![2N2O5(g) 2 N2O4(g) + O2(g)
Concentration vs. Time:
Integrated Rate Laws
37
• The reaction is found experimentally to be first order in
N2O5 and first order overall.
• Rate = k[N2O5]
plots of the first order integrated rate equations
for this reaction…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-31-320.jpg)
![Concentration vs. Time:
Integrated Rate Laws
38
[N2O5] = [N2O5]0e-kt
ln[N2O5] = -kt + ln[N2O5]0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-32-320.jpg)
![Concentration vs. Time:
Integrated Rate Laws
Define the half-time, t1/2, of a reaction as the time
required for half of the reactant to be consumed, i.e., the
time, t, at which [A]=1/2[A]0, then at t1/2, [A]0/[A] = 2.
39
ln 2 = 0.693 = kt1/2
• So, the half-time for any overall first order reaction is
given by:
t1/2 = 0.693/k MEMORIZE (or take ln 2)
• The half-time is independent of [A]0!
[A]0/[A] = 2 = ekt at t = t1/2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-33-320.jpg)
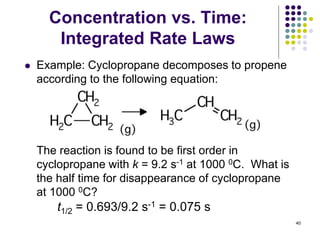

![Concentration vs. Time:
Integrated Rate Laws
42
ln [A]0 - ln [A] = kt
[A]0 = 3, t = 0.50 s, k = 9.2 s-1, solve for [A]:
ln 3 - ln [A] = 9.2 s-1(0.5 s)
1.1 - ln [A] = 4.6
ln [A] = -(4.6-1.1) = -3.5
[A] = e-3.5 = 0.03 g ~ 1% remains
Use the integrated first order rate equation:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-36-320.jpg)
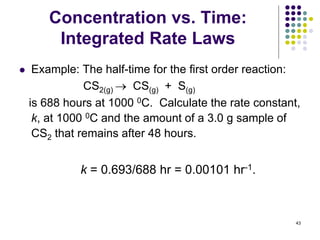
![Concentration vs. Time: The
Integrated Rate Laws
44
ln [A]0 - ln [A] = kt
ln (3.0) - ln [A] = (0.00101 hr-1)(48 hr)
1.1 - ln [A] = 0.048
ln [A] = -(0.048 - 1.1) = 1.052
[A] = e1.052 = 2.86g ~ 2.9 g or 97% unreacted](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-38-320.jpg)
![Concentration vs. Time: The
Integrated Rate Laws
For reactions that are second order with respect to
a single reactant, A, and second order overall, with
rate = k[A]2 = (1/a)(d[A]/dt), the integrated rate law
is:
Where a = stoichiometric coefficient of A in the balanced
overall equation.
If A P, then a = 1.
If 2A P, then a = 2
45
MEMORIZE!
• An alternative form of the 2nd order integrated
rate law:
[A] = [A]0/(1 + akt[A]0).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-39-320.jpg)
![Concentration vs. Time:
Integrated Rate Laws
Half-time, t1/2, for second order reactions:
Use the second order integrated rate-law as a starting
point.
At the half-time, t1/2 is [A] = 1/2[A]0.
46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-40-320.jpg)
![Concentration vs. Time: The
Integrated Rate Equations
If we solve for t1/2:
So the half-time of a second order reaction depends
on [A]0.
Less [A]0, longer half-time
Half-time increases as the reaction proceeds (unlike an
overall first order reaction, where t remains constant).
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-41-320.jpg)
![Concentration vs. Time:
Integrated Rate Laws
Example: Acetaldehyde, CH3CHO, undergoes gas
phase thermal decomposition to methane and carbon
monoxide.
The rate law was found to be:
rate = k[CH3CHO]2, and k = 2.0 x 10-2 M-1hr-1 at 527 oC.
(a) What is the half-time (t1/2) for disappearance of
CH3CHO if 0.10 mole is injected into a 1.0 L vessel at
527 oC? 48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-42-320.jpg)
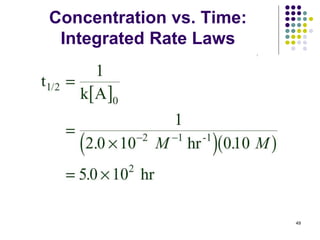
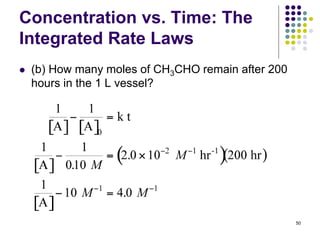
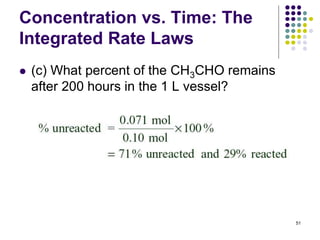
![Concentration vs. Time:
Integrated Rate Laws
52
(a) For the same reaction as the previous example, what is
the half-time (t1/2) for disappearance of CH3CHO if 0.10
mole is injected into a 10.0 L vessel at 527 oC?
● So, if [A]0 decreases by 10-times, t1/2 must increase by 10-
times,
● 10 x 5.0 x 102 hr = 5.0 x 103 hr
● Note that the vessel size is increased by a factor of 10
compared to the previous example, which decreases the
initial concentration by a factor of 10.
● Recall the equation for half time of this 2nd order
reaction (in which the coefficient, a = 1) is:
t1/2 = 1/k[A]0)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-46-320.jpg)
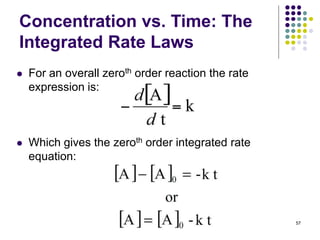
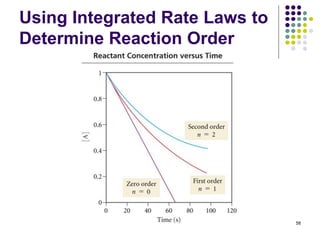
![Using Integrated Rate Laws to
Determine Reaction Order
59
y = mx + b
ln [A] = -kt + ln [A]0
Plots of linear form of the integrated rate
equations can determine the reaction order and
rate constant.
1st order:
zeroth order: [A] = -kt + [A]0
2nd order:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-49-320.jpg)
![Using Integrated Rate Laws to
Determine Reaction Order
Example: For the thermal decomposition of ethyl bromide:
C2H5Br(g) C2H4(g) + HBr(g)
60
Time (min) 0 1 2 3 4 5
[C2H5Br] 1.00 0.82 0.67 0.55 0.45 0.37
ln [C2H5Br] 0.00 -0.20 -0.40 -0.60 -0.80 -0.99
1/[C2H5Br] 1.0 1.2 1.5 1.8 2.2 2.7
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-50-320.jpg)
![Using Rate Integrated Laws to
Determine Reaction Order
Make an x,y plot for each of the three sets of
values in the table:
1. [C2H5Br] (y-axis) vs. time (x-axis)
If the plot is linear, then the reaction is zeroth order
with respect to [C2H5Br].
61
2. ln [C2H5Br] (y-axis) vs. time (x-axis)
If the plot is linear, then the reaction is first order
with respect to [C2H5Br].
3. 1/ [C2H5Br] (y-axis) vs. time (x-axis)
If the plot is linear, then the reaction is second
order with respect to [C2H5Br].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-51-320.jpg)
![Using Integrated Rate Laws to
Determine Reaction Order
Plot of [C2H5Br] versus time.
62Is it linear?
[C2H5Br]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-52-320.jpg)
![Using Rate Laws to Determine
Reaction Order
Plot of ln [C2H5Br] versus time.
Is it linear?
ln [C2H5Br]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-53-320.jpg)
![Using Integrated Rate Laws
to Determine Reaction Order
Plot of 1/[C2H5Br] versus time.
64Is it linear?
1/[C2H5Br]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-54-320.jpg)
![Using Integrated Rate Laws
to Determine Reaction Order
ln[C2H5Br] vs. time is the only linear plot.
The reaction is, therefore, first order with respect to
[C2H5Br] and first order overall.
From the integrated rate law for a first order reaction:
ln[A] = -kt + ln[A]0, slope = -k.
66
● Slope = y2 - y1/x2 - x1.
• So k = 0.2 min-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-55-320.jpg)
![Using Rate Equations to
Determine Reaction Order
Example: Concentration-versus-time data for the reaction:
2NO2(g) --> 2NO(g) + O2(g),
are given in the table below. Plot each of these time
functions to determine the rate of the reaction and the value
of the rate constant.
67
Time(min) 0 1 2 3 4 5
[NO2] 1.0 0.53 0.36 0.27 0.22 0.18
ln [NO2] 0.0 -0.63 -1.0 -1.3 -1.5 -1.7
1/[NO2] 1.0 1.9 2.8 3.7 4.6 5.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-56-320.jpg)
![Using Rate Equations to
Determine Reaction Order
Plot of [NO2] versus time.
69
Is it linear?
[NO2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-57-320.jpg)
![Using Rate Equations to
Determine Reaction Order
Plot of ln [NO2] versus time.
70
Is it linear?
ln [NO2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-58-320.jpg)
![Using Rate Equations to
Determine Reaction Order
Plot of 1/[NO2] versus time.
71Is it linear?
1/[NO2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-59-320.jpg)
![Using Rate Equations to
Determine Reaction Order
1/[NO2] vs. time is the only linear plot.
The reaction is, therefore, second order in
[NO2] and second order overall.
72
● Determine the value of the rate constant from
the slope of the line.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-60-320.jpg)


![Collision Theory of
Reaction Rates
For a simple second order reaction between two different
gaseous atoms, A and B:
80
A B
A B
A B
B
A B
A B
A B
A B
4 different possible A-B
collisions
6 different possible A-B
collisions
9 different possible A-B
collisions
A(g) + B(g) products, where rate = k[A][B]
Increasing the number of atoms per unit volume (equivalent
to increasing their concentrations) increases the probability
of A/B collisions per unit time and, thereby increases the
reaction rate.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-63-320.jpg)


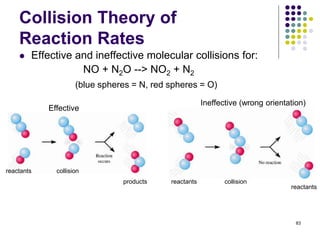

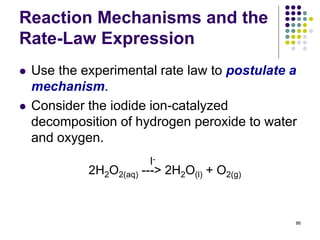
![Reaction Mechanisms and the
Rate-Law Expression
This reaction has been experimentally determined to
be first order in H2O2, first order in I- , and second
order overall, i.e.
Rate = k[H2O2][I-]
87
Step 1, slow: H2O2 + I- --> IO- +H2O
Step 2, fast: IO- + H2O2 --> H2O + O2 + I-
Overall reaction: 2H2O2 --> 2H2O + O2
A mechanism consistent with this rate law is:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-70-320.jpg)
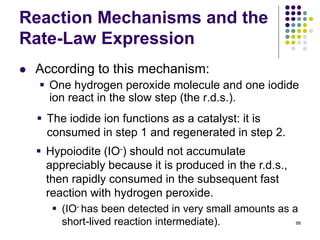
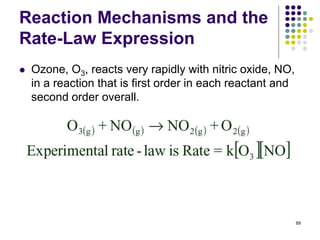
![Reaction Mechanisms and the
Rate-Law Expression
One possible mechanism that is consistent with the
rate law is:
90
k1
k2
Rate = k1[O3][NO]
• k2 >> k1, so the slow step is the “bottleneck” which
limits the overall reaction rate
• k1 = k, i.e., the rate constant for the overall reaction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-73-320.jpg)
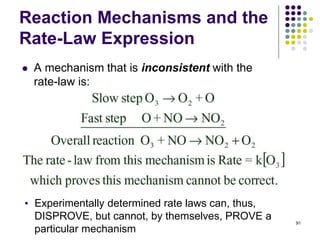
![Reaction Mechanisms and the
Rate-Law Expression
92
• Consider the reaction:
2NO(g) + Br2(g) 2NOBr(g)
• The experimentally determined rate law is:
Rate = k[NO]2[Br2]
• One possible mechanism consistent with the rate law is a
simultaneous collision and reaction of two NO molecules
and one Br2 molecule. However, simultaneous three-body
collisions are highly improbable.
• More likely mechanisms would consist of a sequence
of bimolecular steps.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-75-320.jpg)
![Reaction Mechanisms and the
Rate-Law Expression
93
NO + Br2 NOBr2 fast pre-equilibrium
NOBr2 + NO ---> 2NOBr
2NO + Br2 --> 2NOBr overall reaction
• According to this mechanism, the rate law for the slow step is:
Rate = k2[NOBr2][NO]
How to reconcile with the experimental rate law, rate = k[NO]2[Br2]?
• For the fast pre-equilibrium, the rates of the forward and
reverse reactions must be equal: k1[NO][Br2] = k-1[NOBr2].
• Rearrange to [NOBr2] = k1/k-1[NO][Br2], substitute into the rate
law for the r.d.s.:
• Rate = k2(k1/k-1[NO][Br2])[NO] = k[NO]2[Br2], where k = k2k1/k-1
k2
k-1
k1
slow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-76-320.jpg)

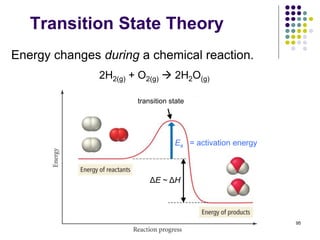
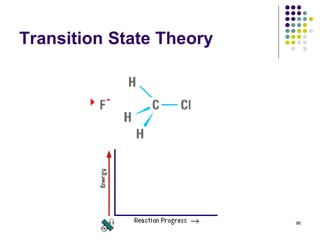
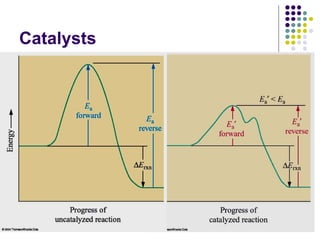
![97
Transition State Theory
NO2(g) + CO(g) NO(g) + CO2(g)
experimental rate law: Rate = k[NO2]2
• Step 1) is the r.d.s (k1 << k2).
• Step 1) is slower than step 2)
because Ea1 > Ea2.
• The rate law of step 1) is the
same as the rate law of the
overall reaction.
A mechanism consistent with the rate law:
step 1: NO2(g) + NO2(g) NO3(g) + NO(g) Rate1 = k1[NO2]2 slow
step 2: NO3(g) + CO(g) NO2(g) + CO2(g) Rate2 = k2[NO3][CO] fast](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trochapter13kineticsspring20151-150422012013-conversion-gate02/85/Tro-chapter-13-kinetics-spring-2015-1-80-320.jpg)