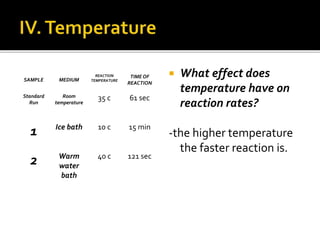
The document summarizes the results of a group chemistry experiment investigating factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions. The experiment tested how changing concentration, temperature, surface area, and use of catalysts influenced the rates of various reactions. It was found that increasing concentration, temperature, and surface area, and adding catalysts increased reaction rates. Catalysts were shown to speed up reactions without being used up in the process.