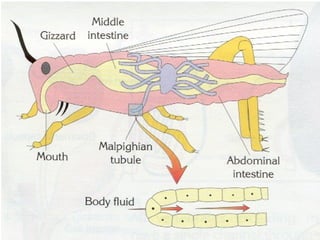
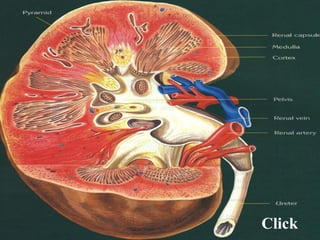
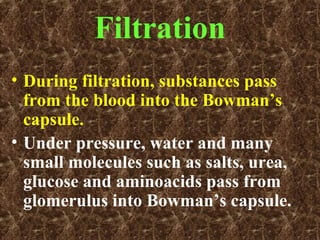
The document discusses the human excretory system. It explains that the kidneys filter waste from the blood and regulate homeostasis. The nephrons are the functional units of the kidneys that filter blood to form urine via filtration, reabsorption of needed substances, and secretion of unwanted compounds. Urine contains waste products and is stored in the bladder before being expelled through the urethra.








![UREA [CO (NH2)2]
•Urea is less toxic than ammonia.
•It is formed in the liver by ornithin cycle.
•Urea is excreted by the kidney.
•Urea is the excretory substances of
amphibians,mammals,fish and human.
• O rganisms use more energy in formation
of urea than formation of ammonia.
•Living things need normal amount of
water.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/excretorysystems-141215042208-conversion-gate01/85/Excretory-systems-9-320.jpg)