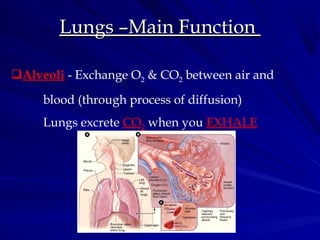
The human excretory system removes waste from the body through four main organs. The lungs exhale carbon dioxide, while the skin sweats out water, salts, and urea. The liver converts nitrogenous wastes to urea and excretes bile, and the kidneys filter wastes like urea, salts, and water from the blood to produce urine for excretion. Together, these organs maintain homeostasis by removing harmful cellular wastes that could otherwise build up to toxic levels.