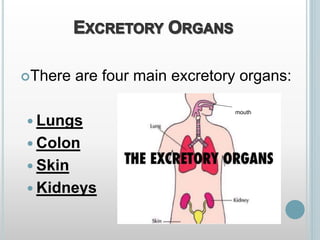
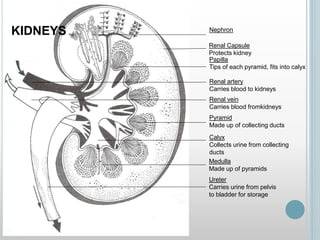
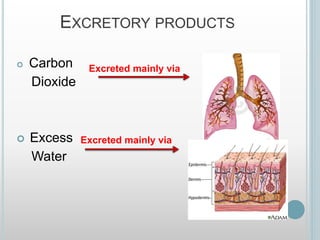
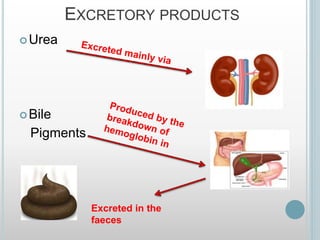
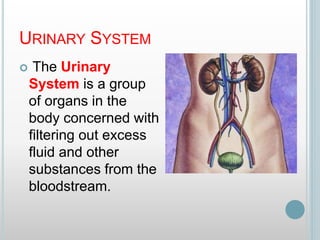
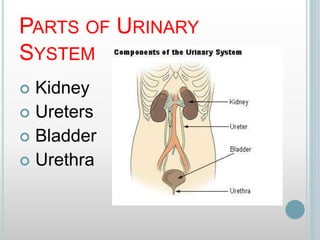
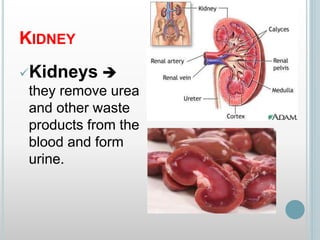
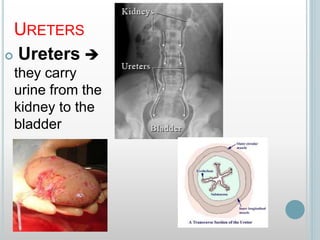
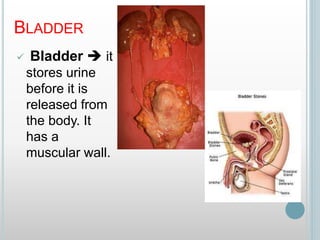
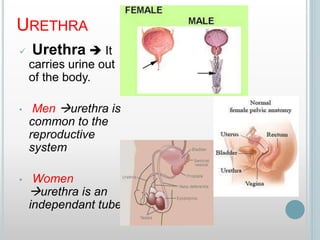
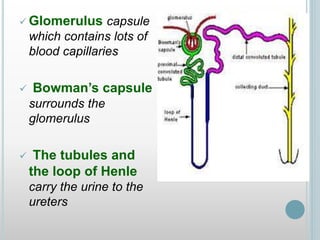
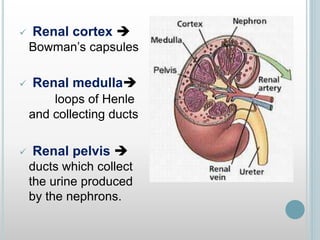
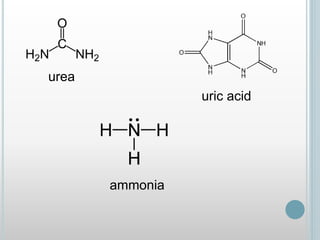
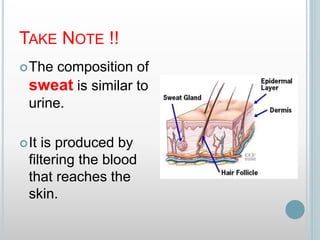
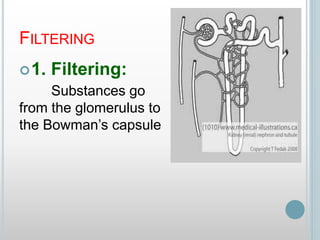
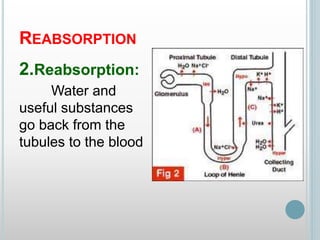
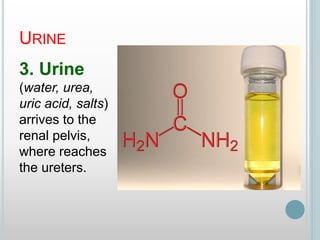
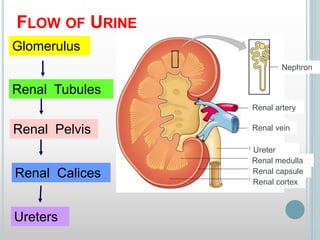
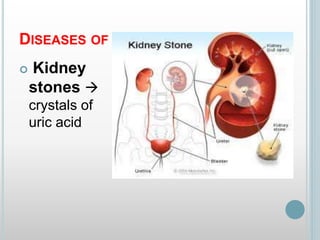
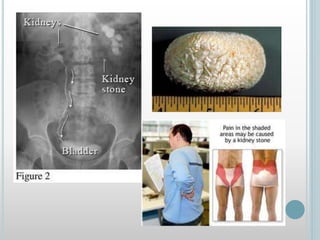
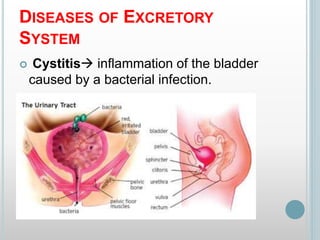
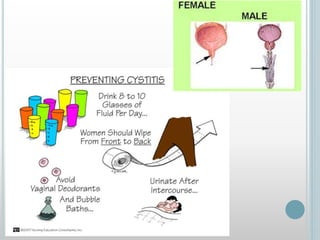
The excretory system removes waste from the body through various organs including the lungs, skin, colon and kidneys. The kidneys filter blood and produce urine by selectively reabsorbing useful substances and excreting waste like urea and salts. Urine travels from the kidneys through the ureters to the bladder for storage and then exits through the urethra. The main functions of the excretory system are to eliminate cellular waste and maintain chemical balance in the body. Diseases can occur if the system is not working properly, such as kidney stones, cystitis and renal insufficiency.