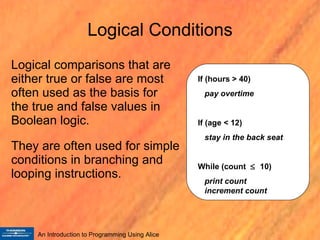
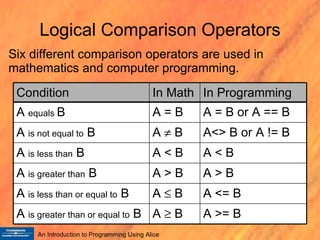
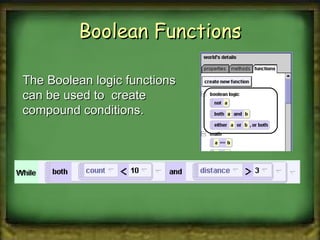
Boolean logic is a form of mathematics that represents true and false values. It was outlined by George Boole in 1854 and forms the basis of modern computing. There are three basic Boolean logic operations - AND, OR, and NOT - that allow combining true and false values to form compound conditions. Logical comparisons and operators are used to evaluate conditions as either true or false, and these values can then be manipulated using Boolean logic.