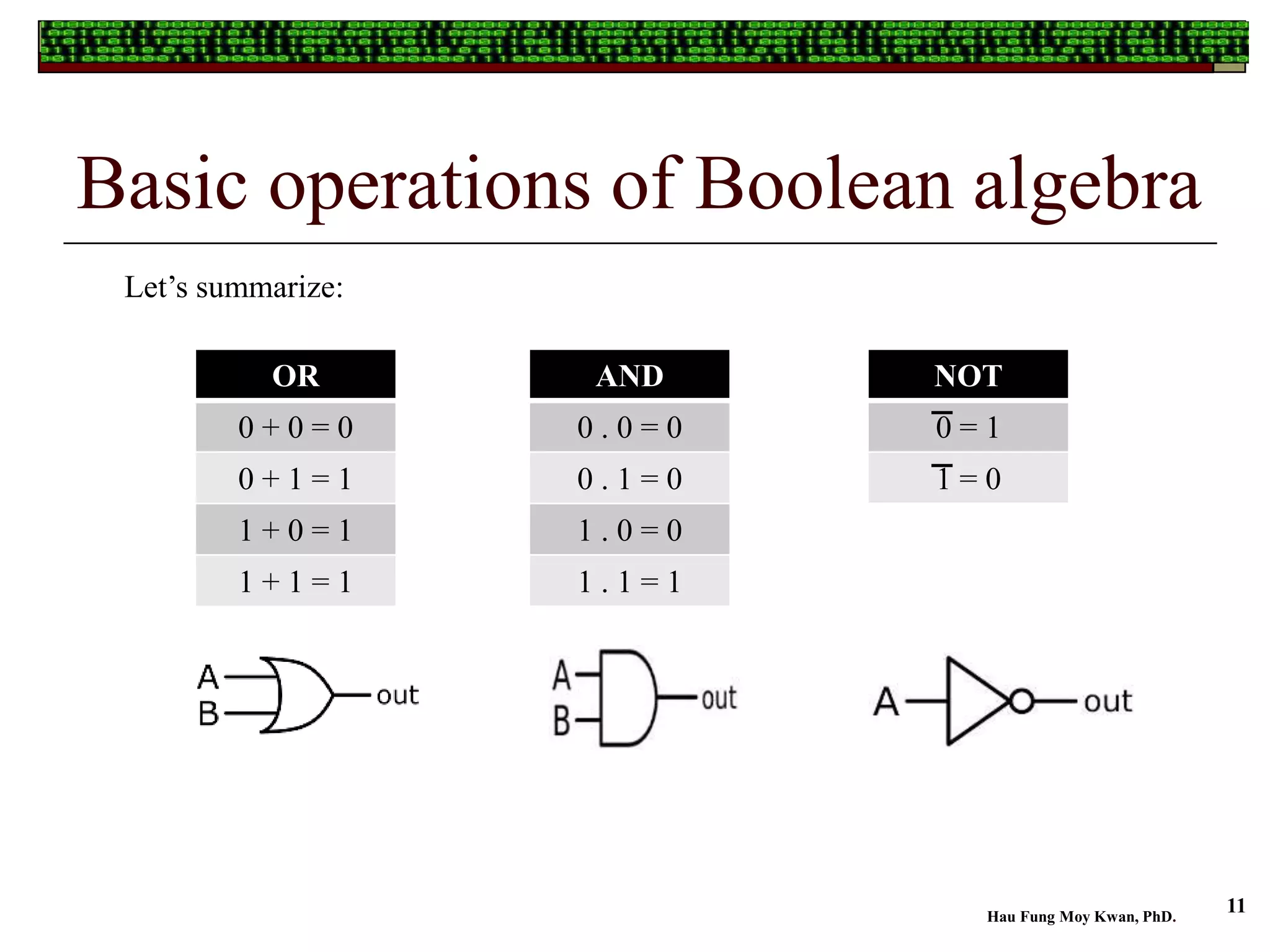
The document provides an overview of Boolean algebra, which is essential for simplifying logic expressions used in digital circuits. It covers the basic definitions, operations, and theorems of Boolean algebra and explains its practical applications, including the functioning of logic gates in everyday technology. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of using Boolean algebra for cost-effective circuit design in modern computing.