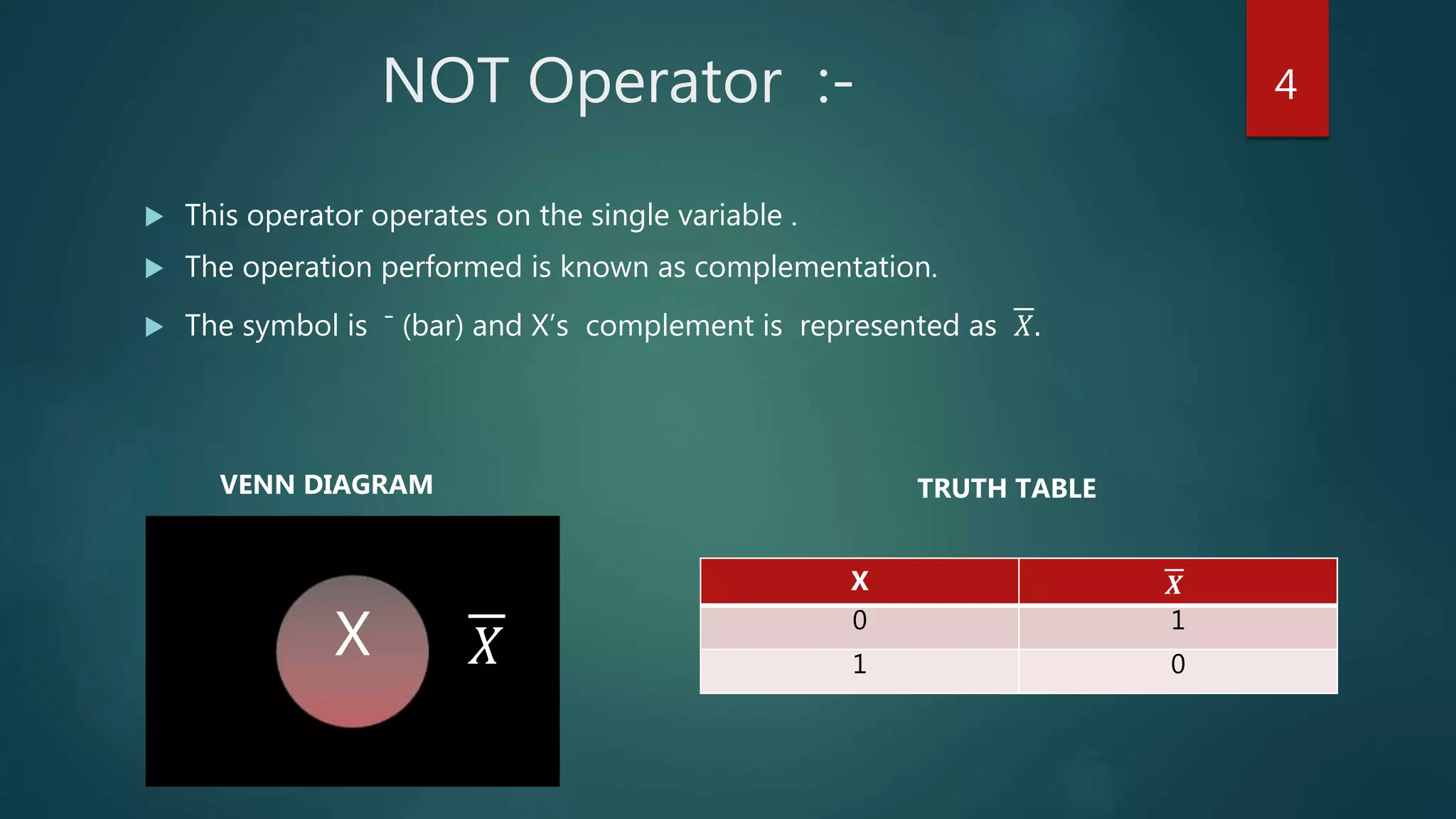
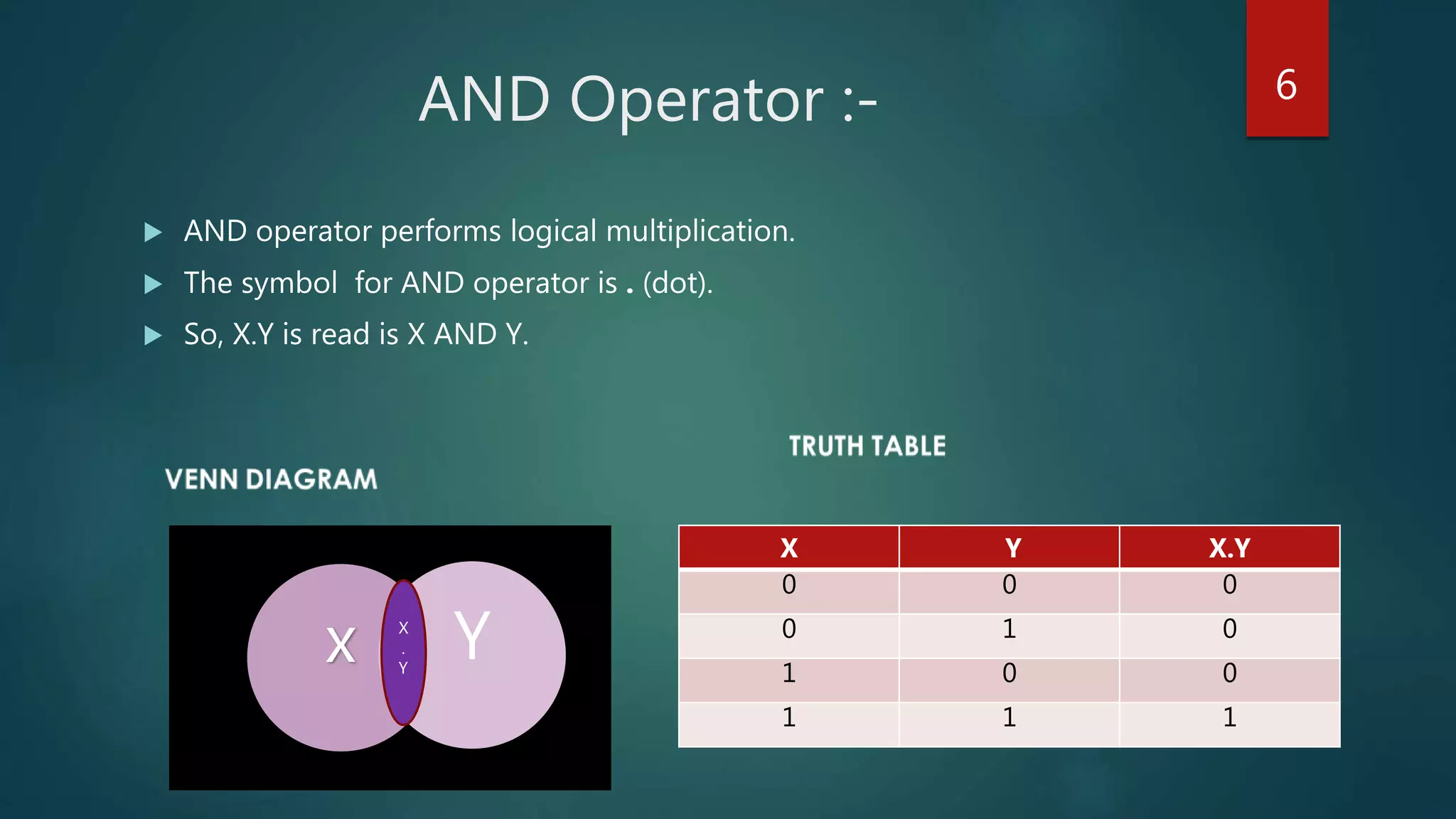
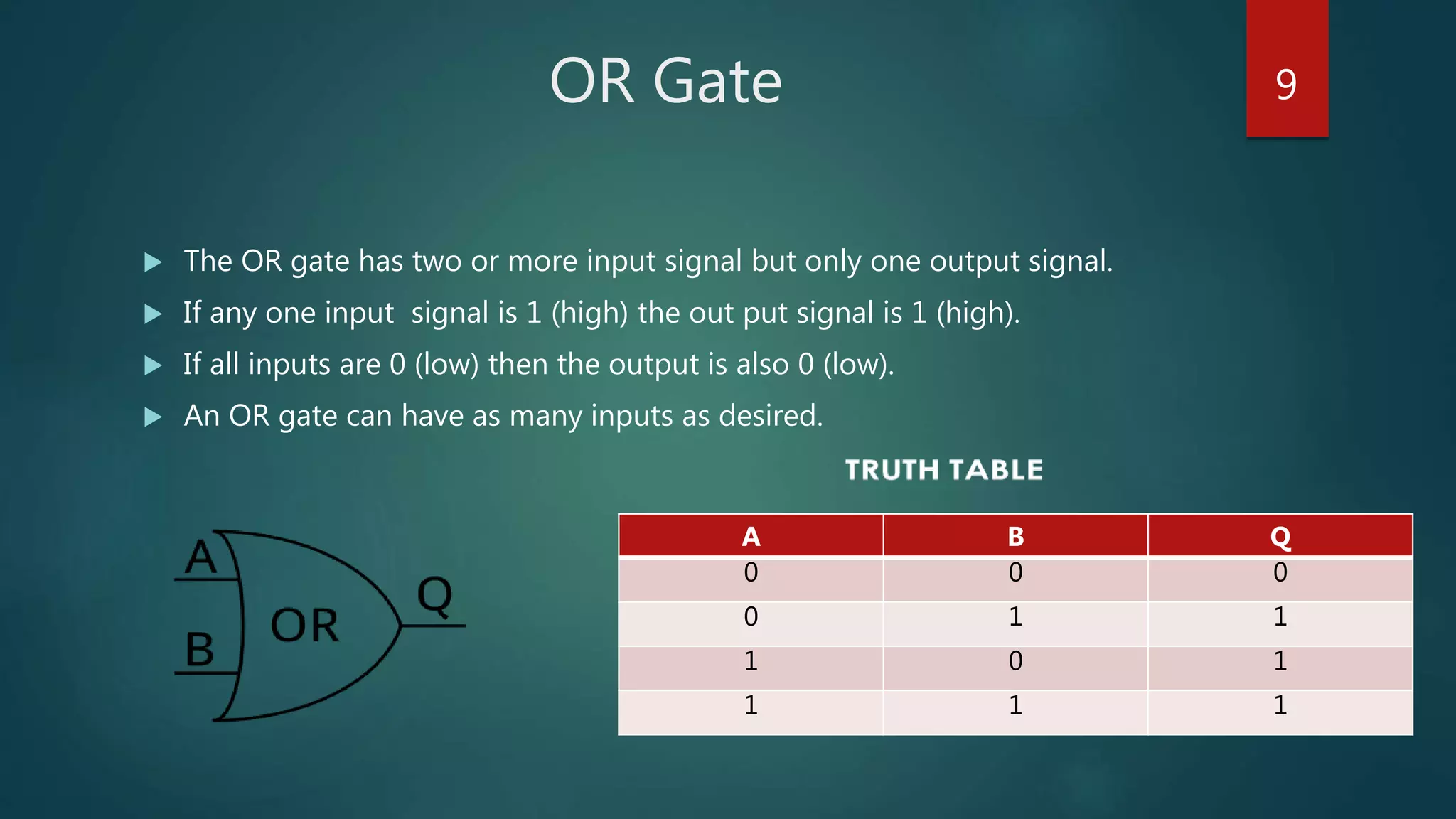
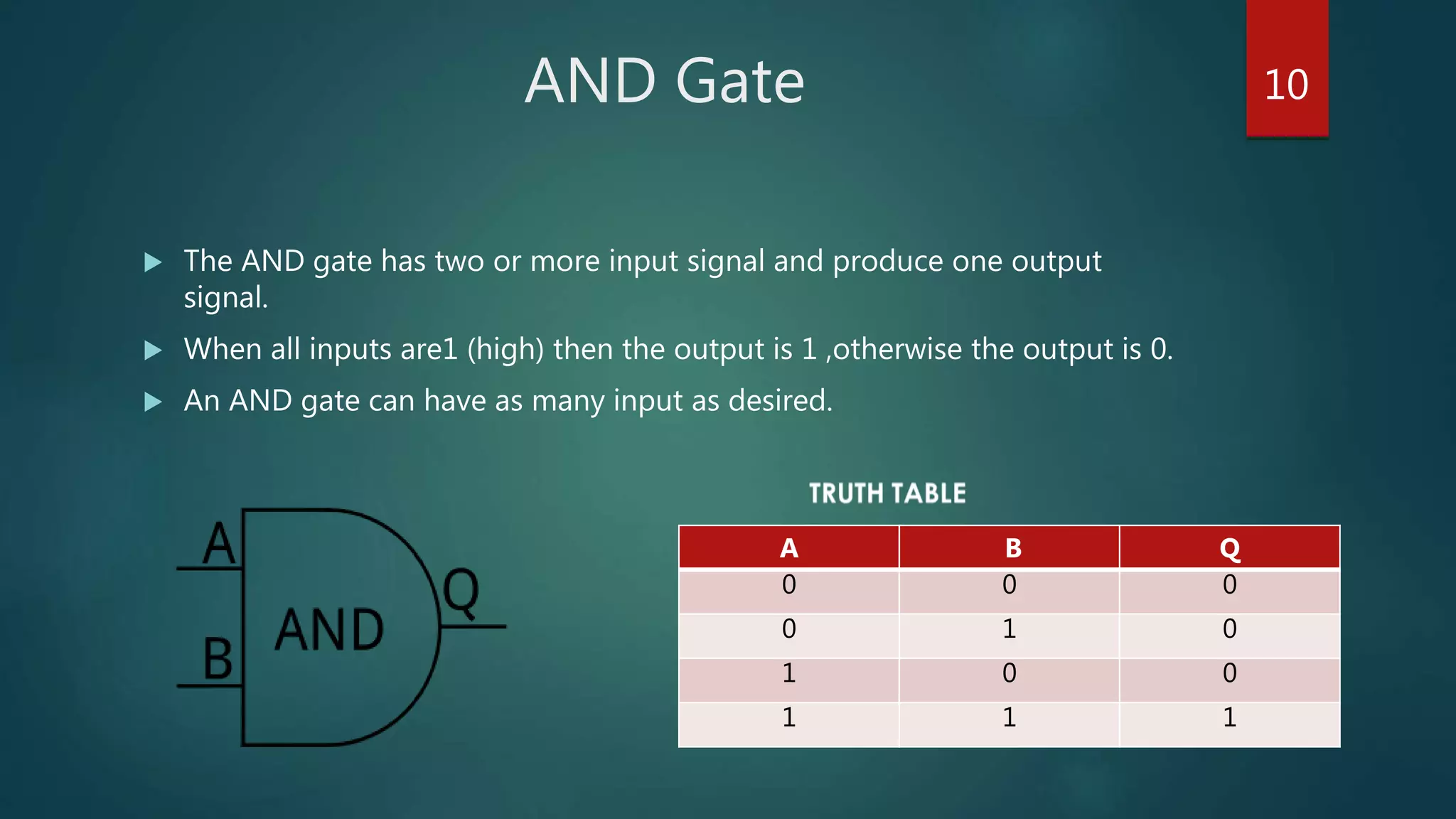
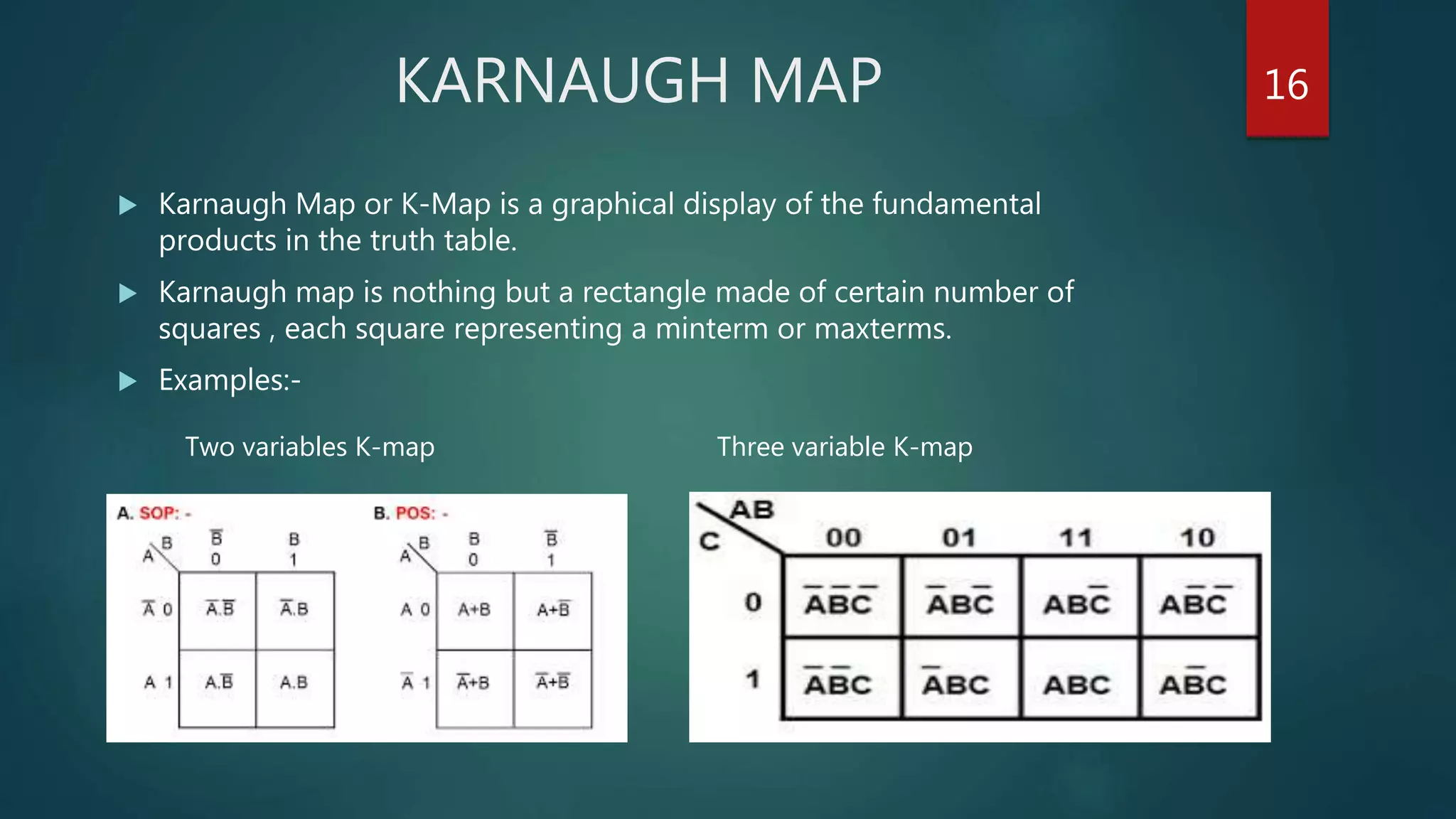
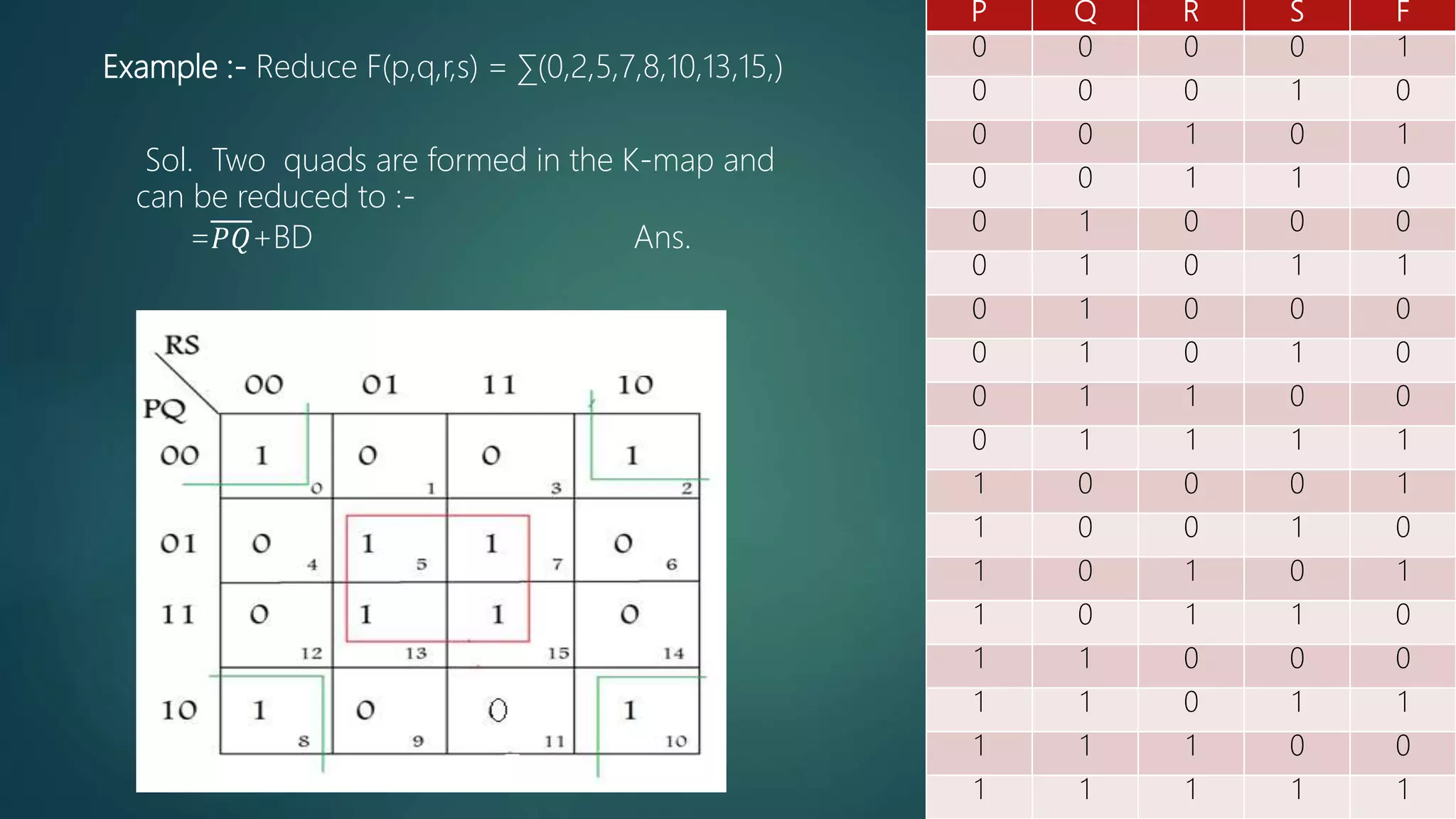
The document summarizes a seminar presentation on Boolean algebra. The presentation covered the development of Boolean algebra, logical operators like NOT, OR, AND, logic gates, derivation of Boolean expressions, canonical expressions, and methods for minimizing Boolean expressions including algebraic methods and Karnaugh maps. It provided examples to illustrate different concepts like logical operators, logic gates, canonical expressions, Karnaugh maps, and minimizing expressions.