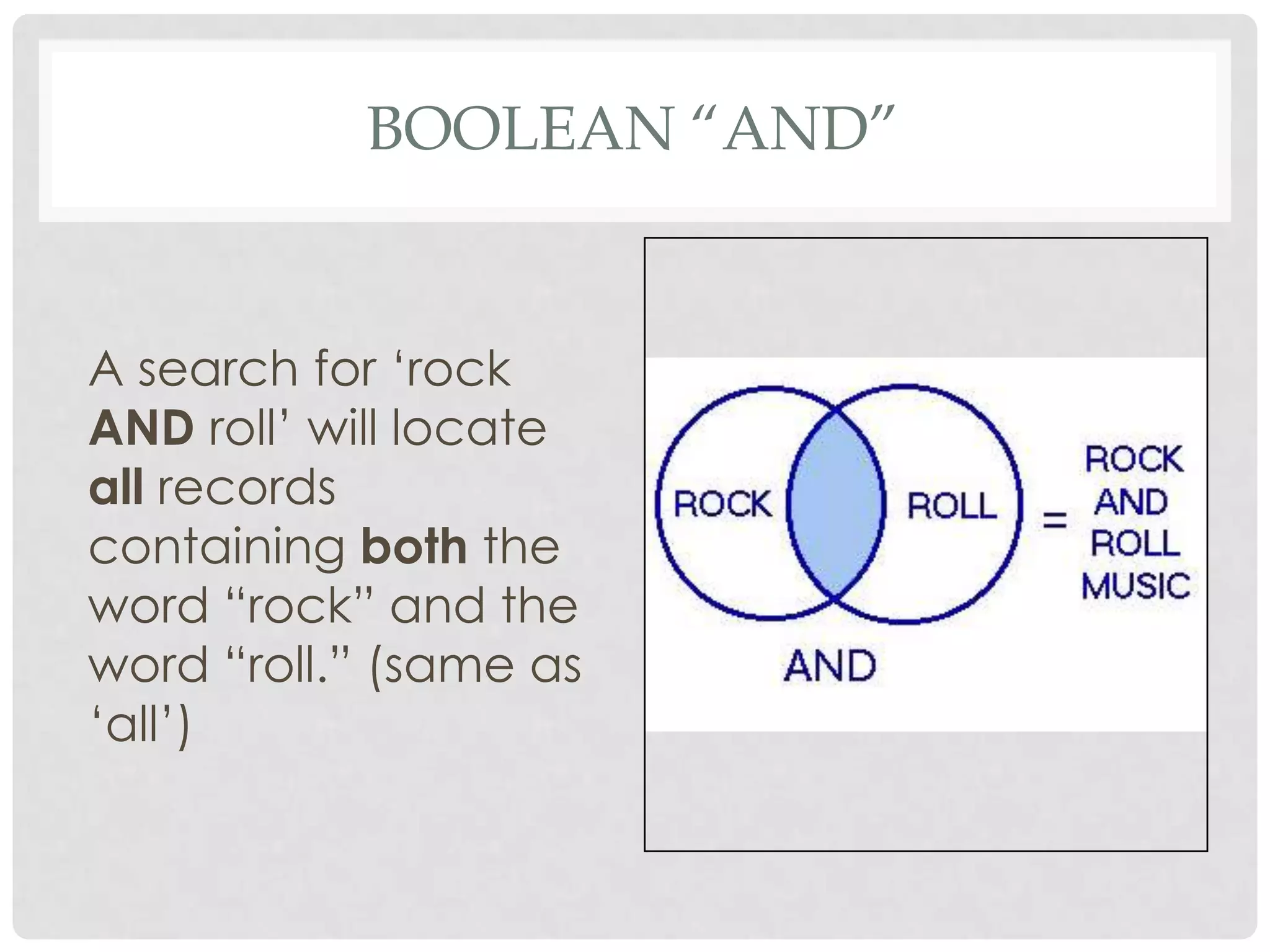
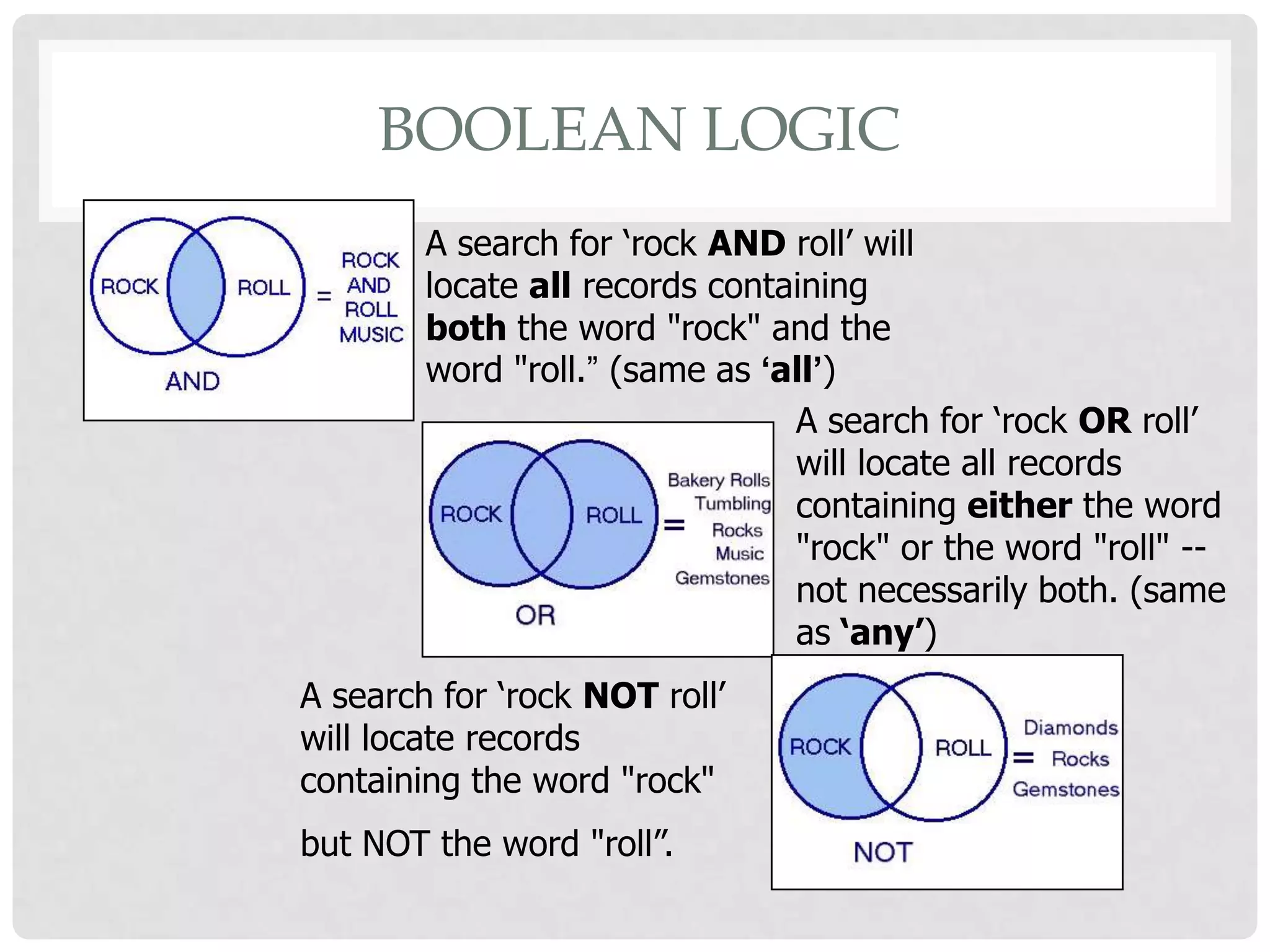
Boolean searching is a technique that uses Boolean operators like AND, OR and NOT to conduct more precise online searches. It was named after mathematician George Boole who developed a system of logic for better search results. AND narrows results by requiring all search terms, OR expands them by including either term, and NOT limits by excluding specific terms. Boolean logic allows combining terms and nesting search statements for optimal results, though implementation varies across search systems.