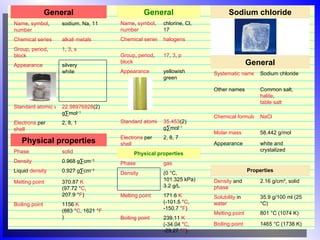
Elements, compounds, and mixtures are discussed. Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further, while compounds are formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together. Compounds have unique properties and can be broken down into their constituent elements through chemical or electrolytic processes. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids based on their physical properties such as conductivity.