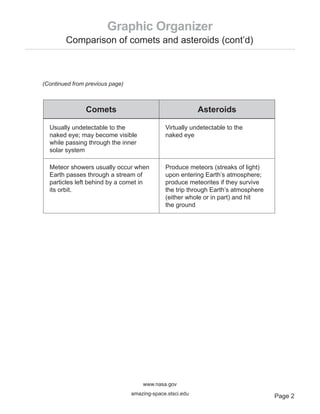
The document compares and contrasts comets and asteroids. It notes that comets are made of ice and dust while asteroids are made of rocks and metals. Comets form tails when passing through the inner solar system, while asteroids do not form tails. Comets typically have more elliptical and tilted orbits than asteroids and planets, and originate from the Kuiper Belt or Oort Cloud, while asteroids typically remain in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.