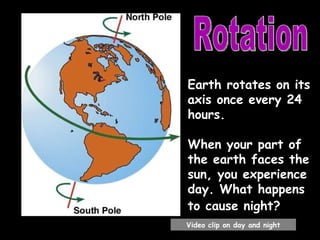
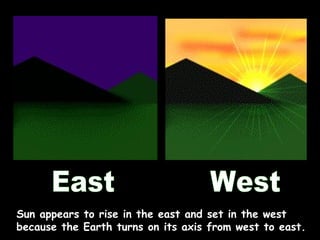
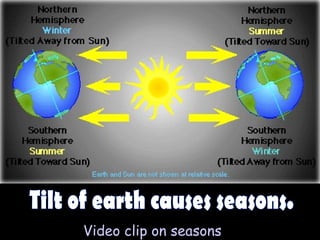
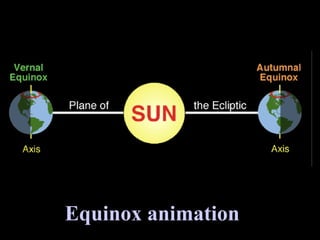
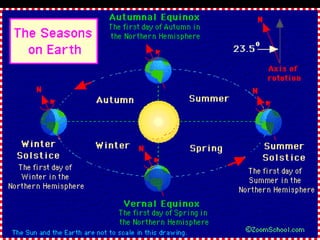
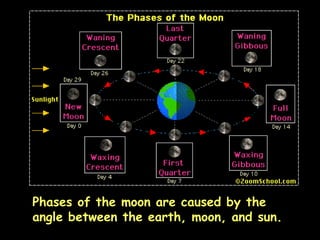
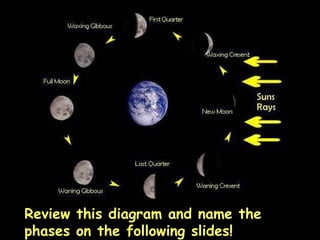
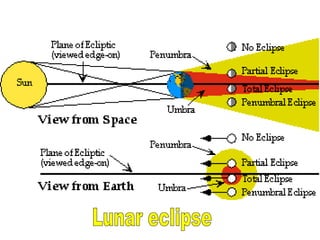
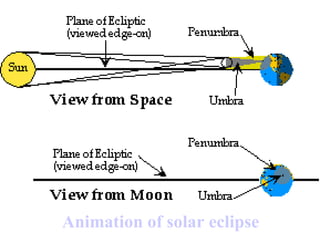
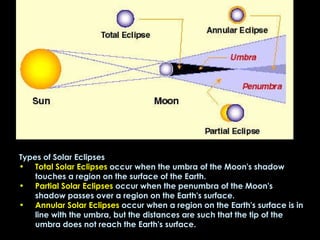
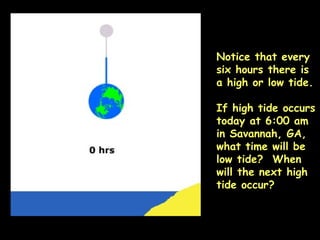
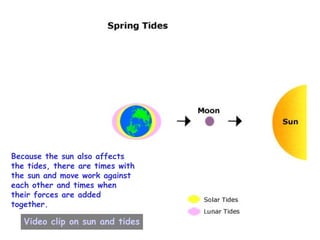
The document summarizes various topics relating to Earth's rotation, revolution, seasons, phases of the moon, eclipses, and tides. It includes animations and diagrams explaining how Earth's tilt and yearly orbit around the sun cause seasons. It also describes the lunar phases and how the moon's position relative to Earth and sun causes phases to change daily. Eclipses of both the sun and moon are explained. Finally, it discusses tides and how the gravitational pull of the sun and moon influence high and low tides each day.