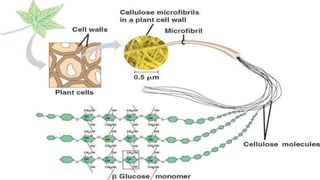
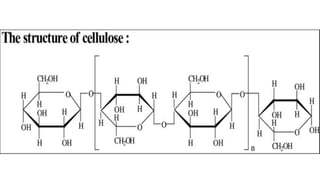
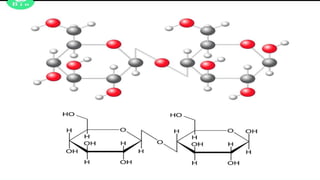
Cellulose is an organic polysaccharide composed of β(1→4) linked d-glucose units, crucial for the structural integrity of plant cell walls. Discovered in 1838 by Anselme Payen, it has various applications including in textiles, pharmaceuticals, and biofuels. Cellobiose, a disaccharide derived from cellulose, consists of two β-glucose molecules and can be hydrolyzed into glucose.