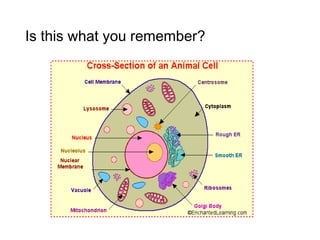
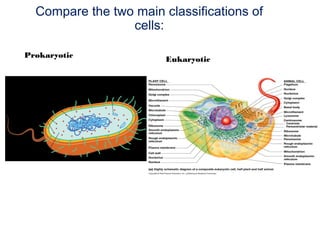
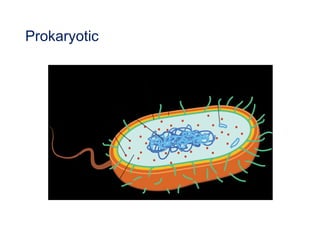
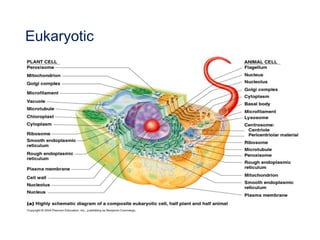
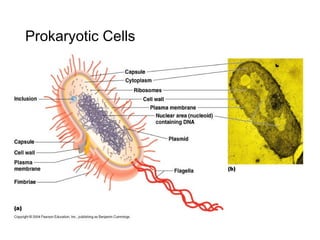
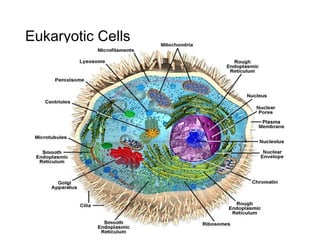
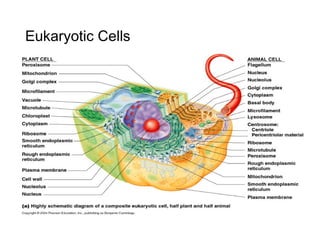
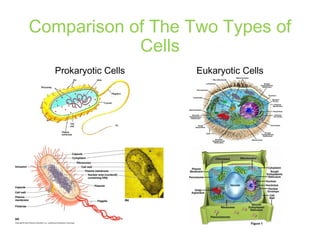
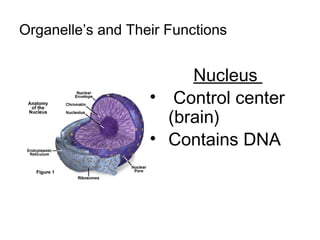
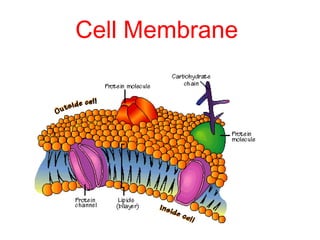
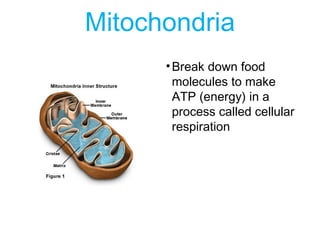
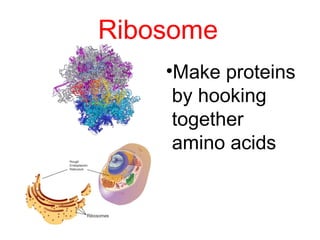
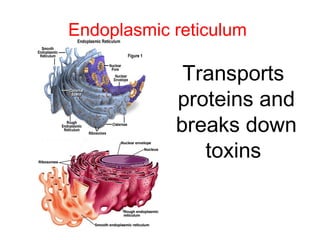
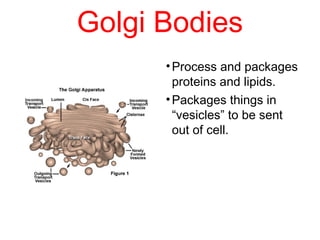
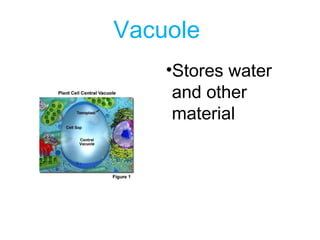
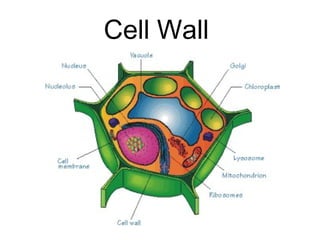
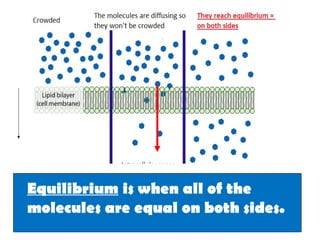
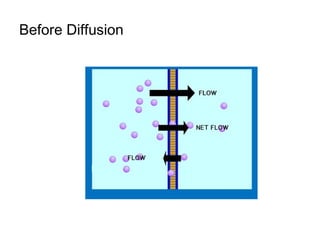
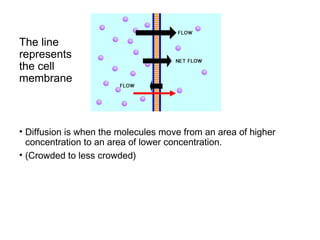
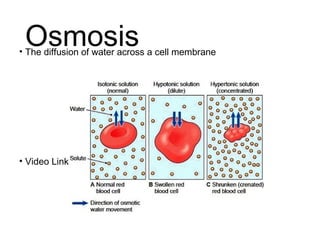
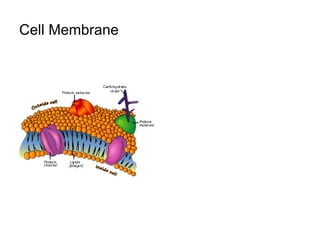
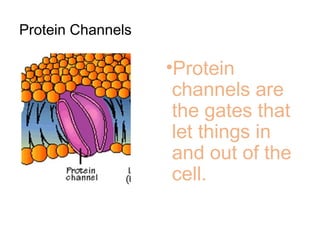
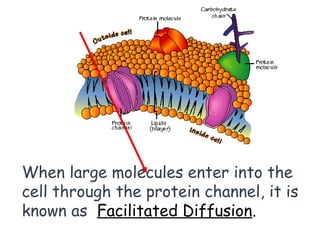
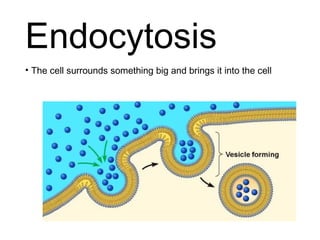
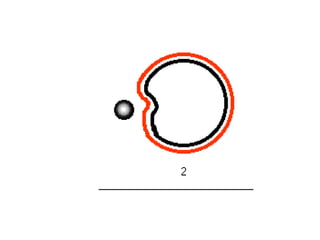
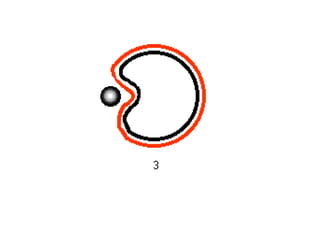
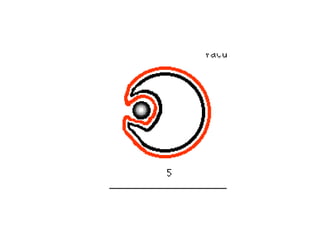
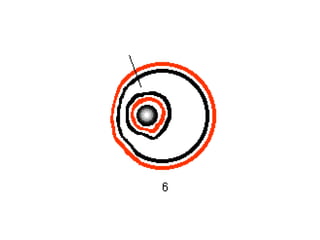
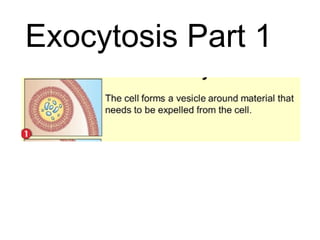
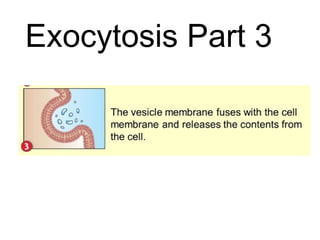
This document discusses the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that houses DNA and various membrane-bound organelles that carry out specific functions. The cell membrane acts as a selectively permeable barrier that allows materials to enter and exit the cell through diffusion, osmosis, protein channels, and active or passive transport processes. Large particles can be transported via endocytosis or exocytosis.