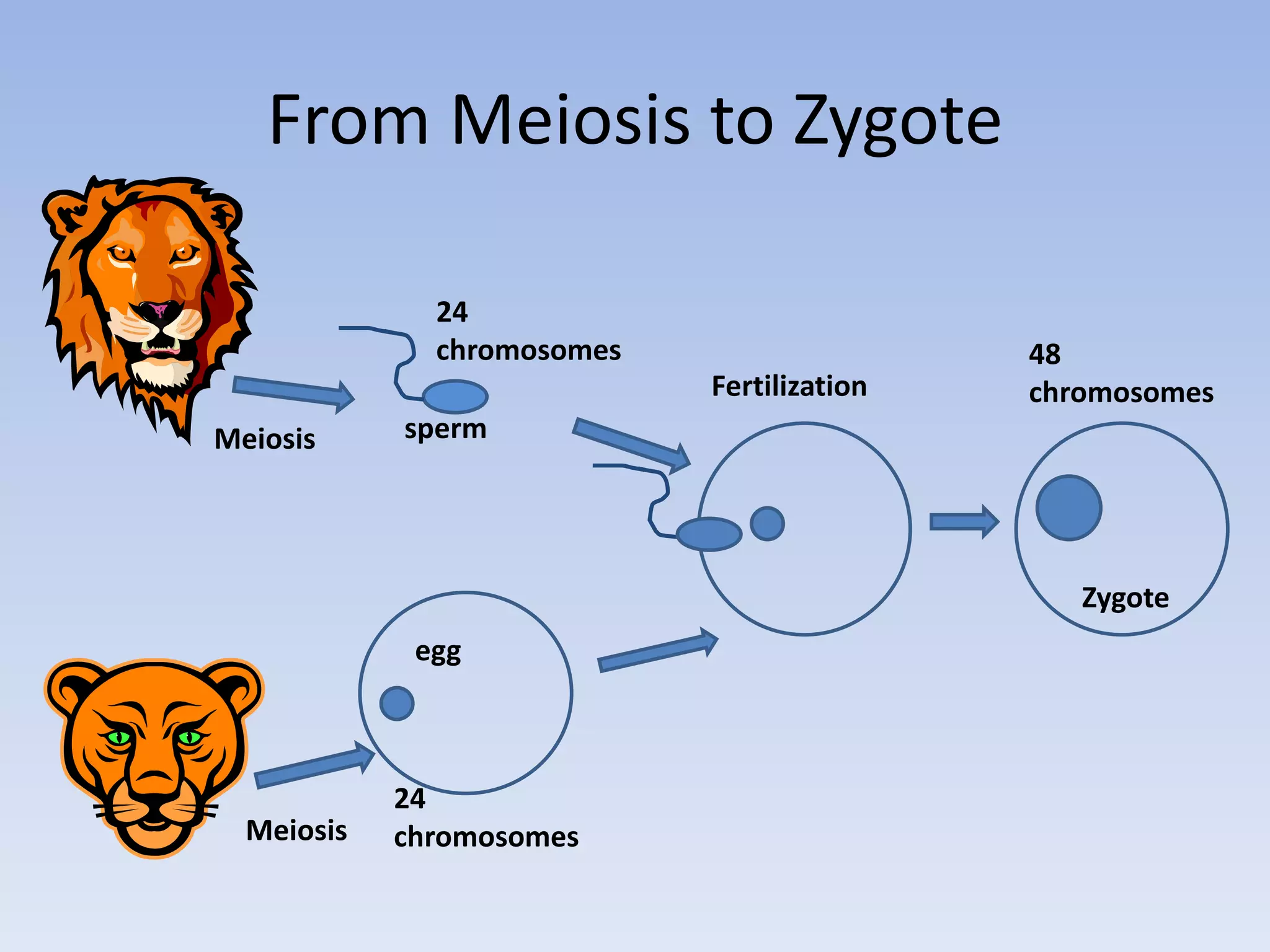
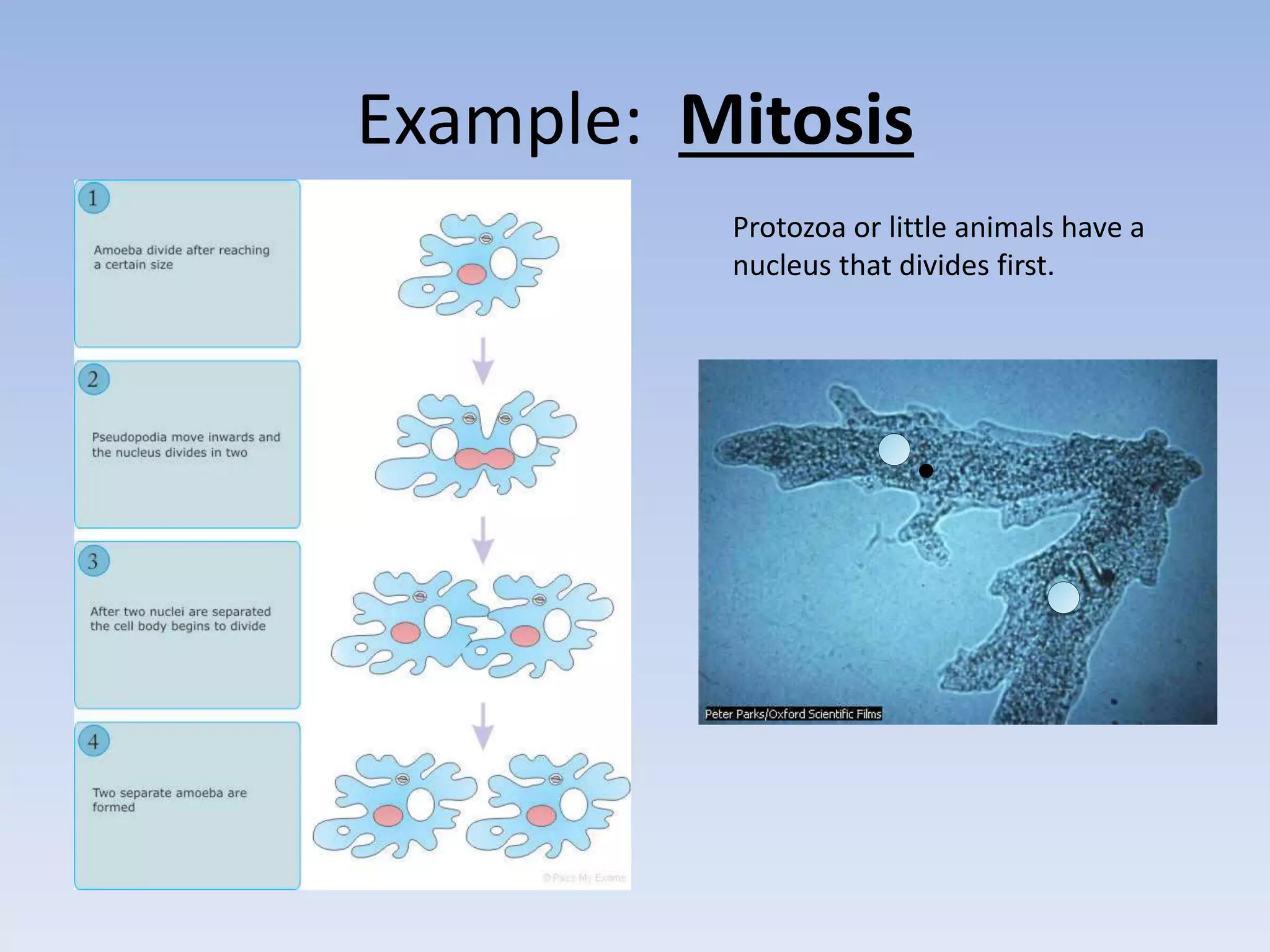
1. Sexual reproduction involves two parents and produces offspring that are genetically different from both parents and each other. Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent and each other.
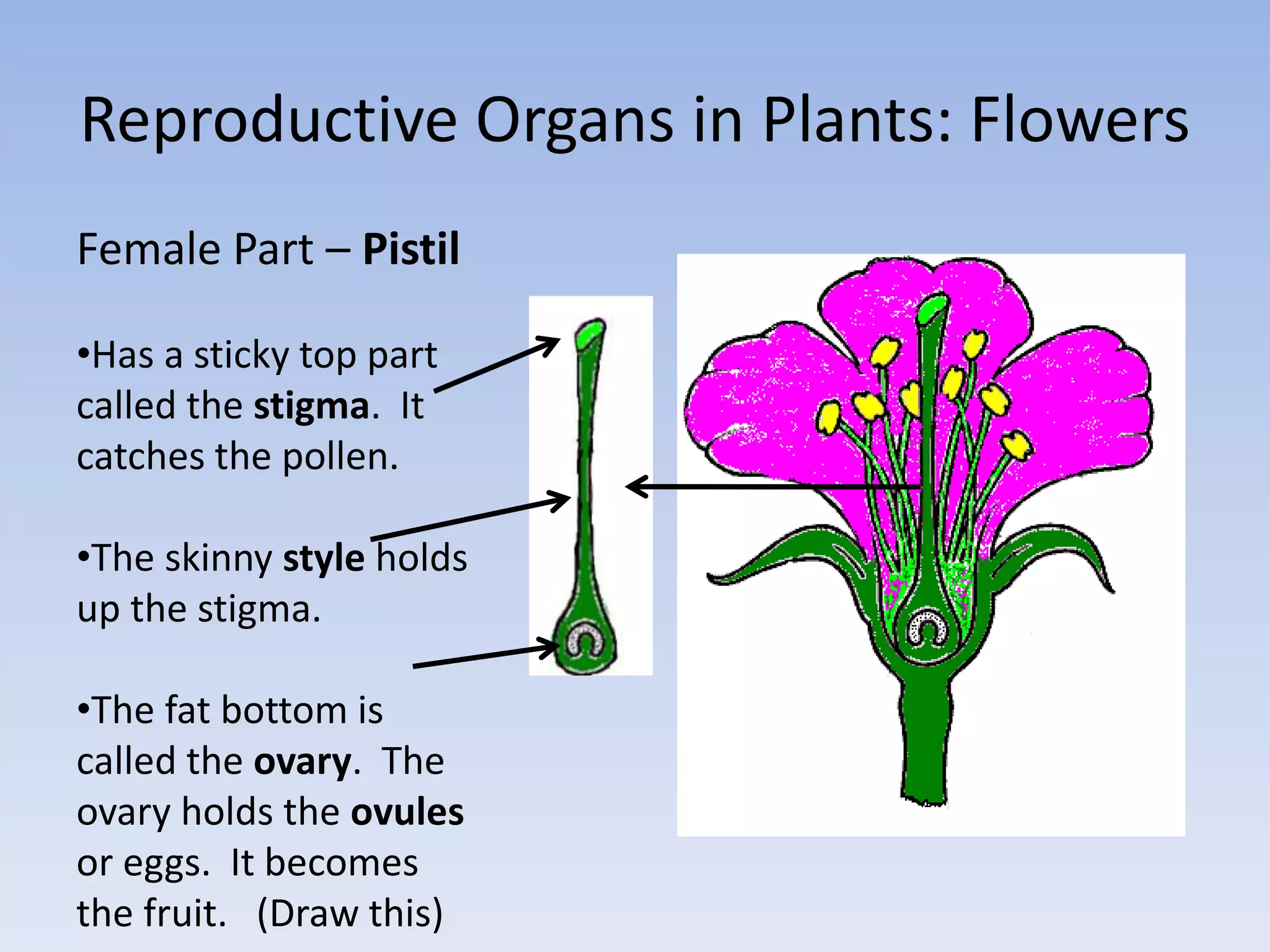
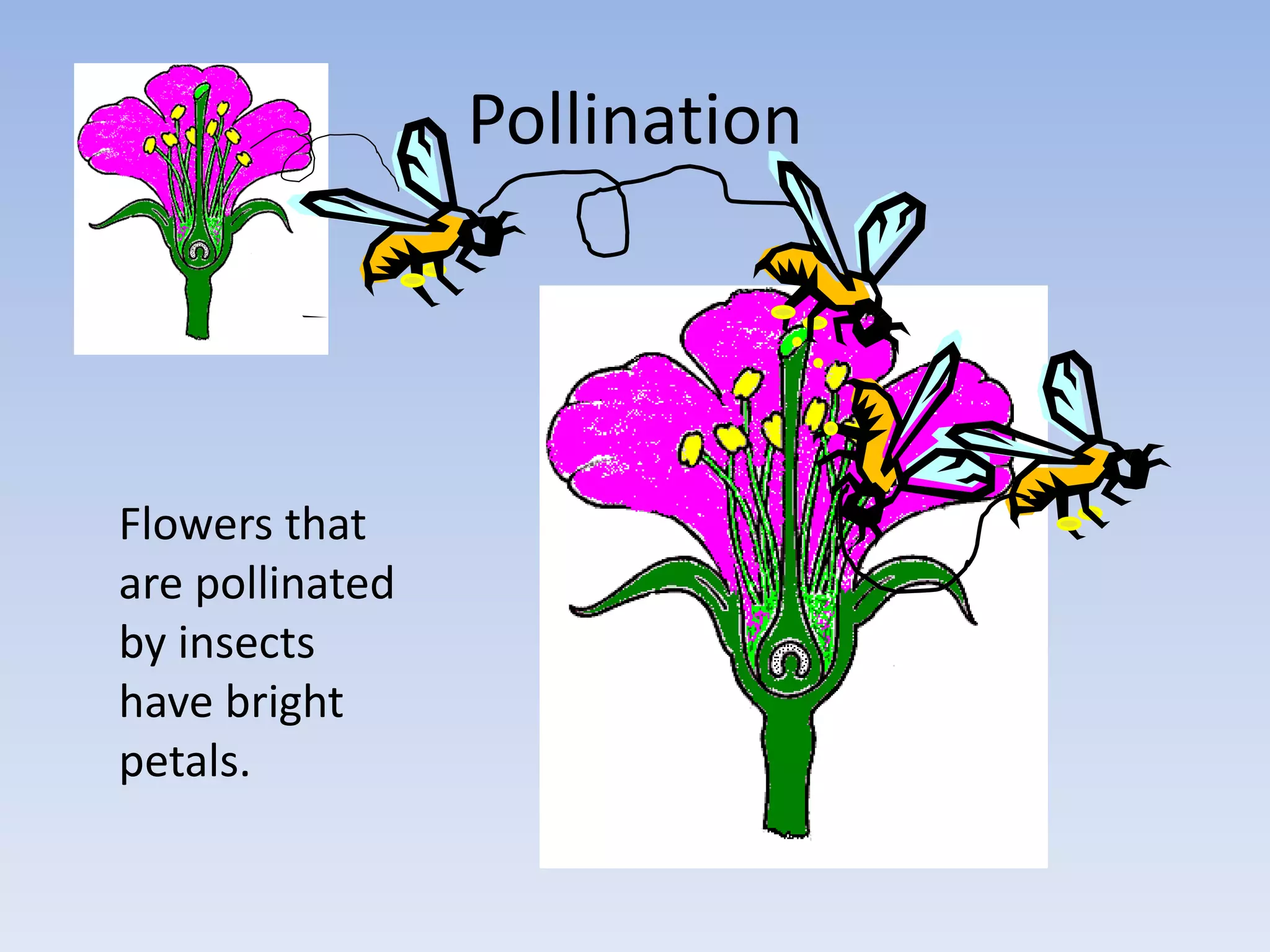
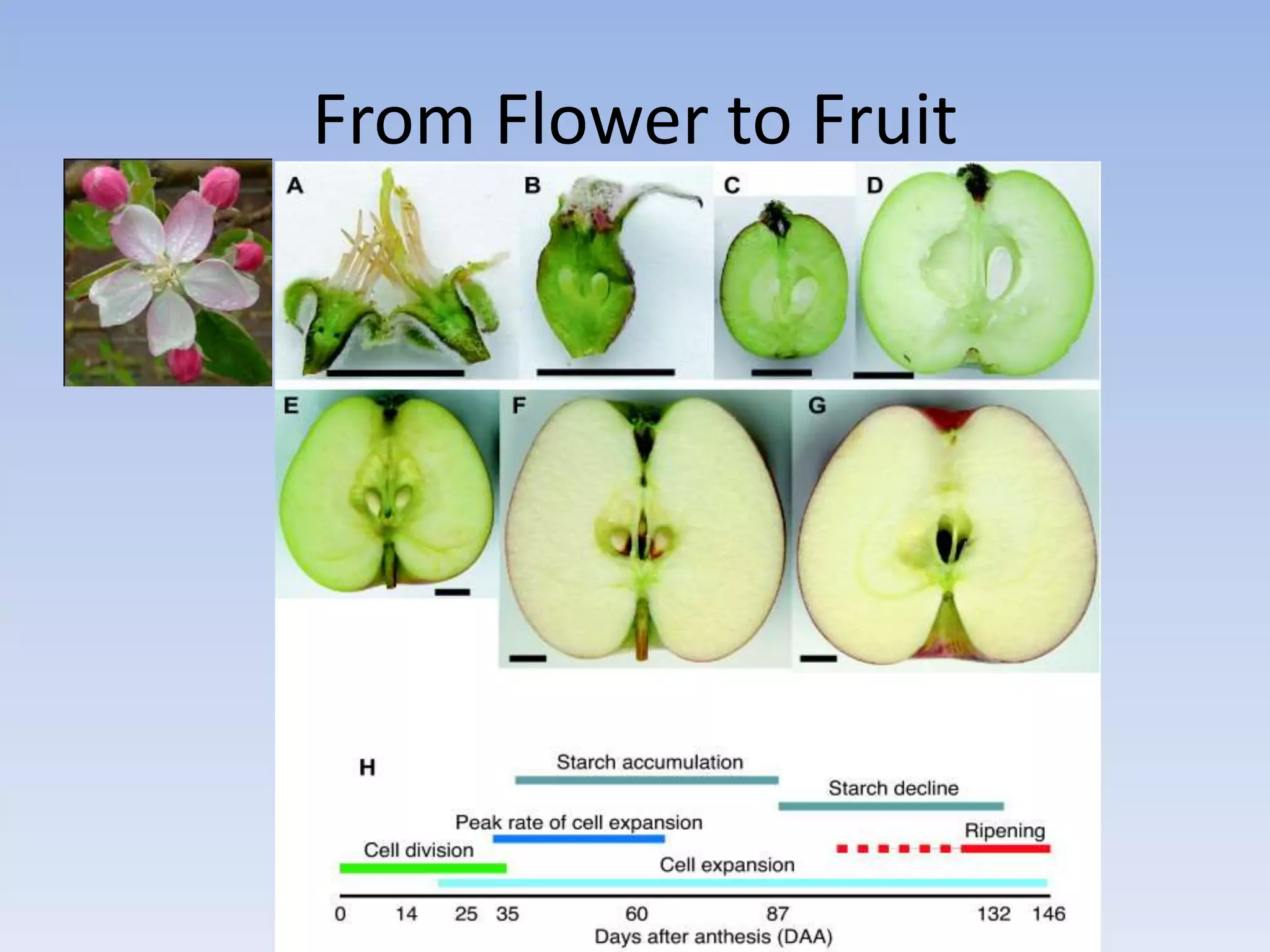
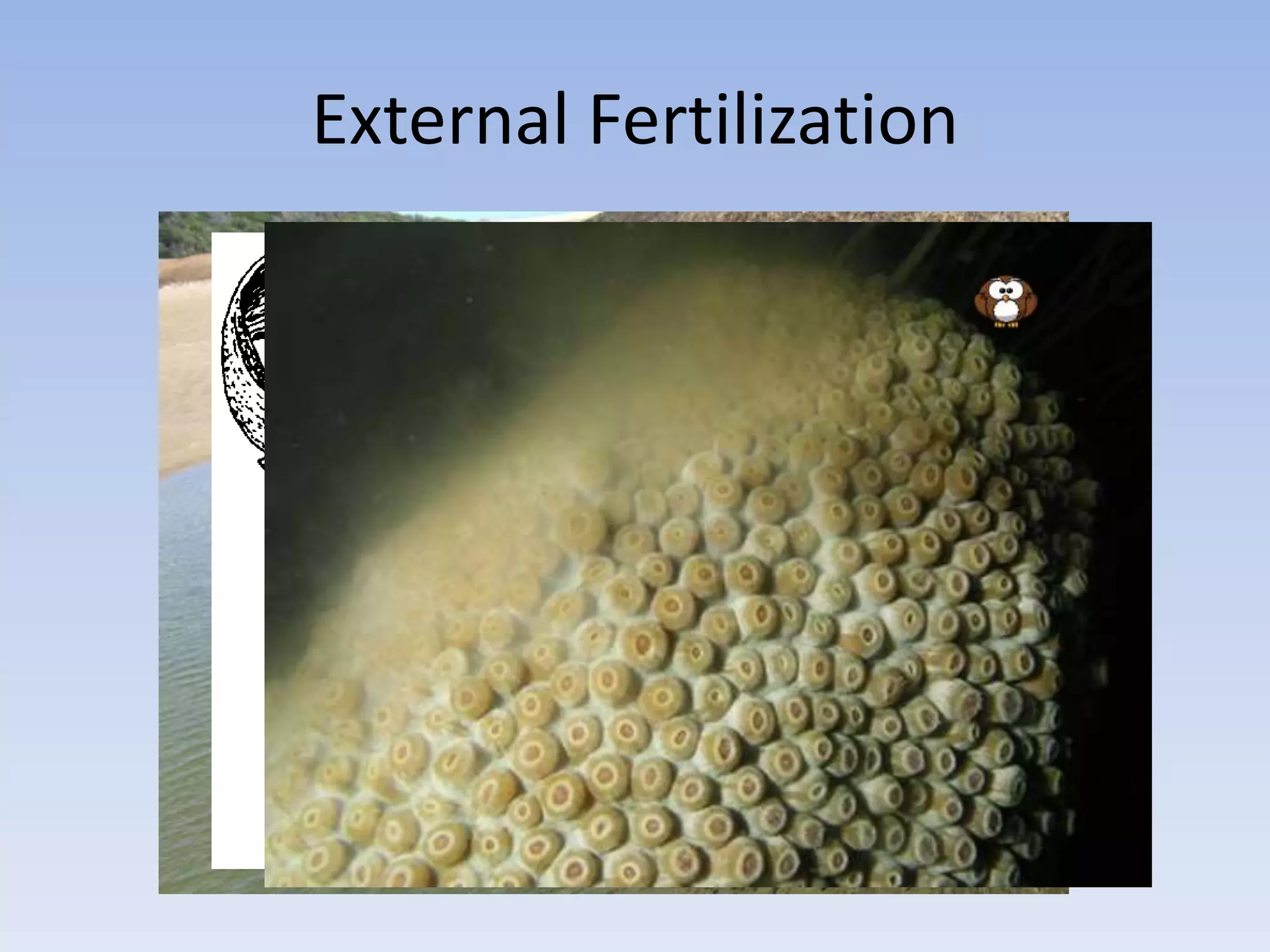
2. In plants, sexual reproduction occurs through flowers and pollination, where pollen contains sperm that fertilizes eggs in ovules. This results in seeds and fruit. In animals, fertilization can be external or internal.
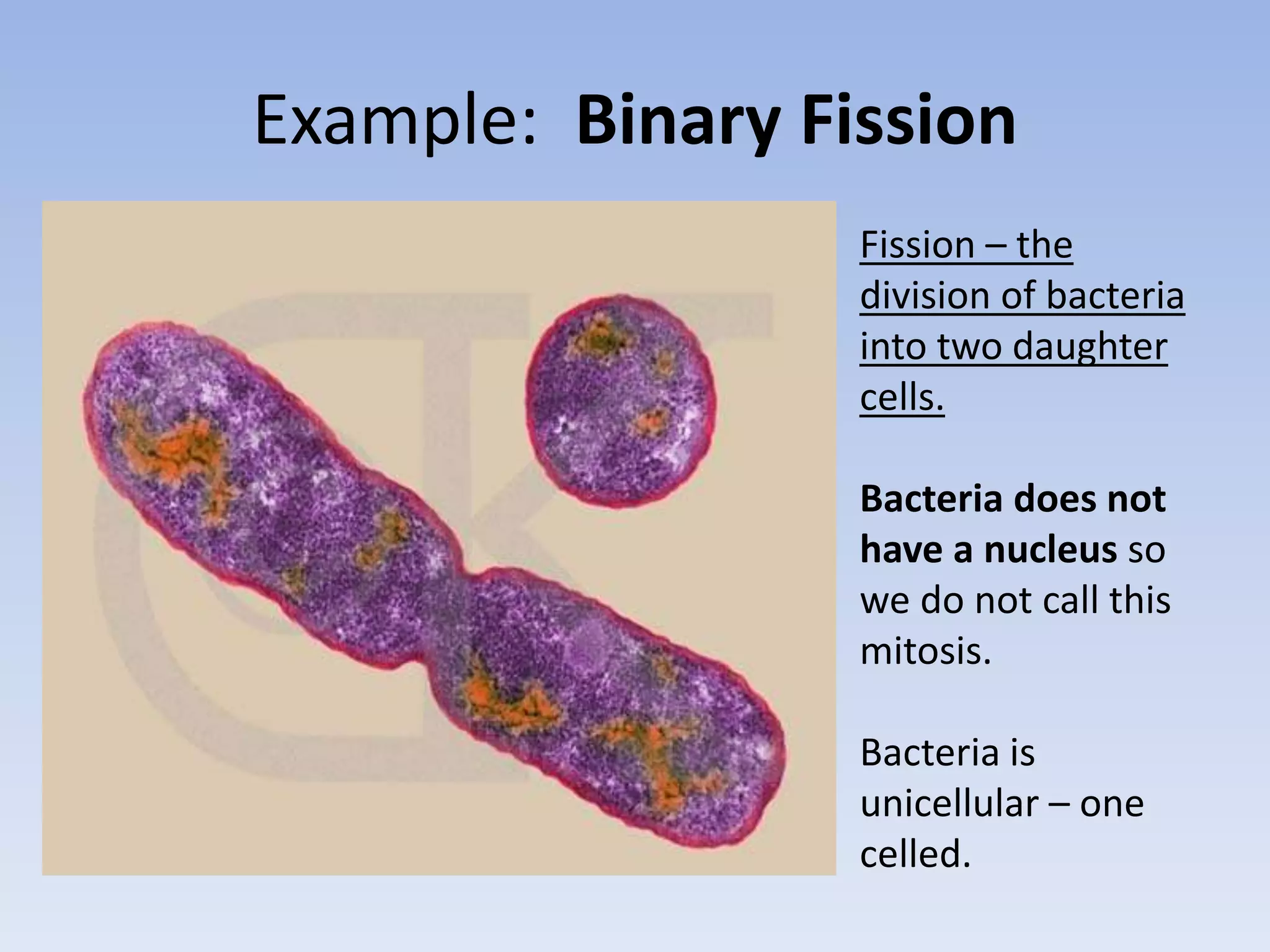
3. Examples of asexual reproduction in organisms include binary fission in bacteria, budding in yeast, and parthenogenesis in some species like whiptail lizards and sharks. Asexual reproduction allows for more rapid reproduction without the need to find a mate.