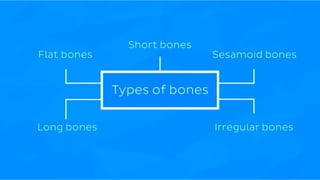
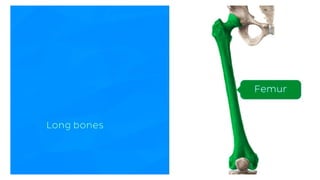
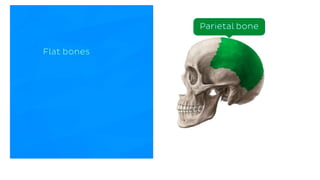
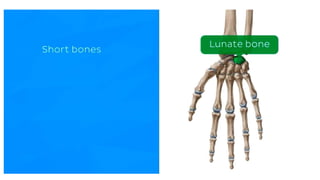
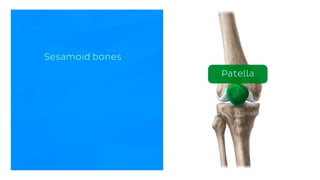
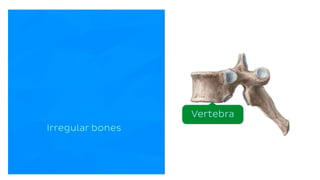
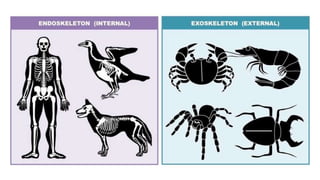
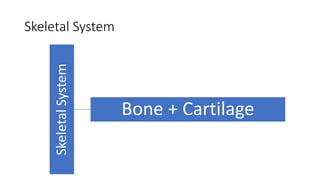
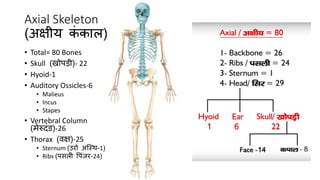
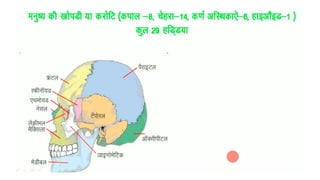
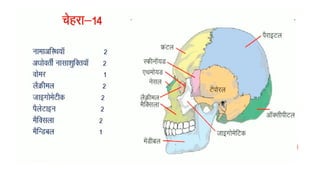
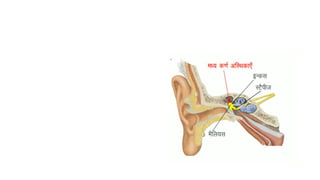
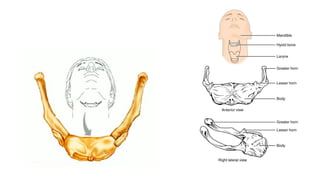
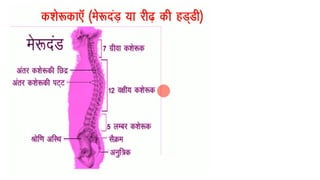
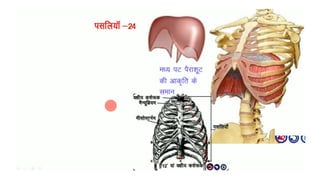
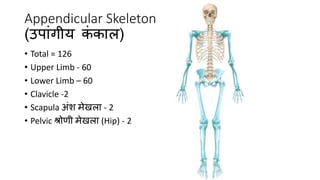
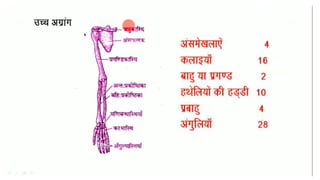
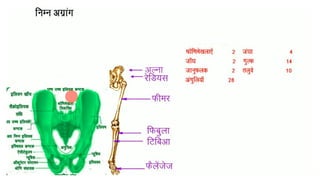
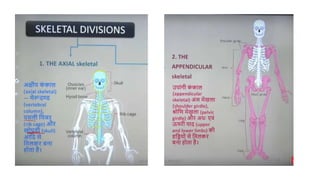
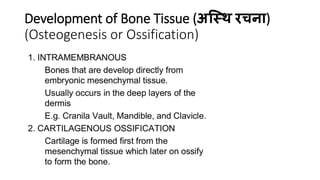
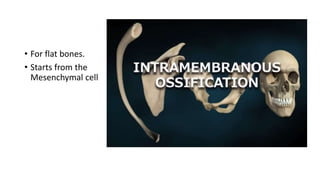
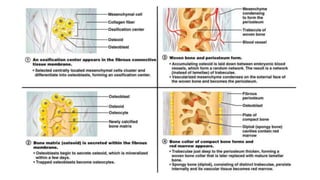
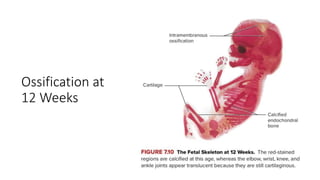
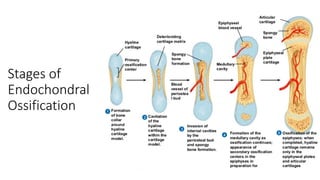
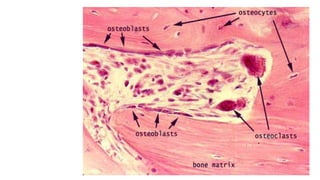
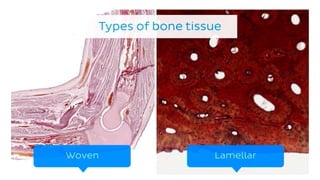
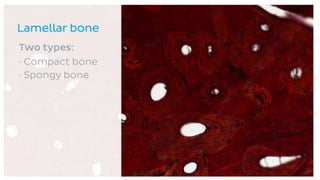
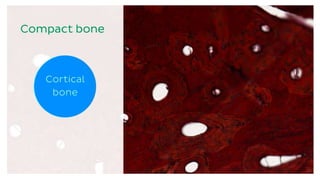
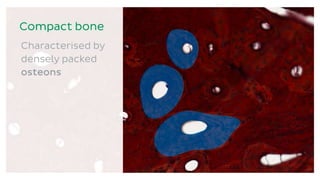
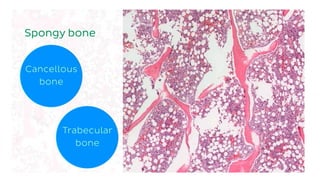
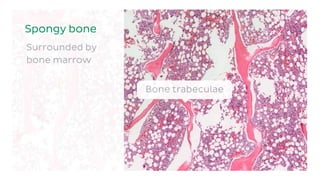
The skeletal system consists of bones and cartilage that make up the endoskeletal framework of the human body. There are two main types of skeletons: exoskeletons, which are external structures that support and protect the body, and endoskeletons, which are internal structures composed of mineralized tissue. The human skeletal system contains 206 bones that make up the axial skeleton including the skull, vertebral column, and thorax, and the appendicular skeleton including the upper and lower limbs. The skeletal system provides structure and support for the body, allows for movement, protects internal organs, produces blood cells, and stores minerals. Bones develop through two processes: intramembranous ossification which forms flat bones,