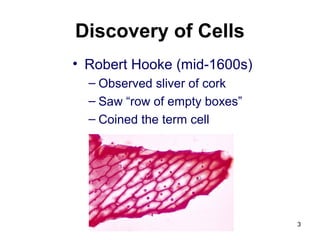
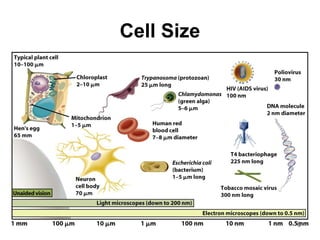
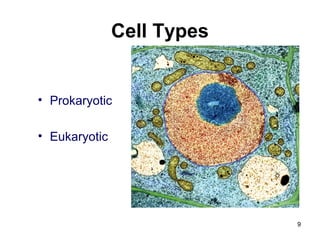
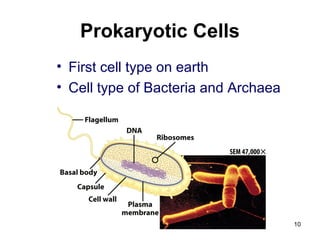
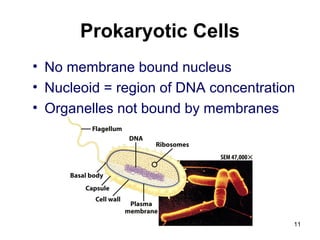
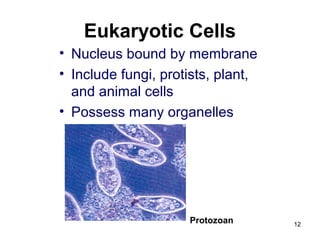
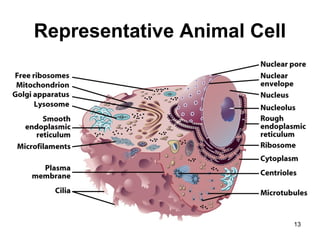
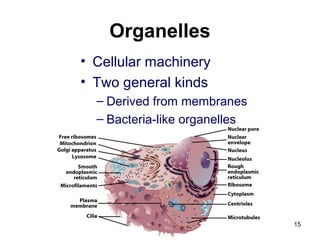
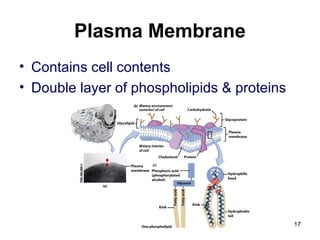
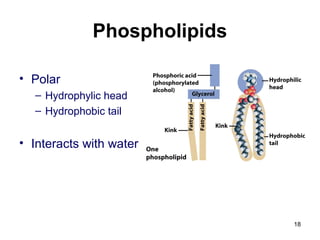
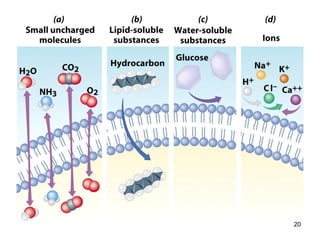
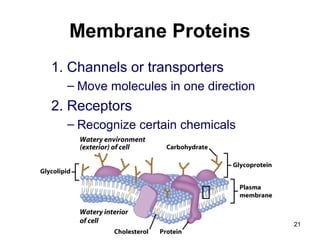
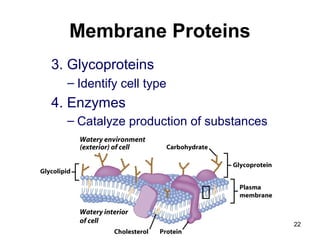
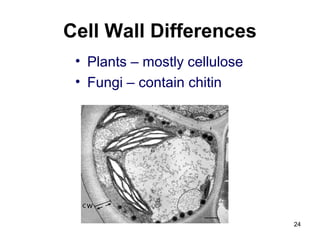
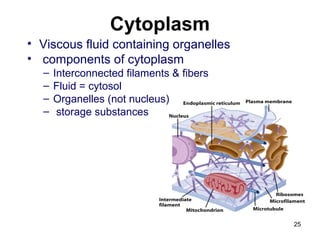
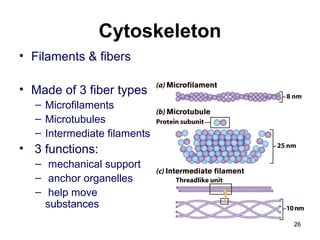
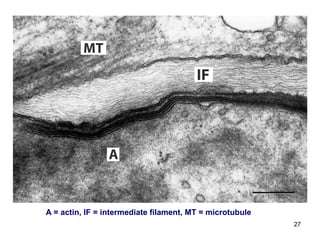
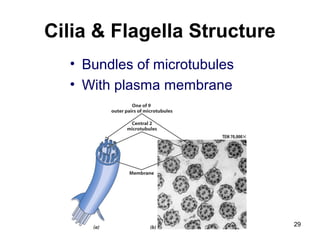
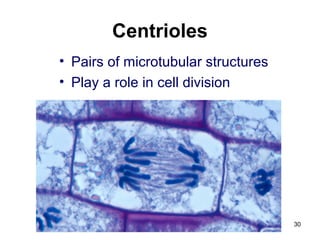
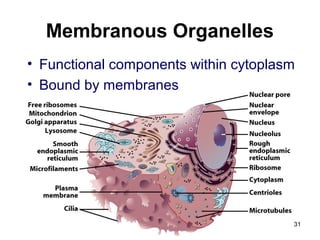
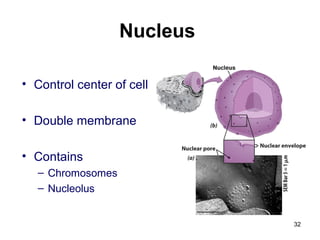
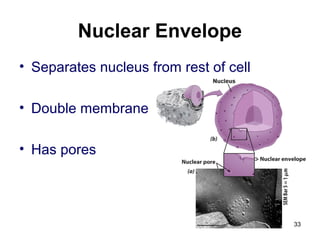
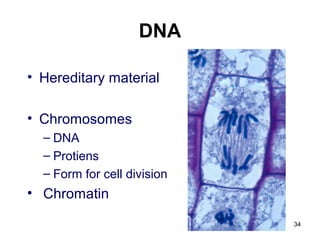
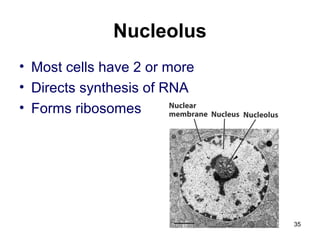
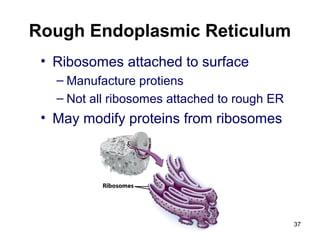
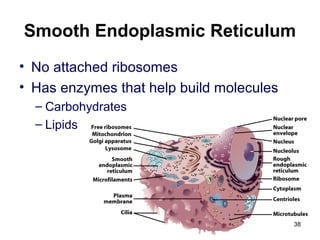
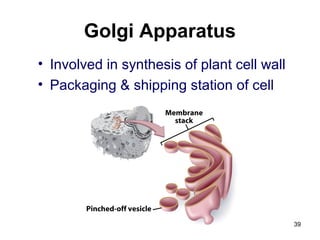
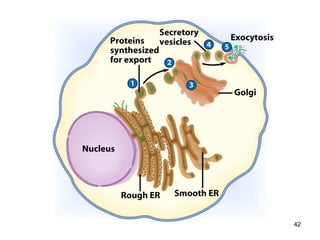
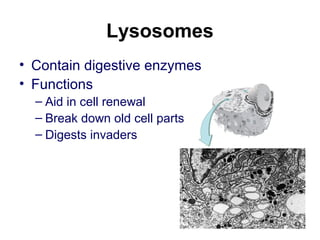
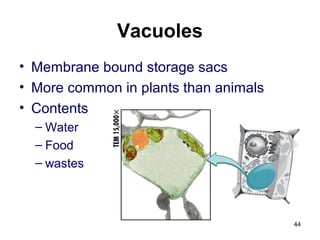
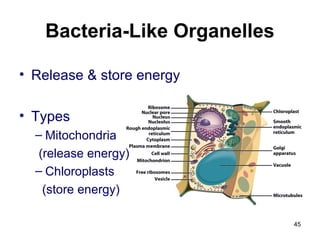
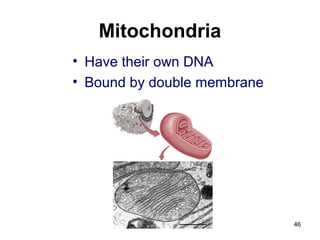
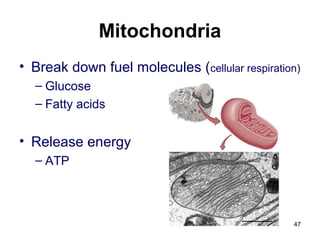
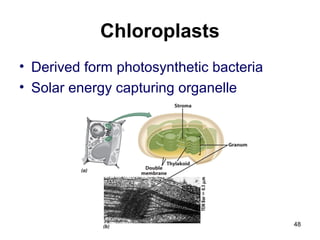
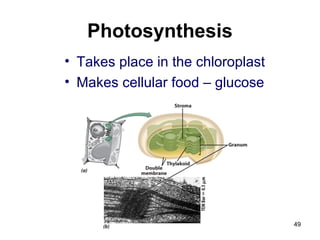
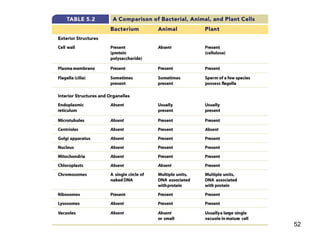
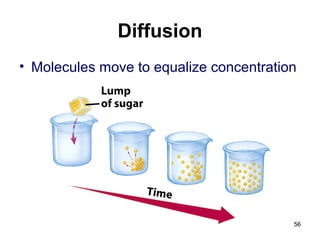
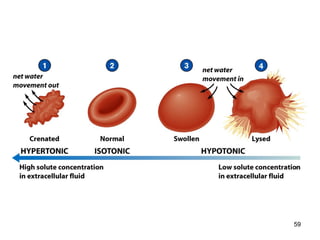
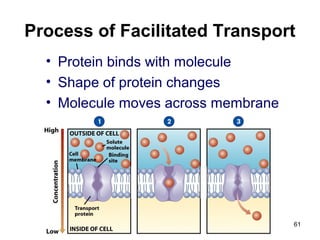
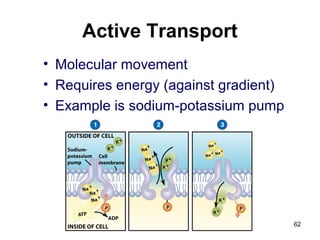
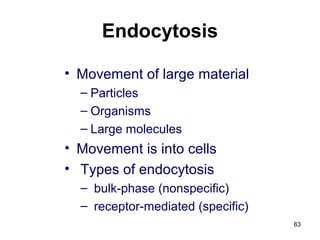
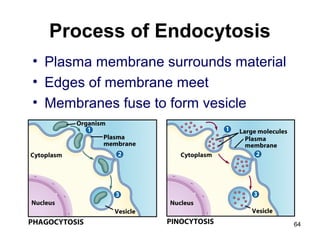
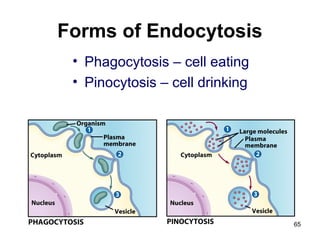
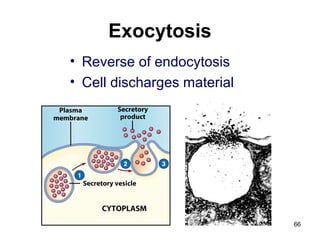
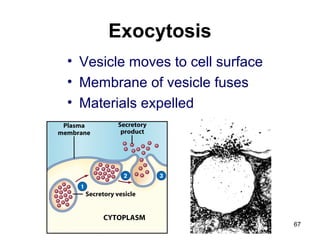
Cell Structure and Function outlines key concepts in cell biology. It discusses that cells are the basic unit of life and were first observed by Robert Hooke in the 1600s. Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden established cell theory in 1839, stating that all living things are made of cells, and Rudolf Virchow later added that all cells come from preexisting cells. All cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and organelles like the nucleus. Prokaryotic cells lack organelles while eukaryotic cells have organelles like the nucleus. The document then describes various organelle structures and functions like the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. It also covers