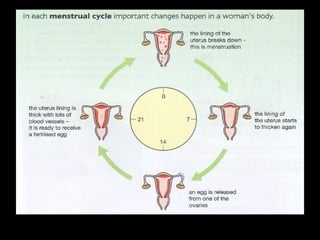
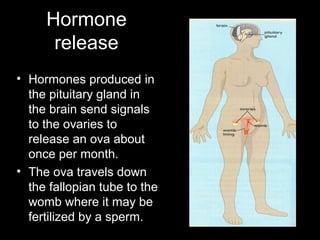
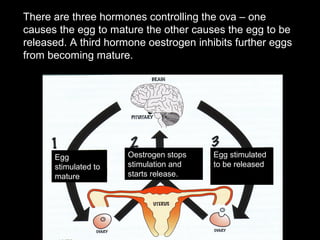
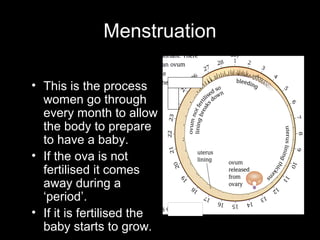
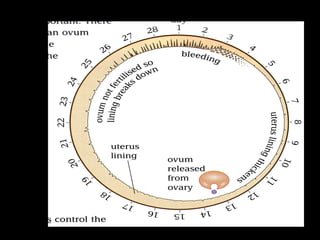
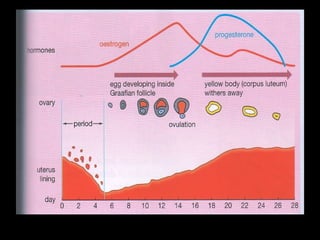
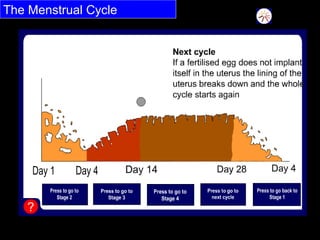
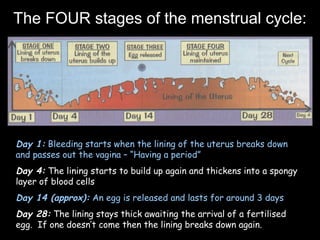
The menstrual cycle occurs monthly and is controlled by hormones from the pituitary gland that signal the ovaries to release an egg (ova) through the fallopian tubes to the uterus. If the egg is not fertilized by a sperm, it disintegrates and the uterine lining breaks down and is passed, along with blood and tissue, through menstruation or a period. The four stages of the menstrual cycle are: bleeding starts on day 1 when the uterine lining breaks down; rebuilding of the lining starts on day 4; an egg is released around day 14 and can be fertilized for 3 days; and the thickened lining remains on day 28 awaiting a fertilized egg before breaking down again if none arrives.