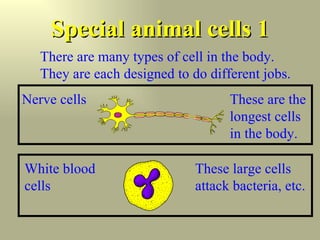
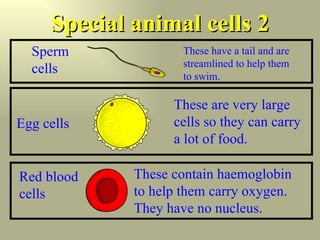
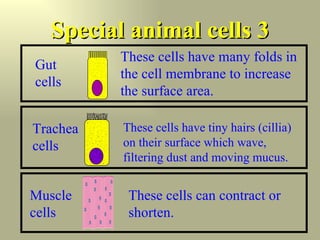
The body contains many different types of cells that are specially adapted to their functions. Nerve cells are long to conduct electrical signals over long distances. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin and lack a nucleus to efficiently carry oxygen throughout the body. Guard cells in plant leaves have specialized structures that allow them to control gas exchange.