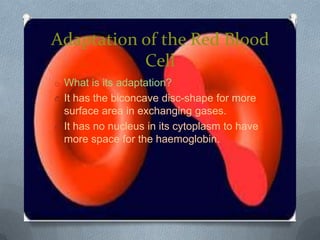
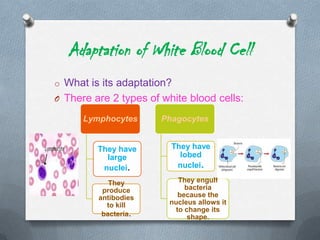
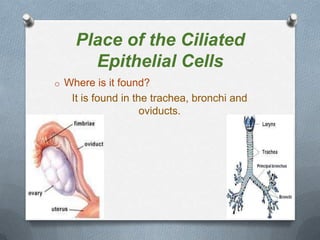
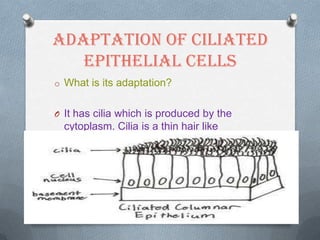
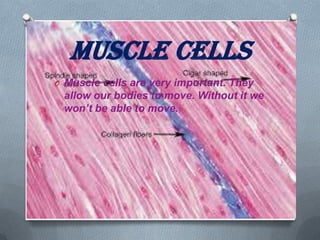
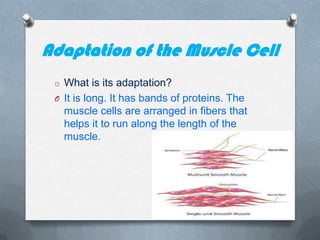
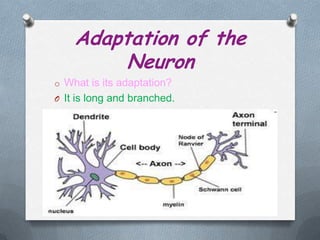
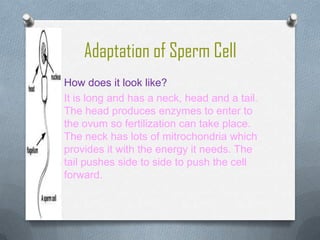
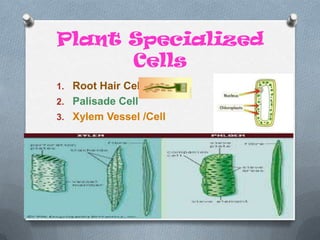
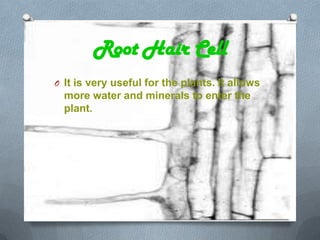
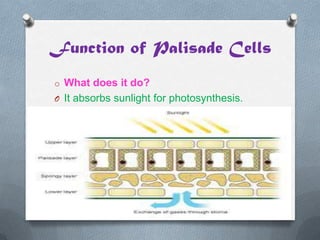
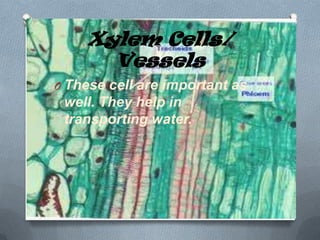
Specialized cells in plants and animals have unique structures and functions. Plant cells like palisade cells and root hair cells help with photosynthesis and water absorption. Animal cells such as red and white blood cells, muscle cells, and neurons each have important roles in oxygen transport, immune response, movement, and nerve impulses.