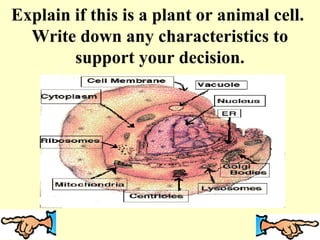
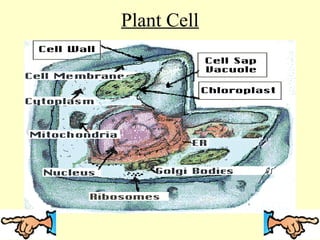
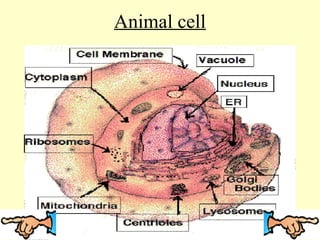
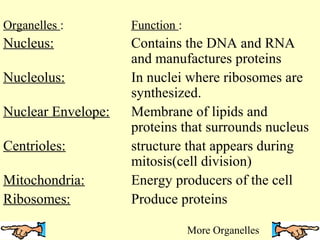
This document discusses the similarities and differences between animal and plant cells. It begins by explaining that cells are the basic functional units of living things and have unique structures that allow them to survive. The key organelles of both cell types are then described, including their functions. Both cell types contain a nucleus, nuclear envelope, mitochondria, and cell membrane. However, plant cells also contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis, a cell wall, and large central vacuoles, while animal cells rely on cellular respiration and have irregular shapes. The document provides examples of plant and animal cells and questions to test the reader's understanding.