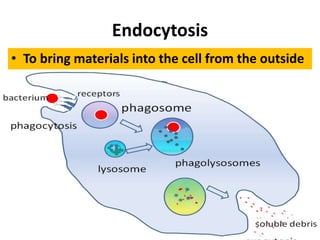
Eukaryotic cells contain specialized subcellular structures called organelles that carry out specific functions. The document describes the functions of various organelles including the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, nucleus, nucleolus, cilia, flagella, and vacuoles. It also discusses the cytoskeleton components of microfilaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments.