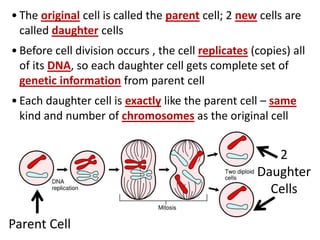
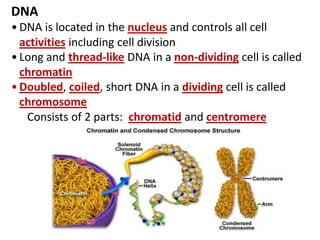
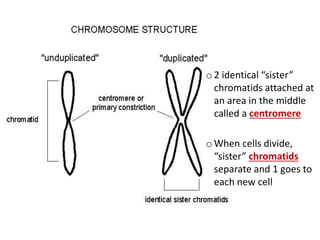
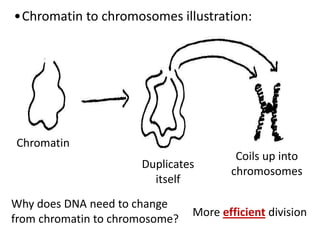
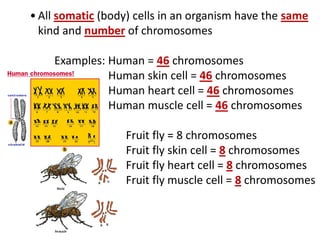
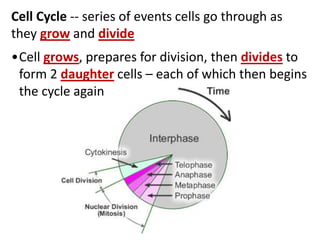
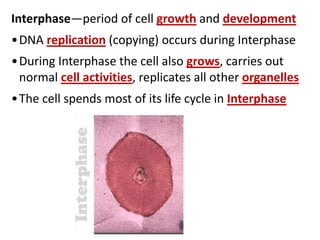
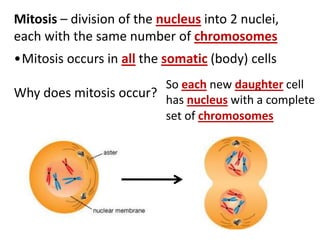
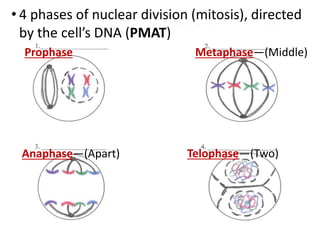
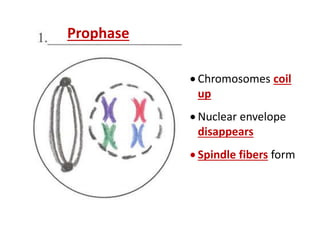
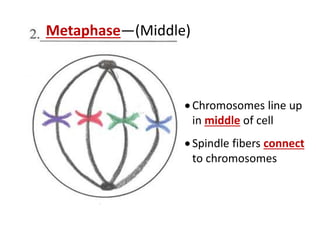
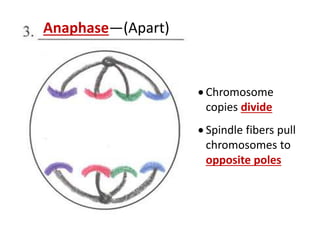
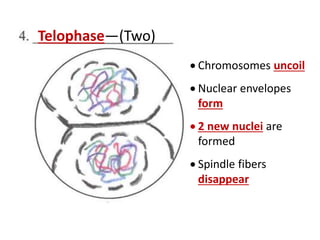
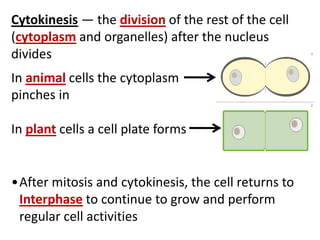
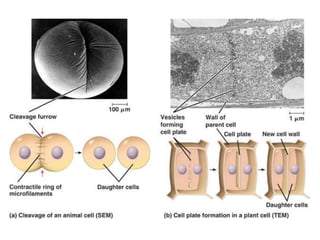
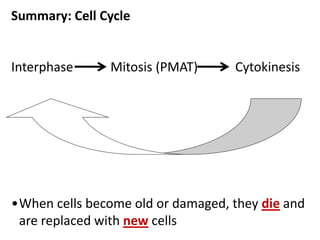
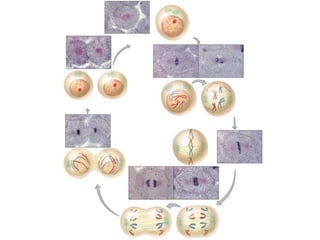
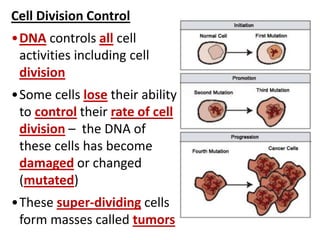
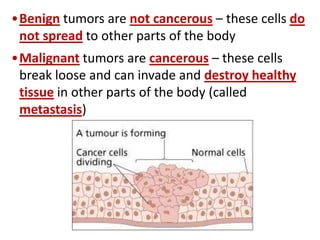
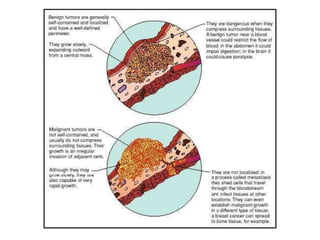
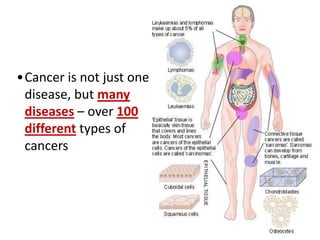
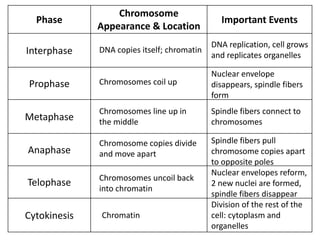
Cell division occurs through mitosis and cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells that are identical to the original parent cell. Mitosis involves four phases - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase - where the genetic material (DNA) is replicated and the chromosomes are separated into two identical sets. Cytokinesis then divides the cytoplasm and organelles to complete the formation of the two new cells from the single original cell. Cell division allows for growth and repair of tissues and is the basic means by which single-celled organisms reproduce asexually.