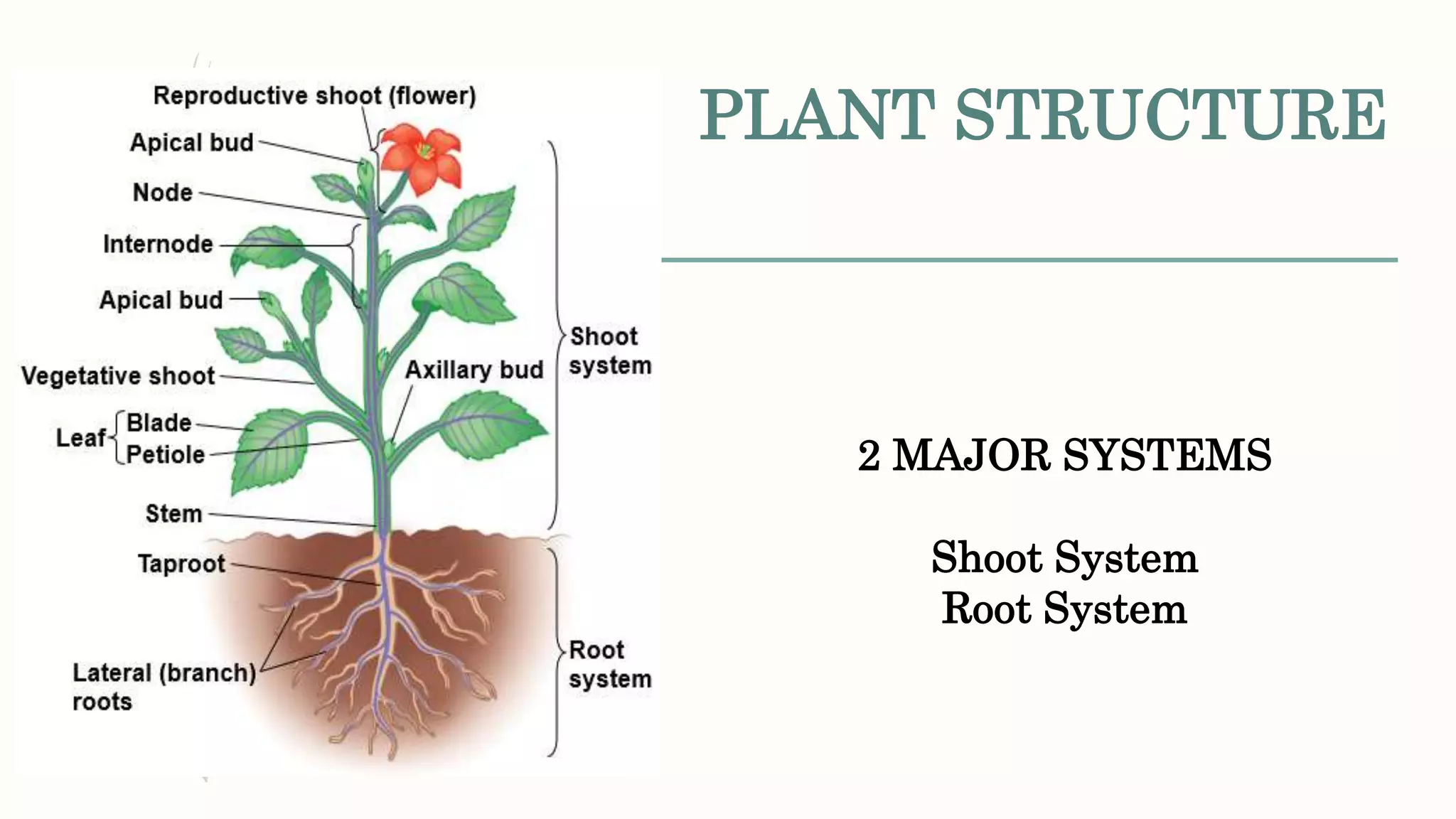
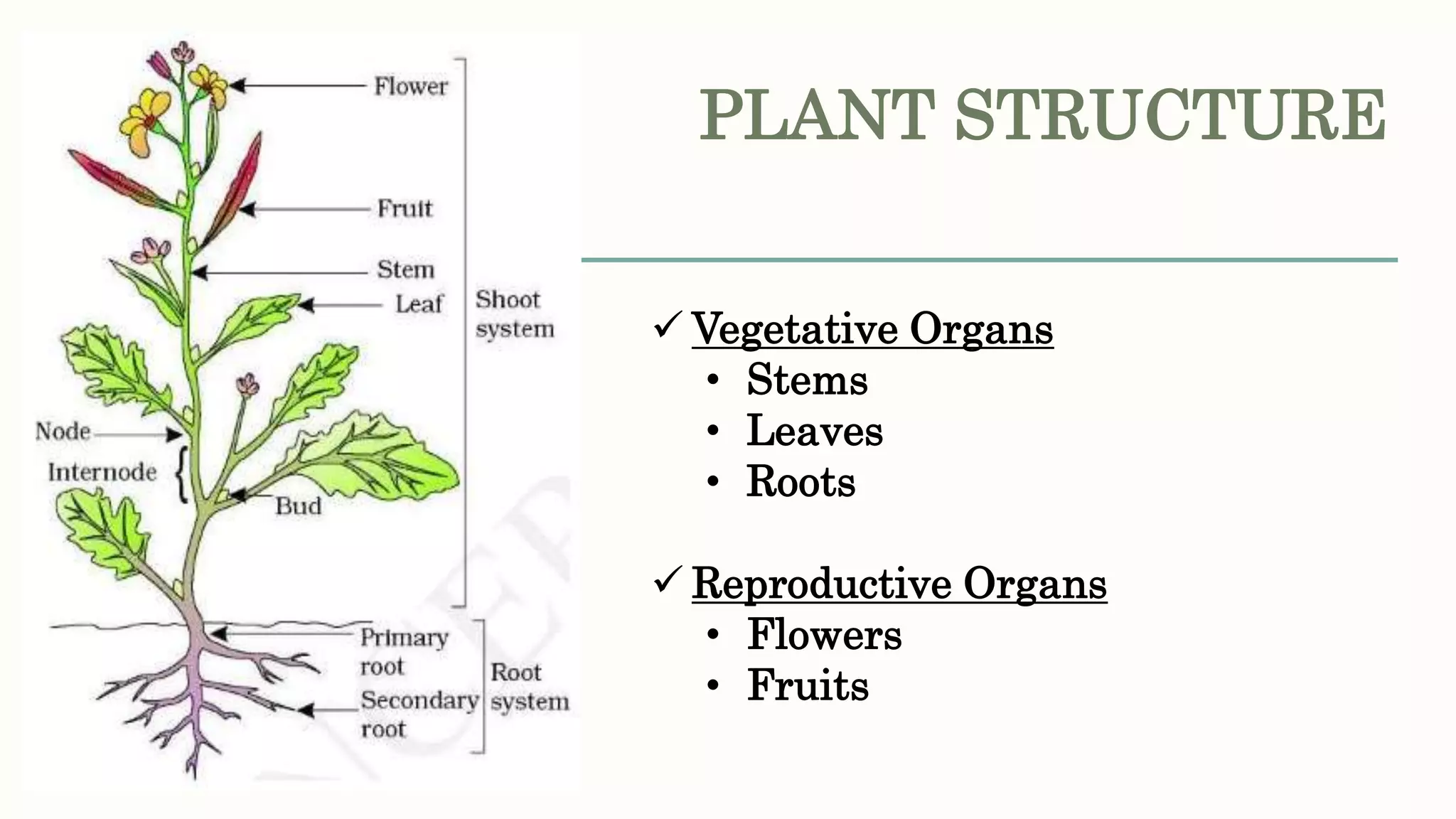
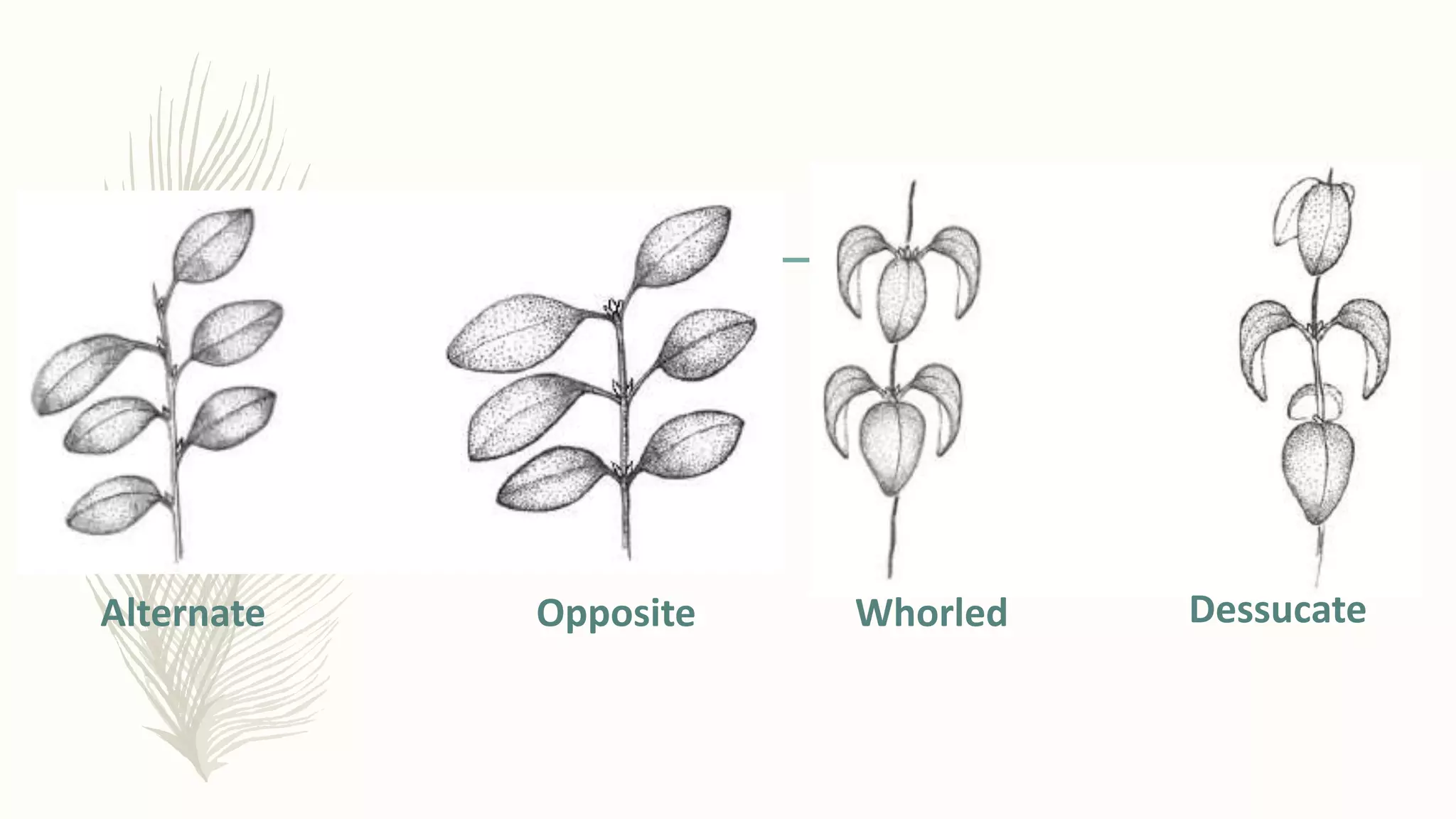
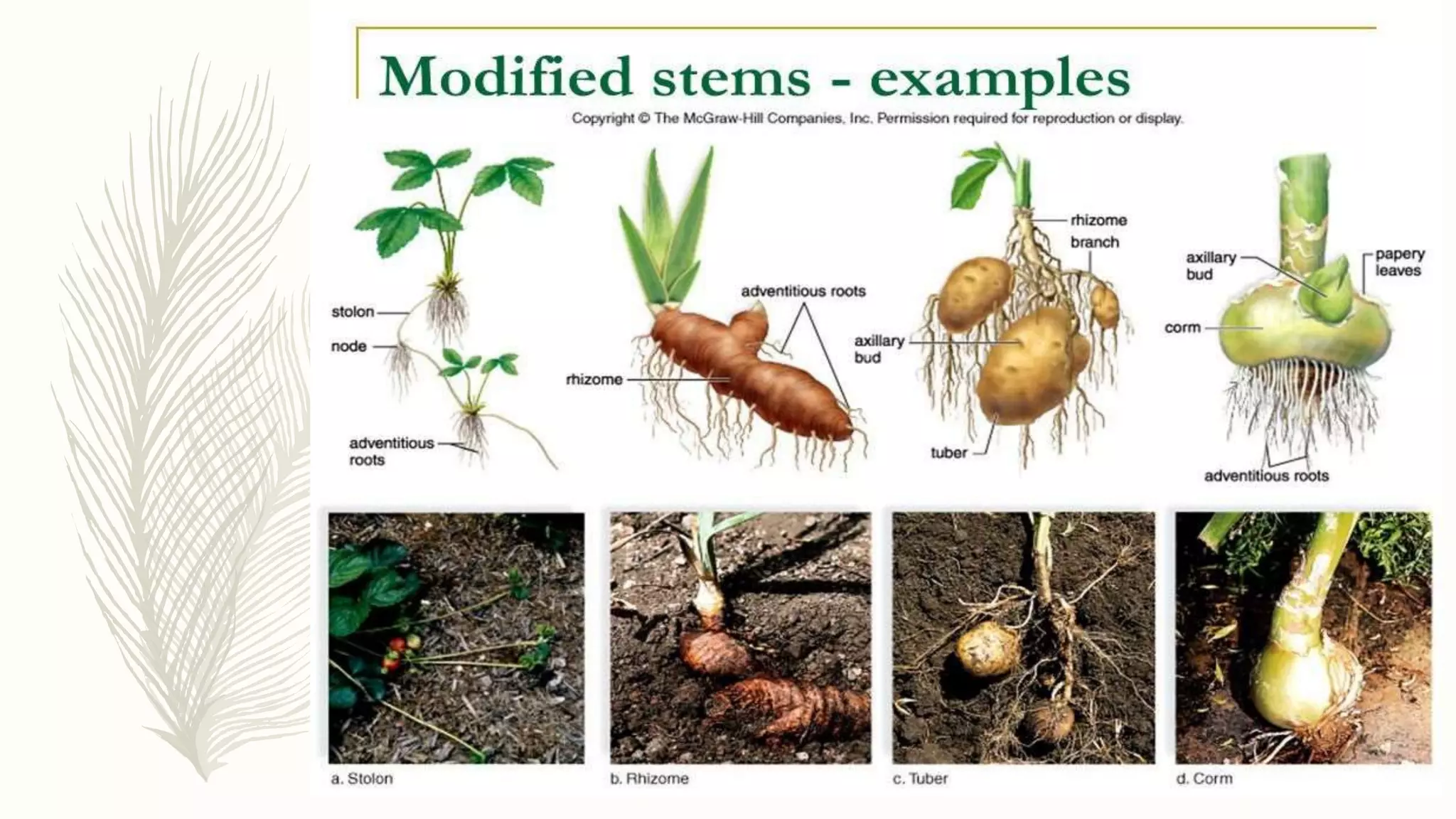
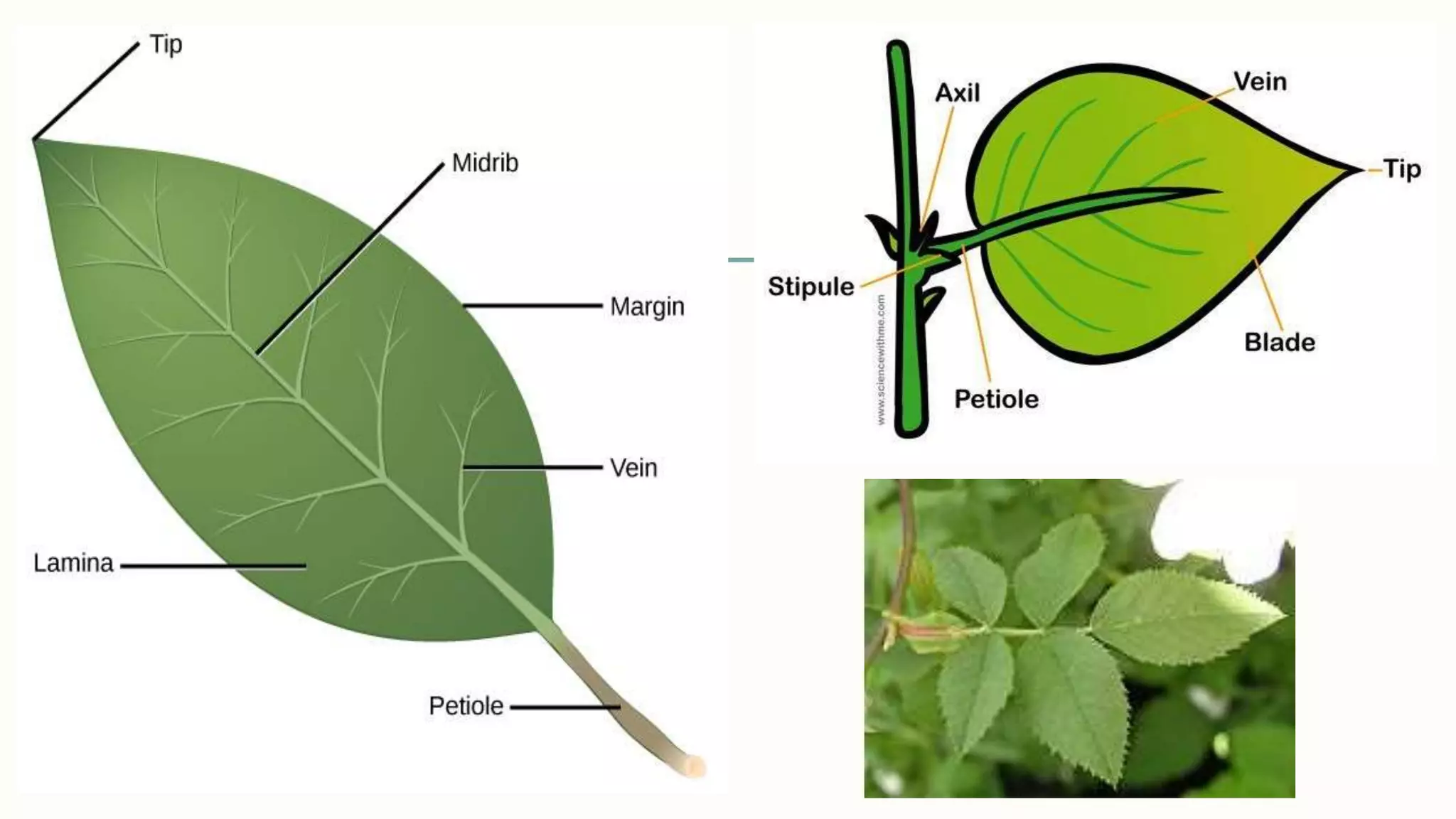
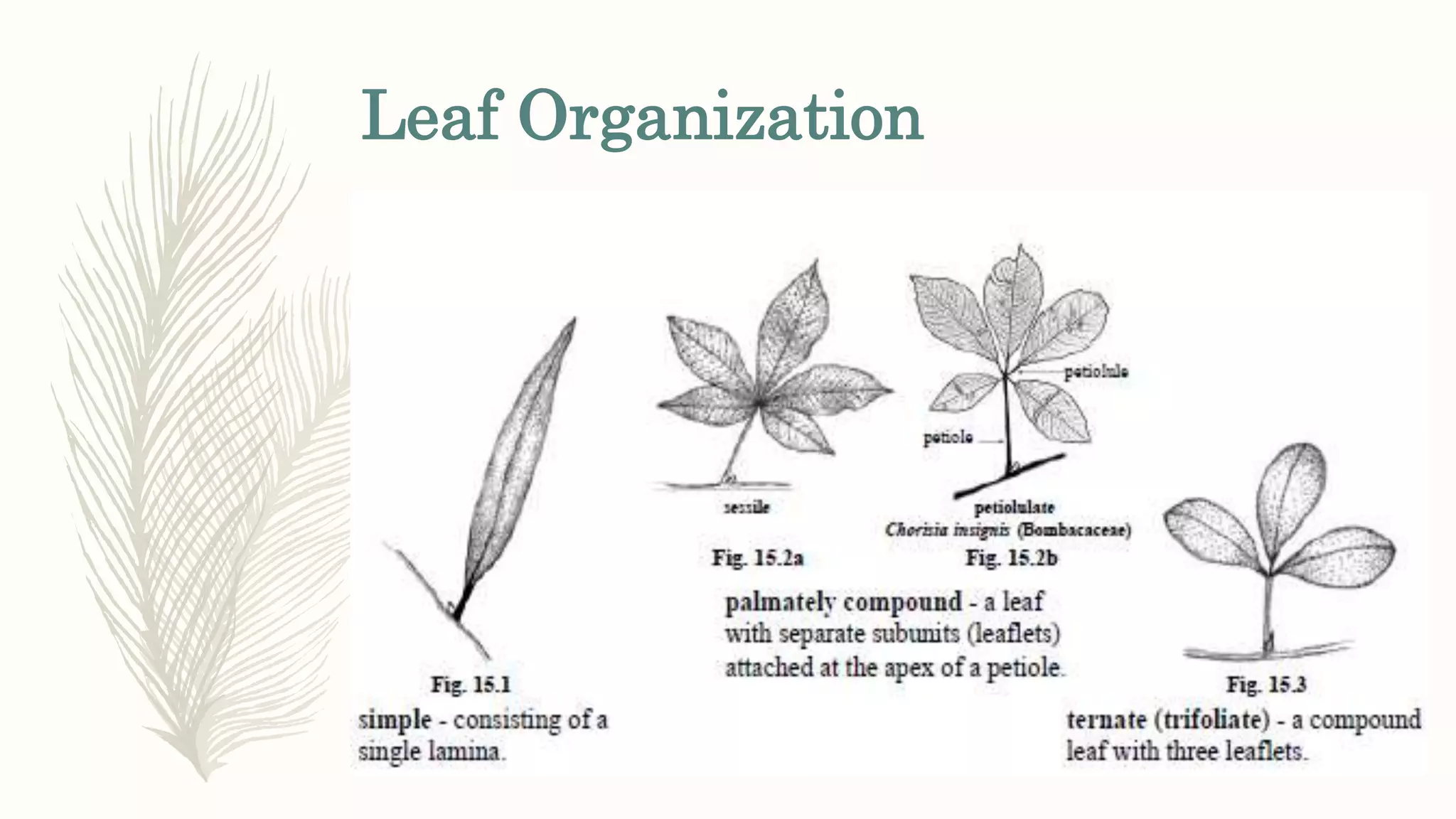
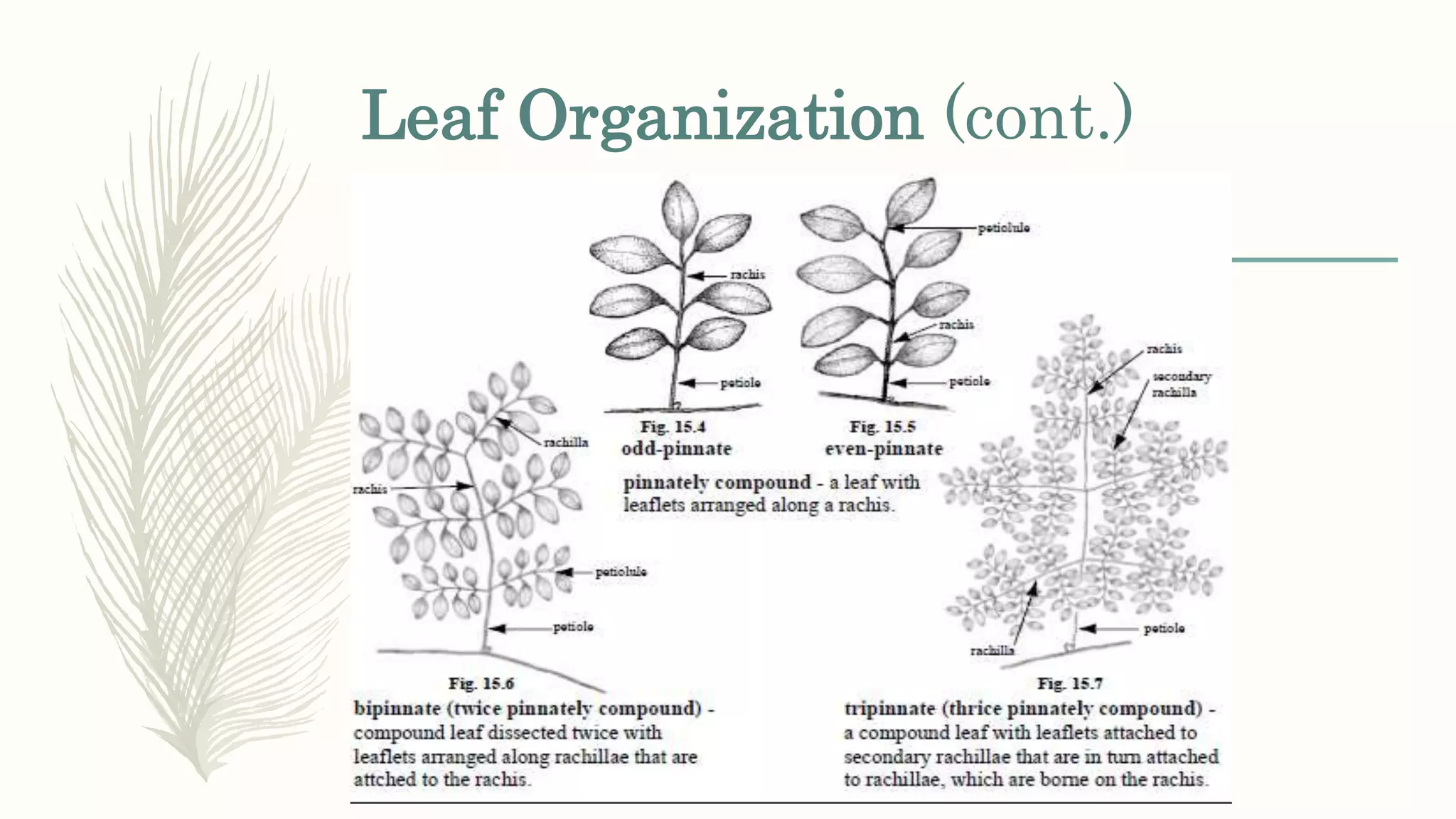
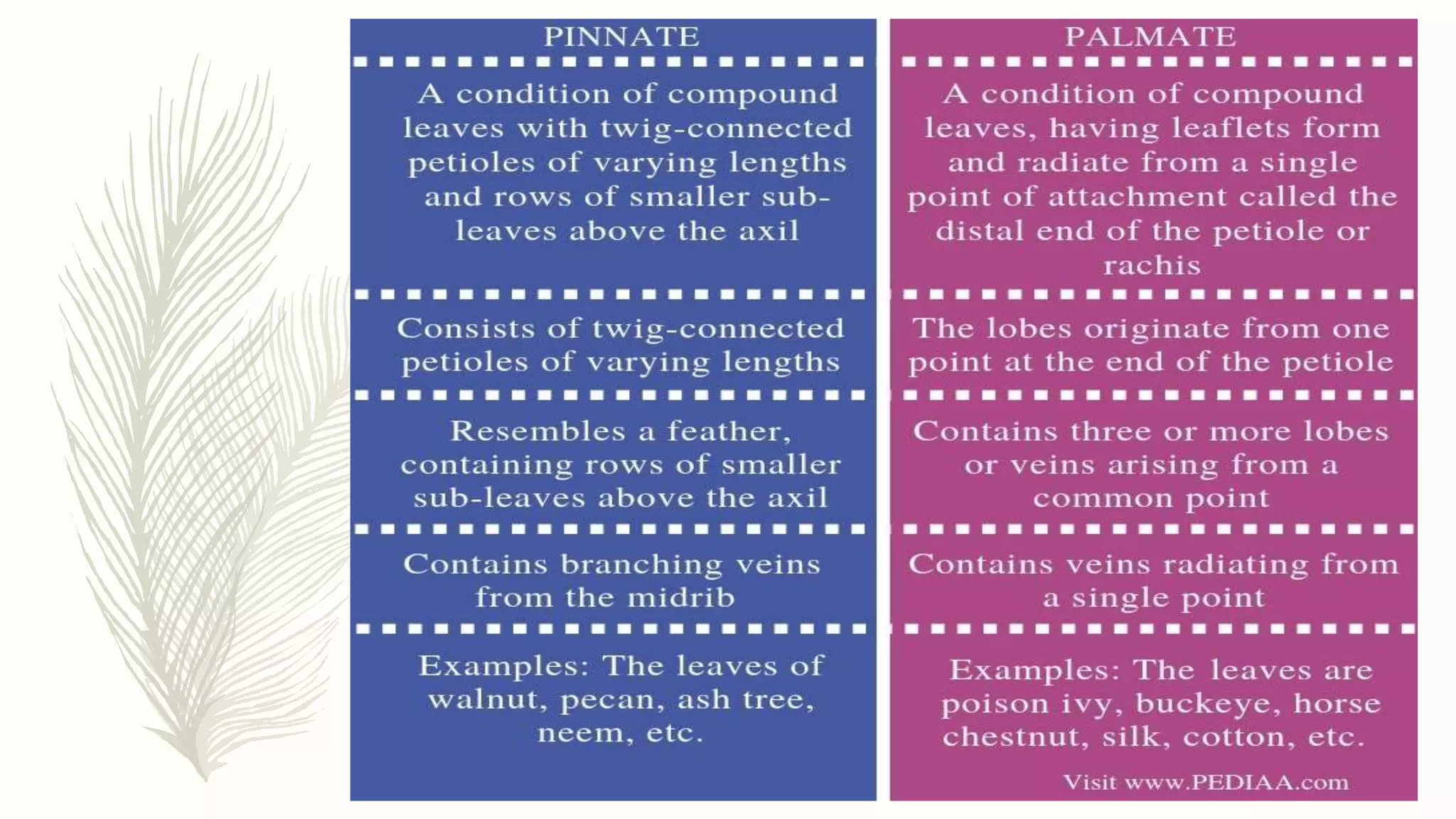
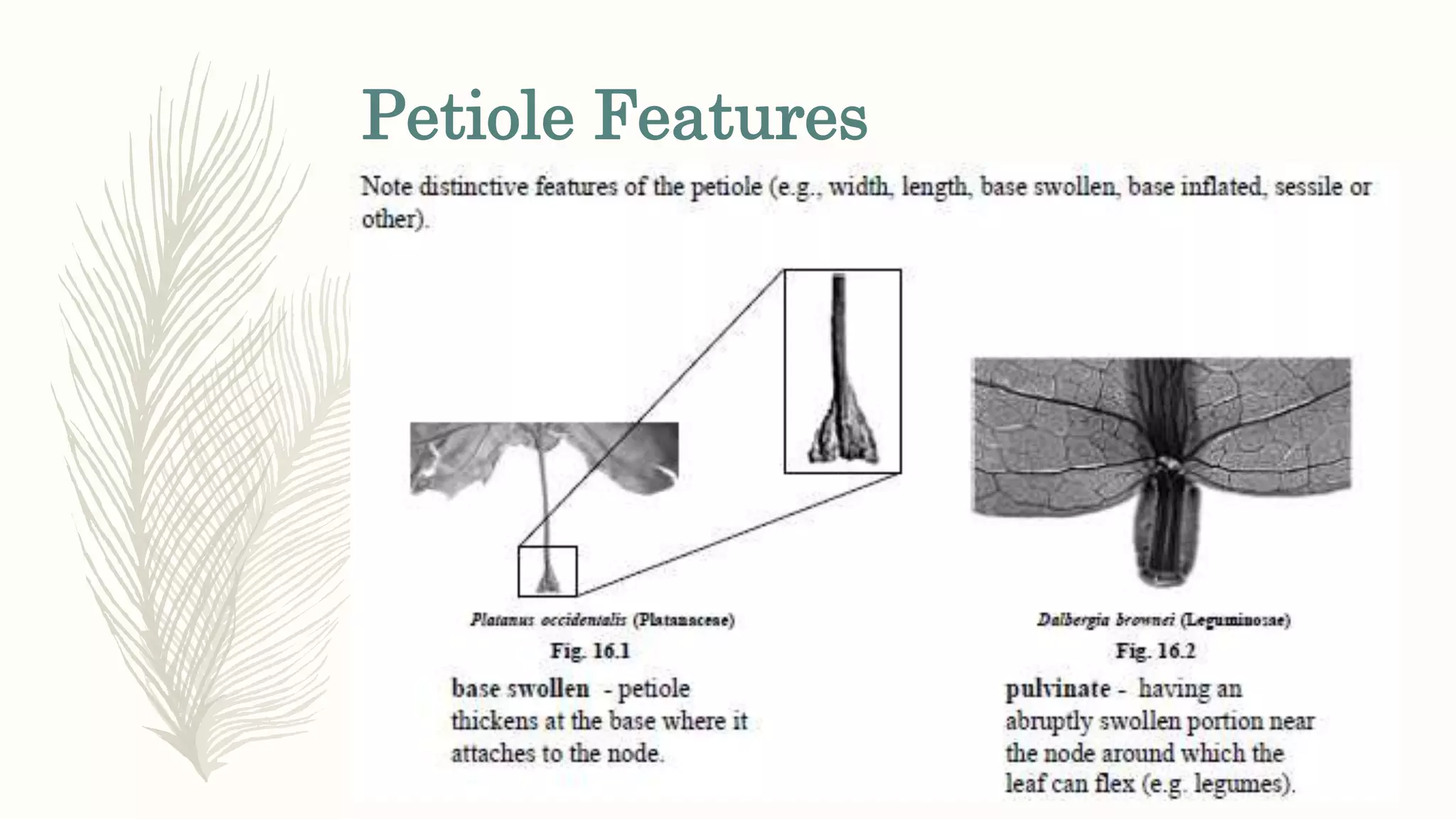
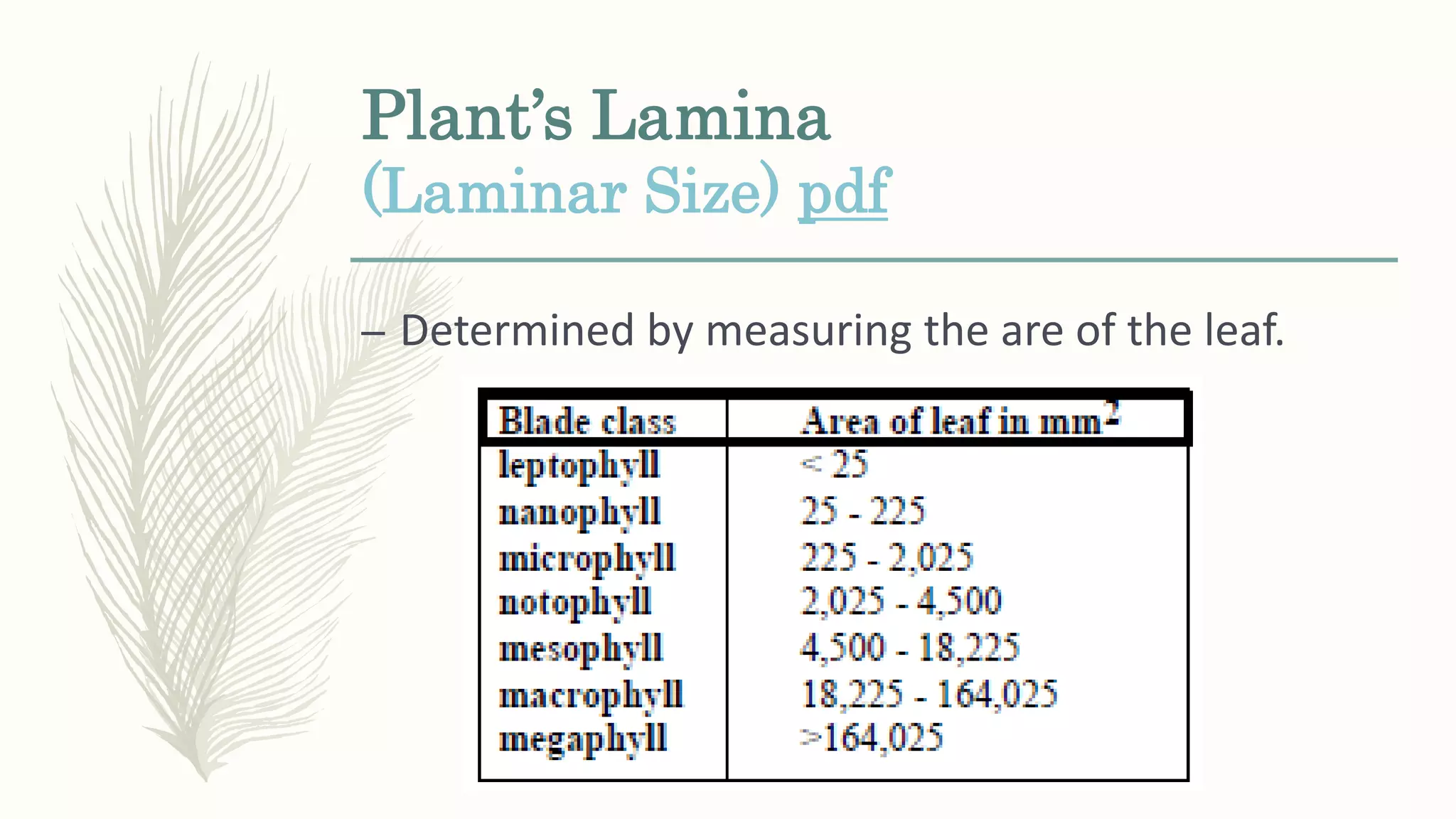
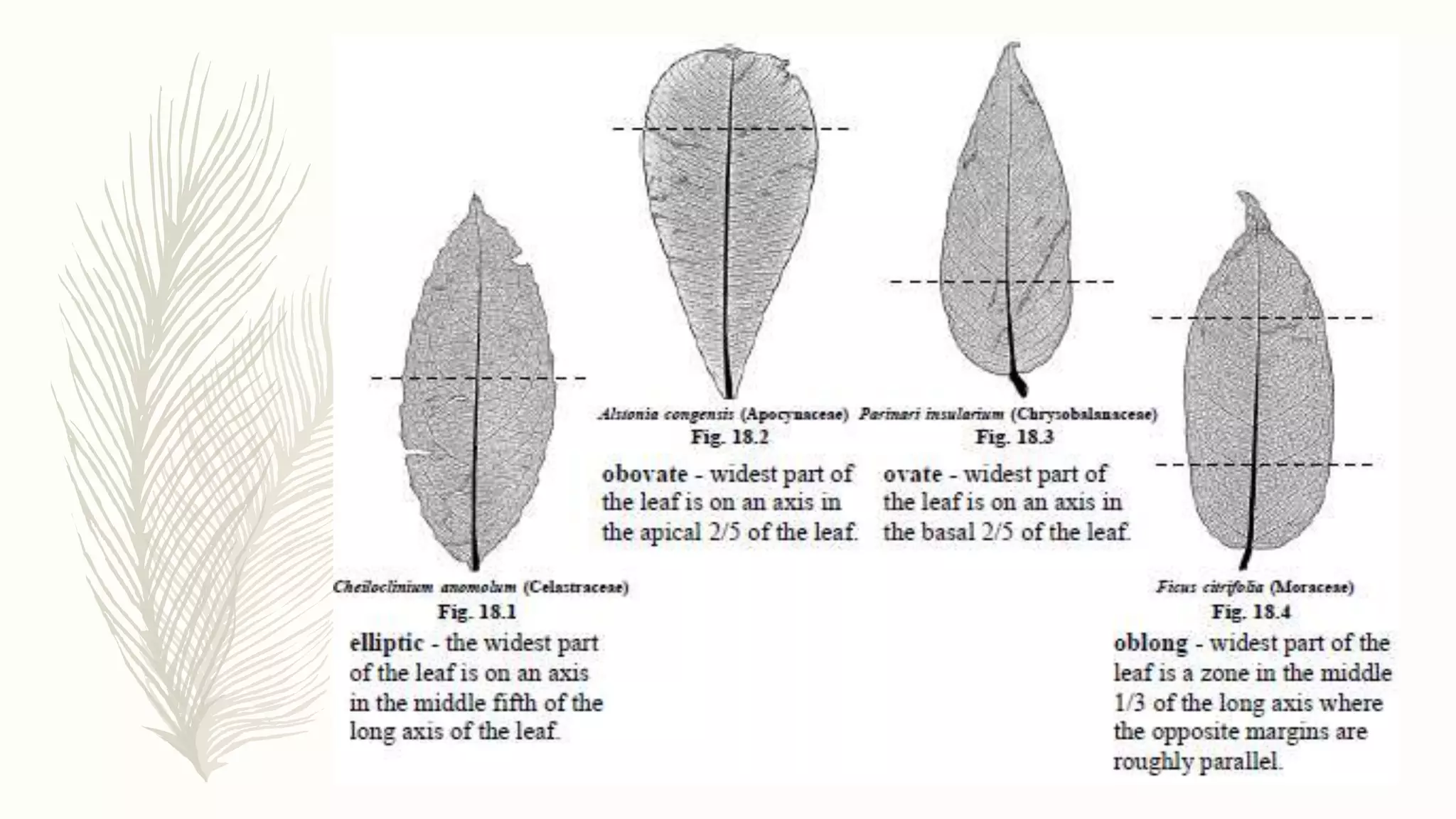
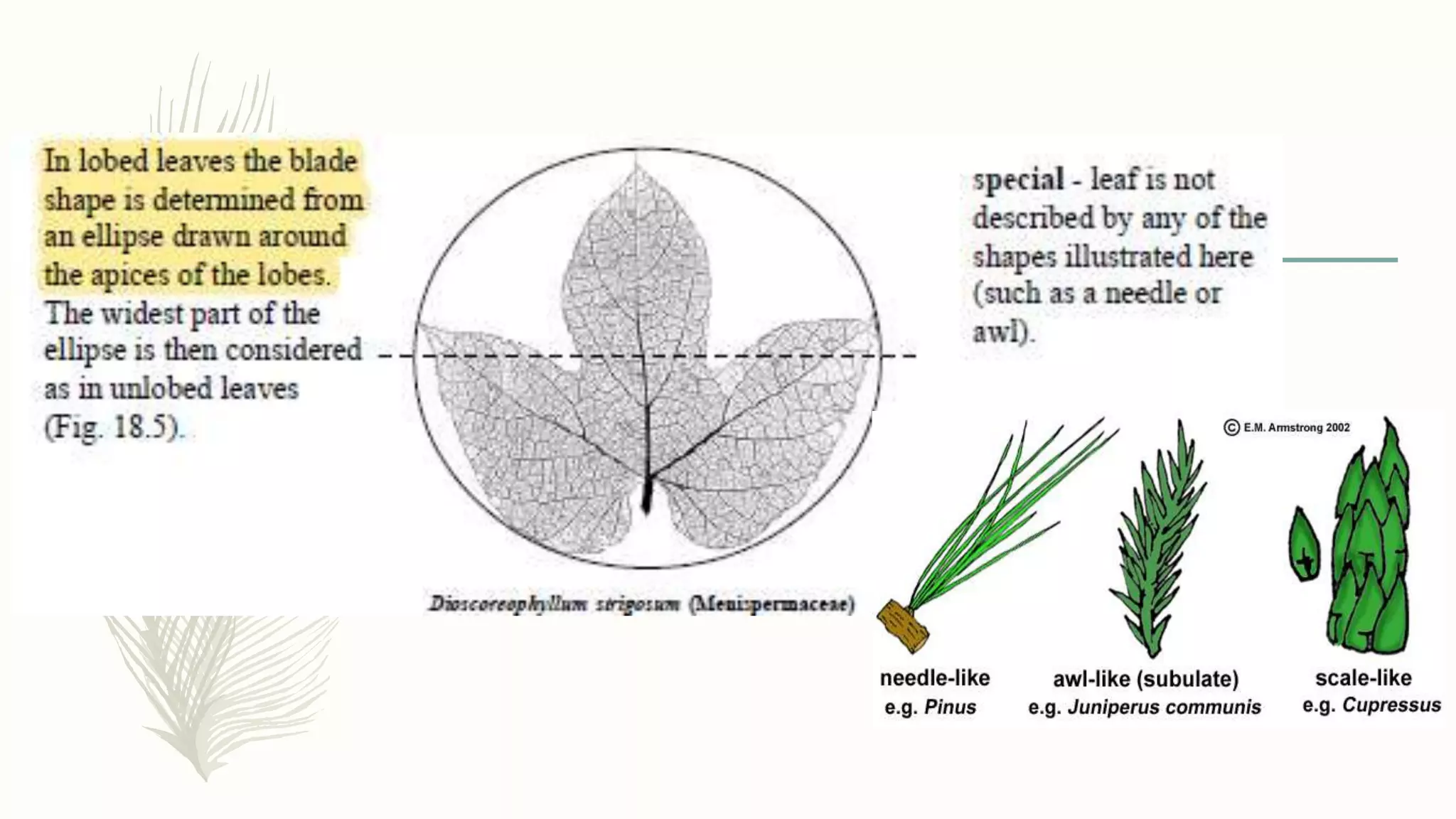
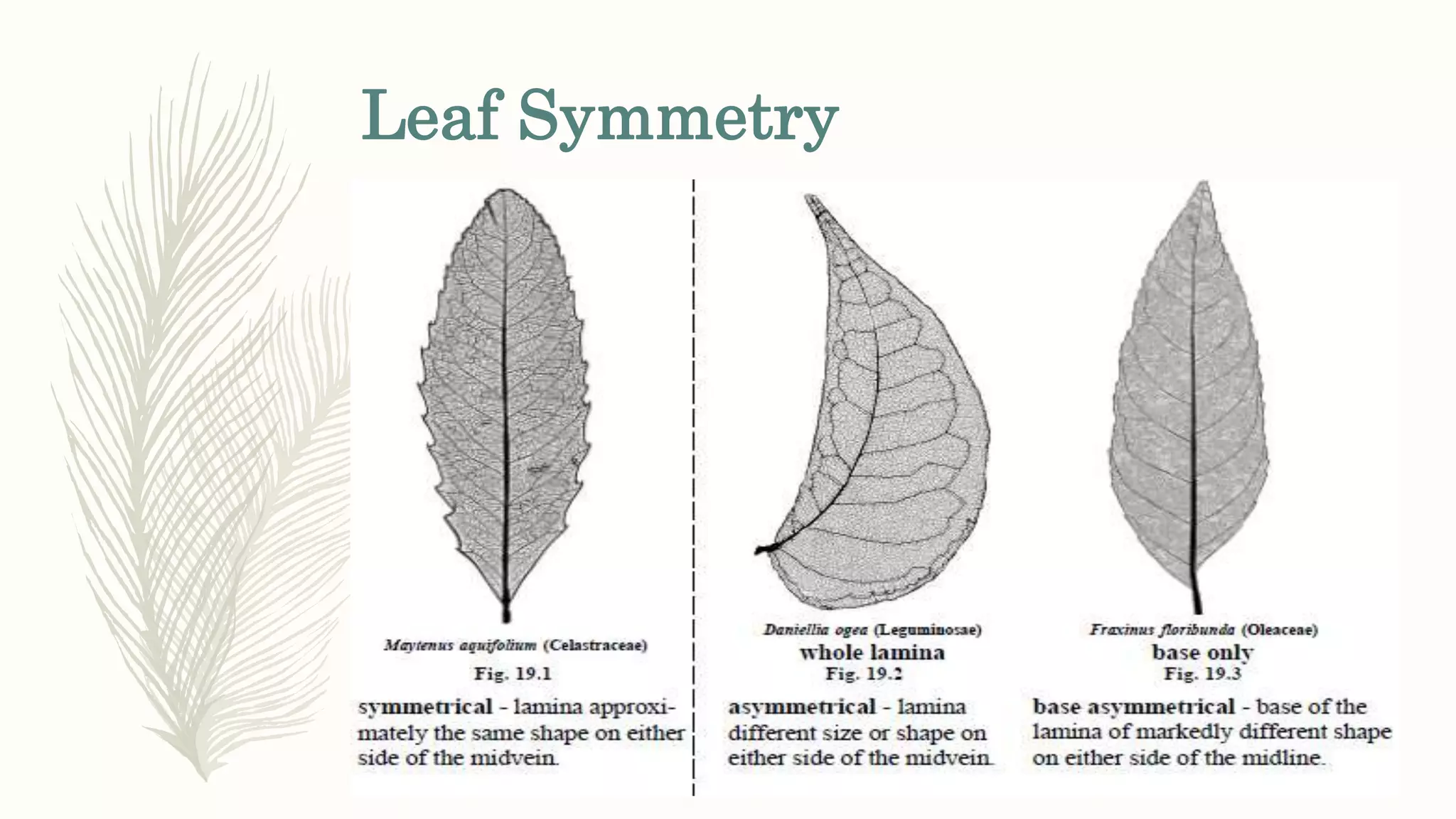
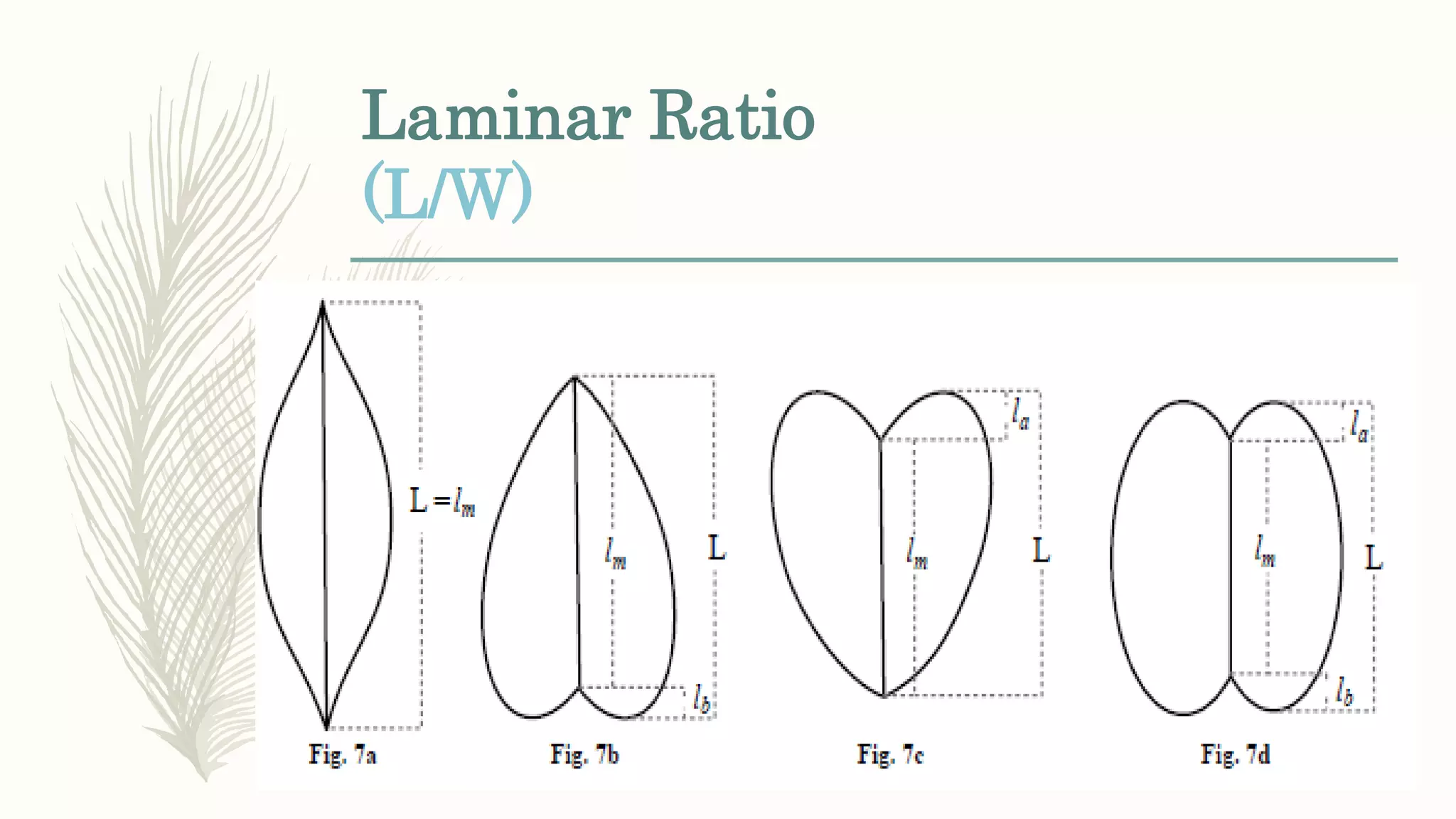
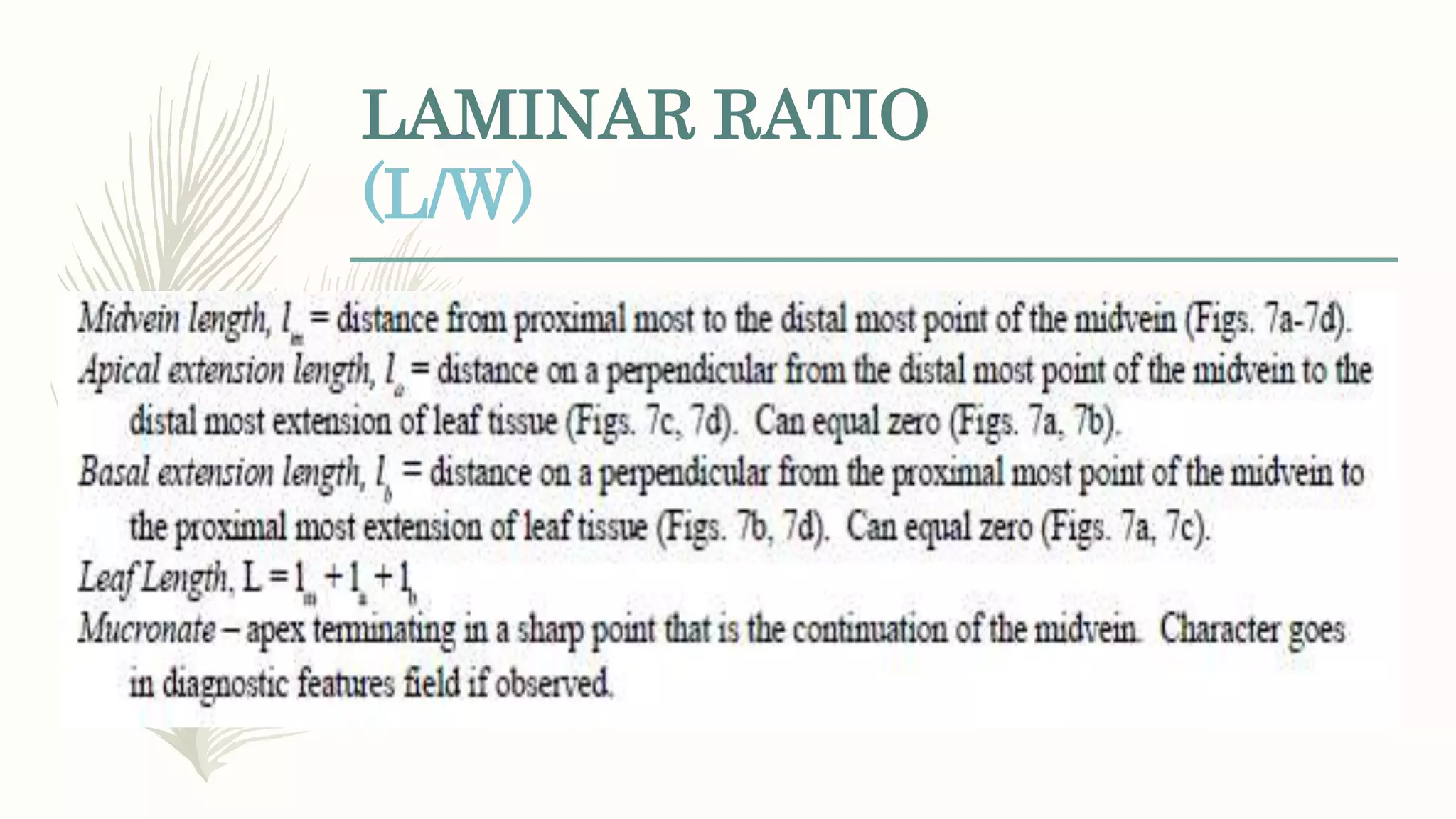
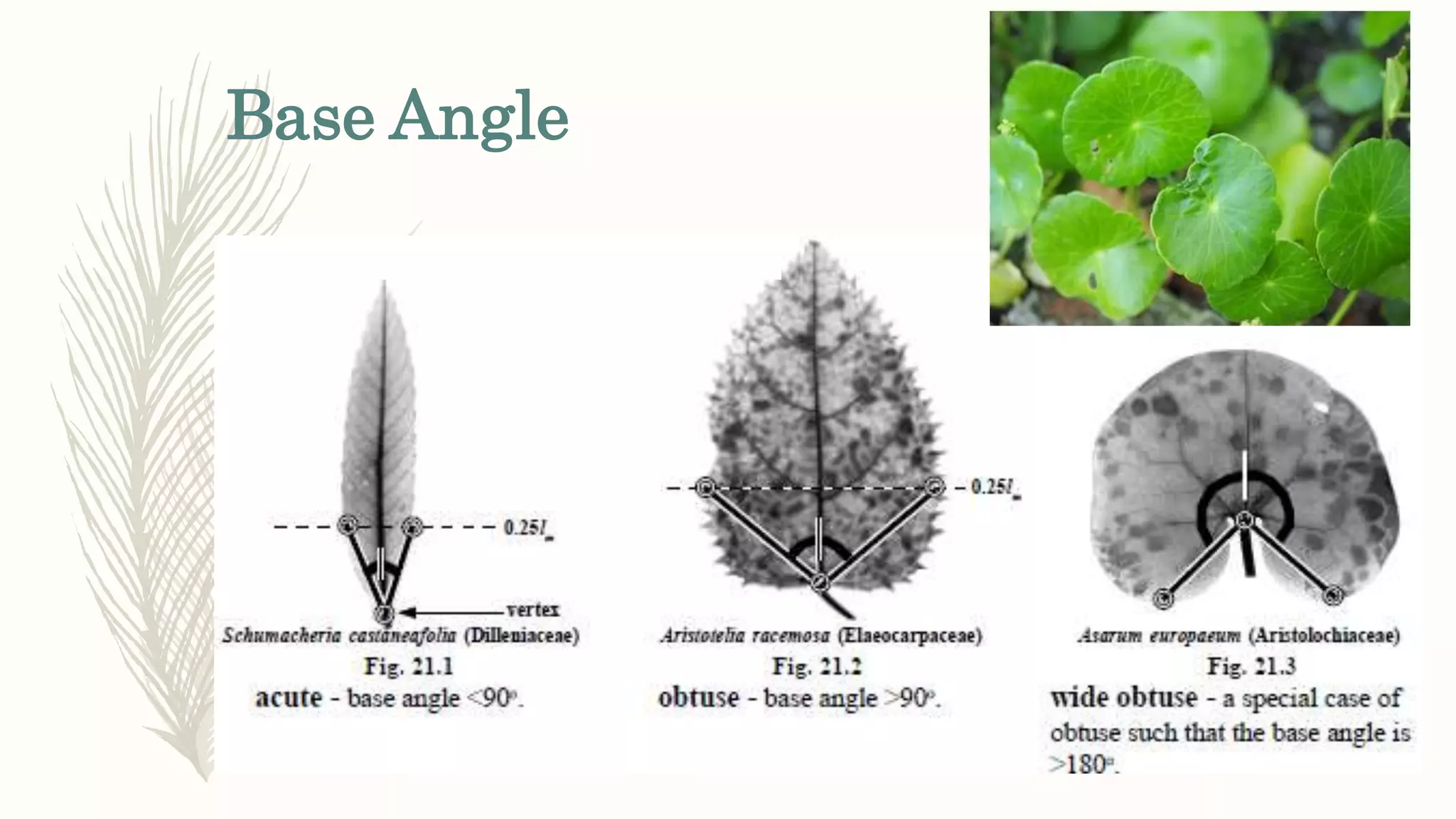
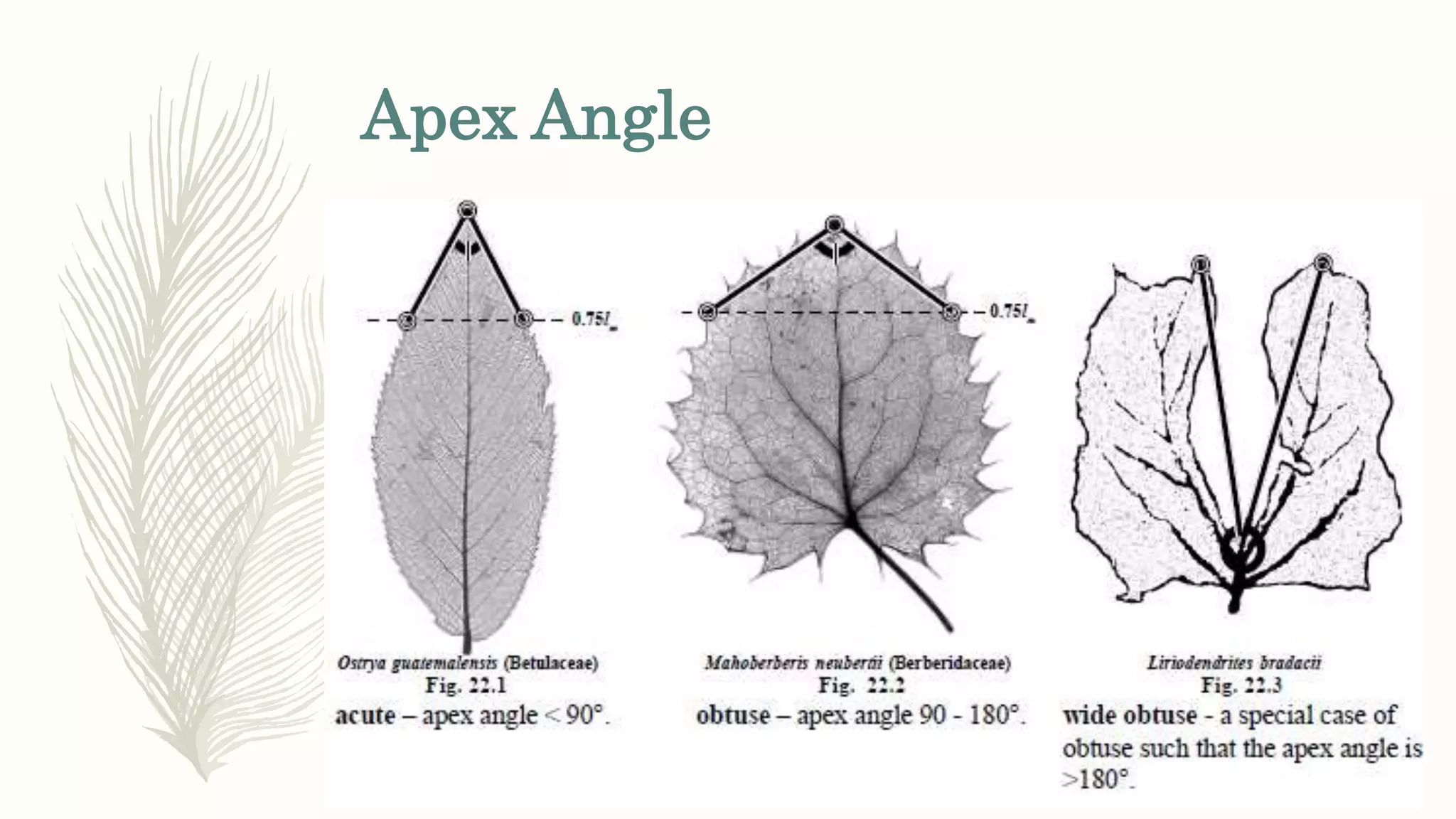
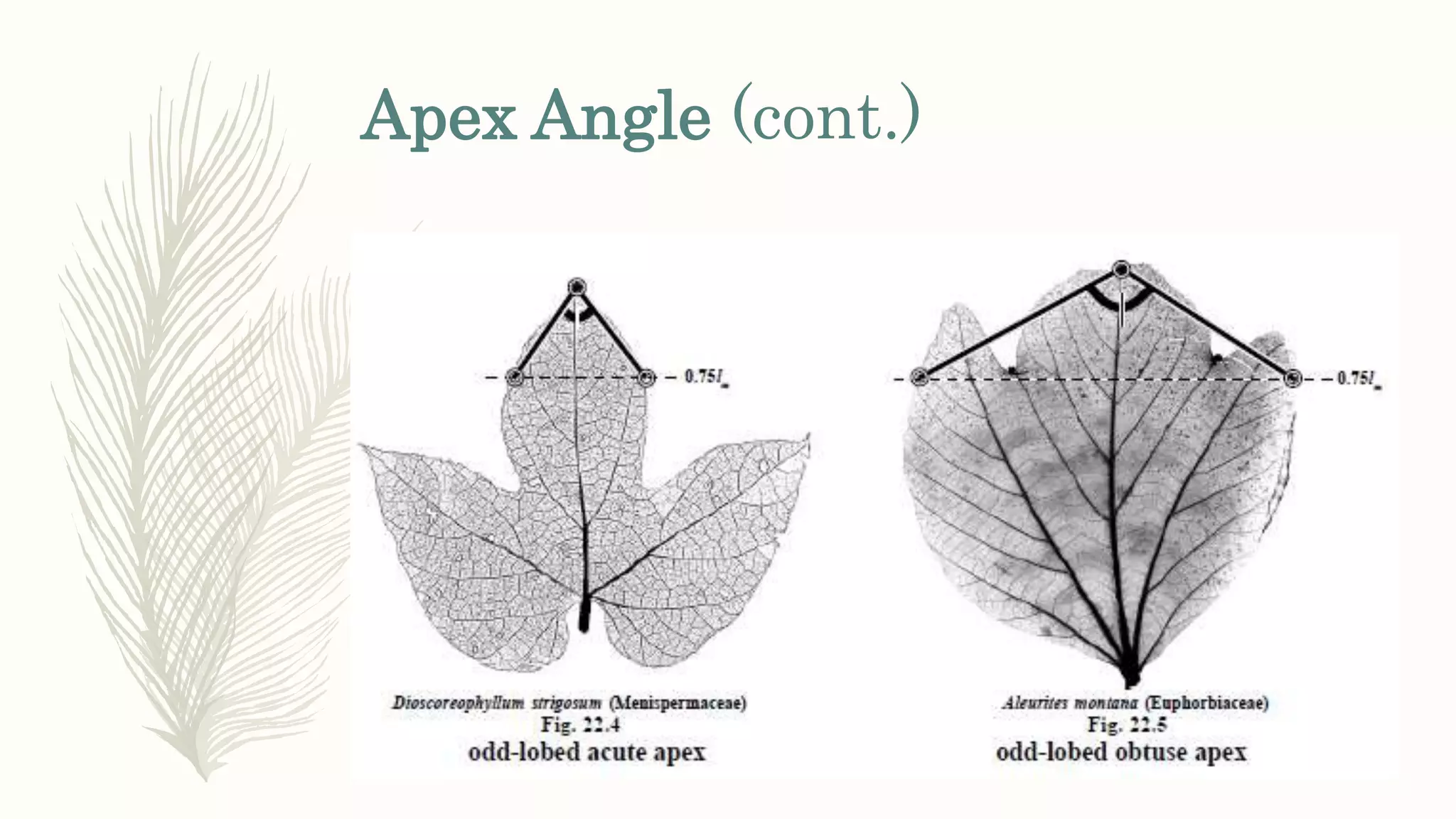
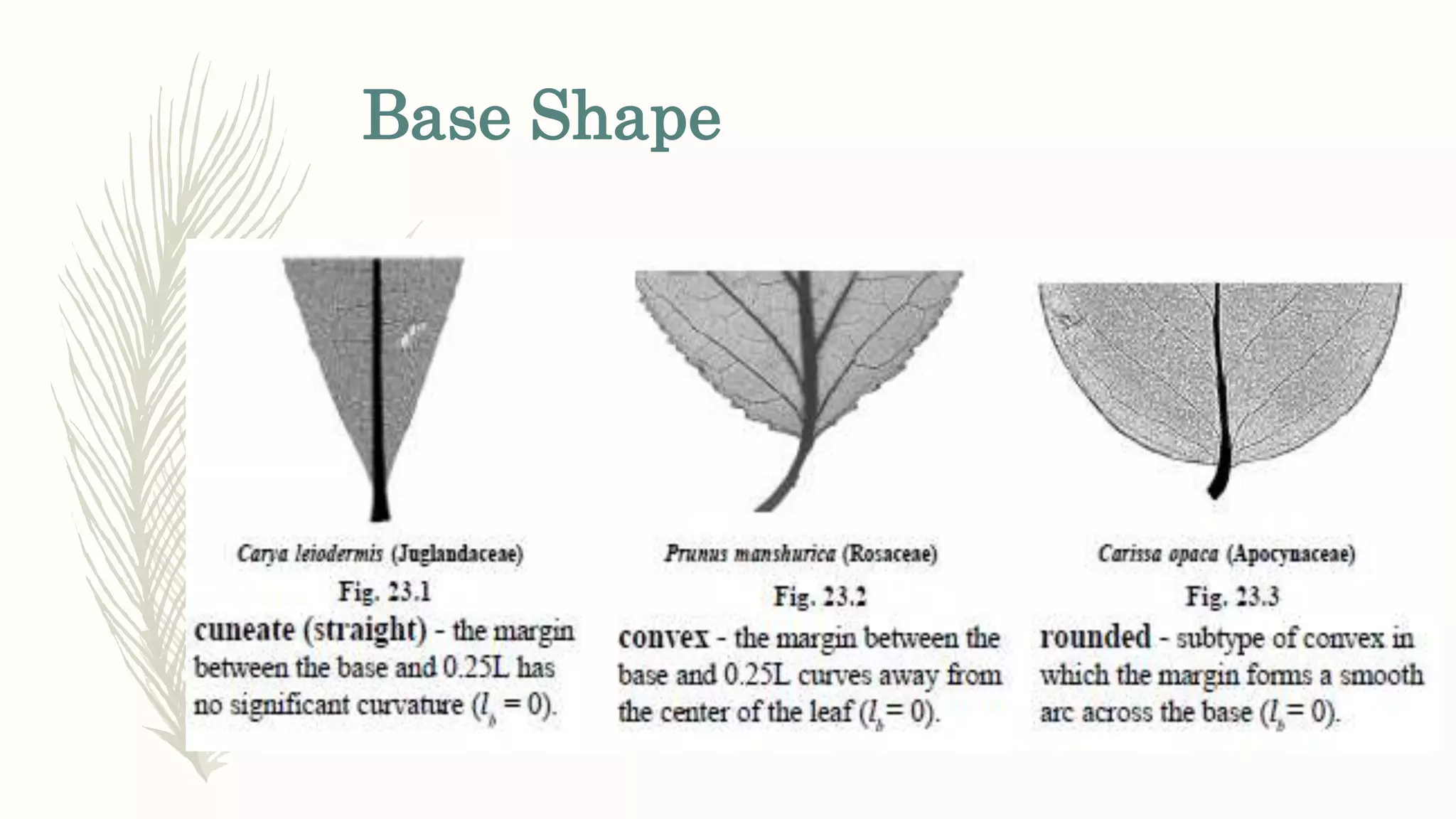
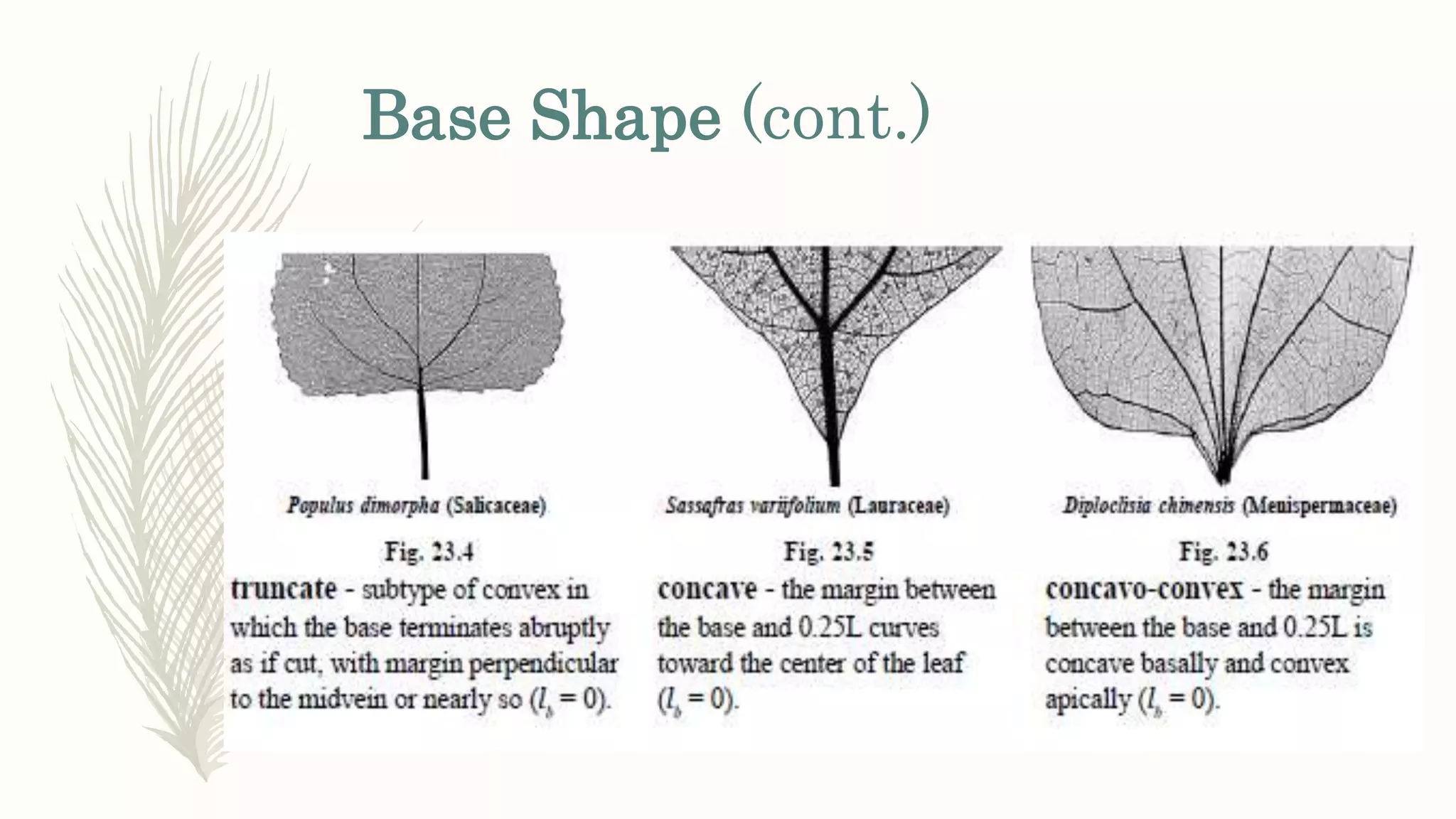
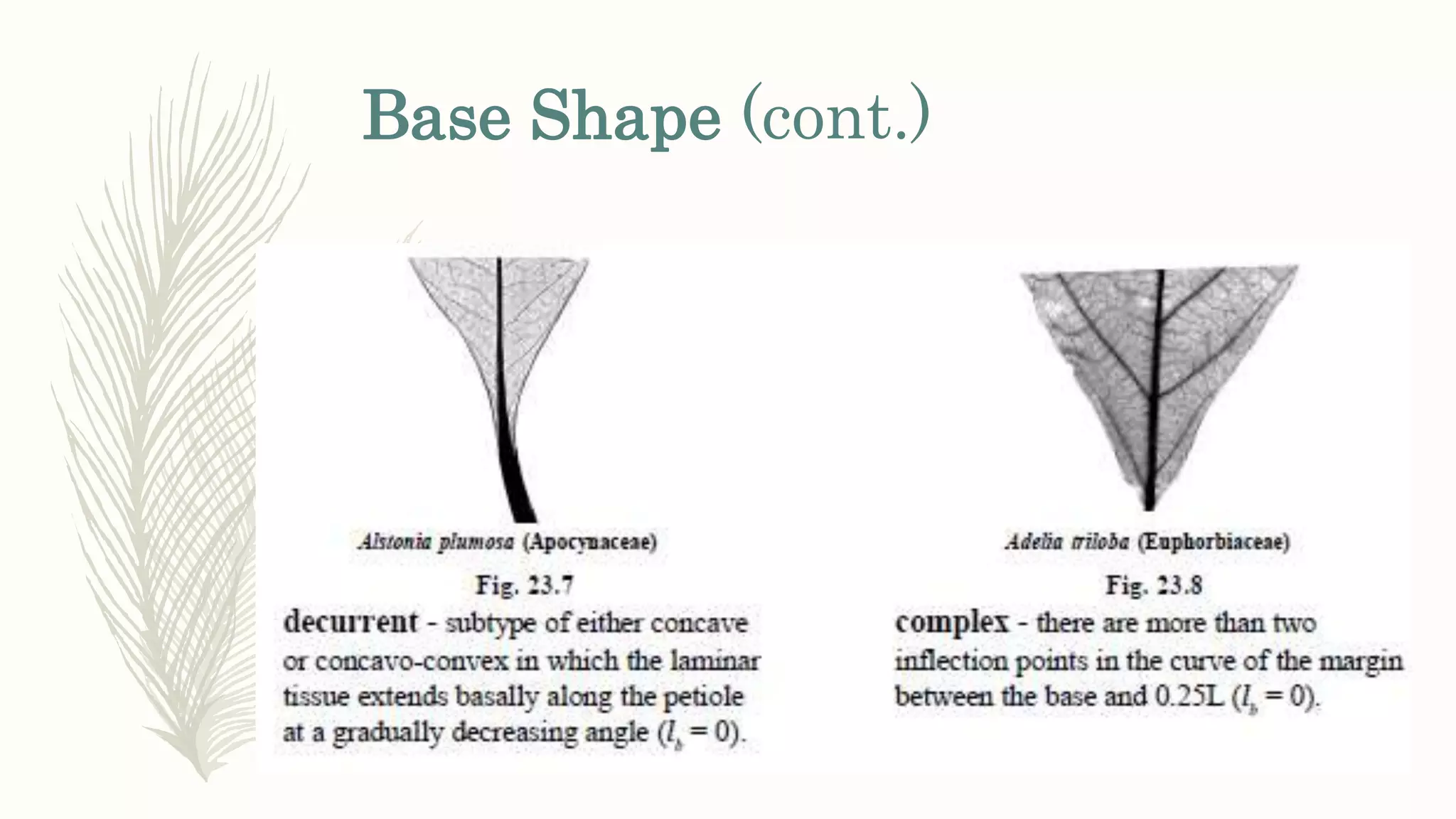
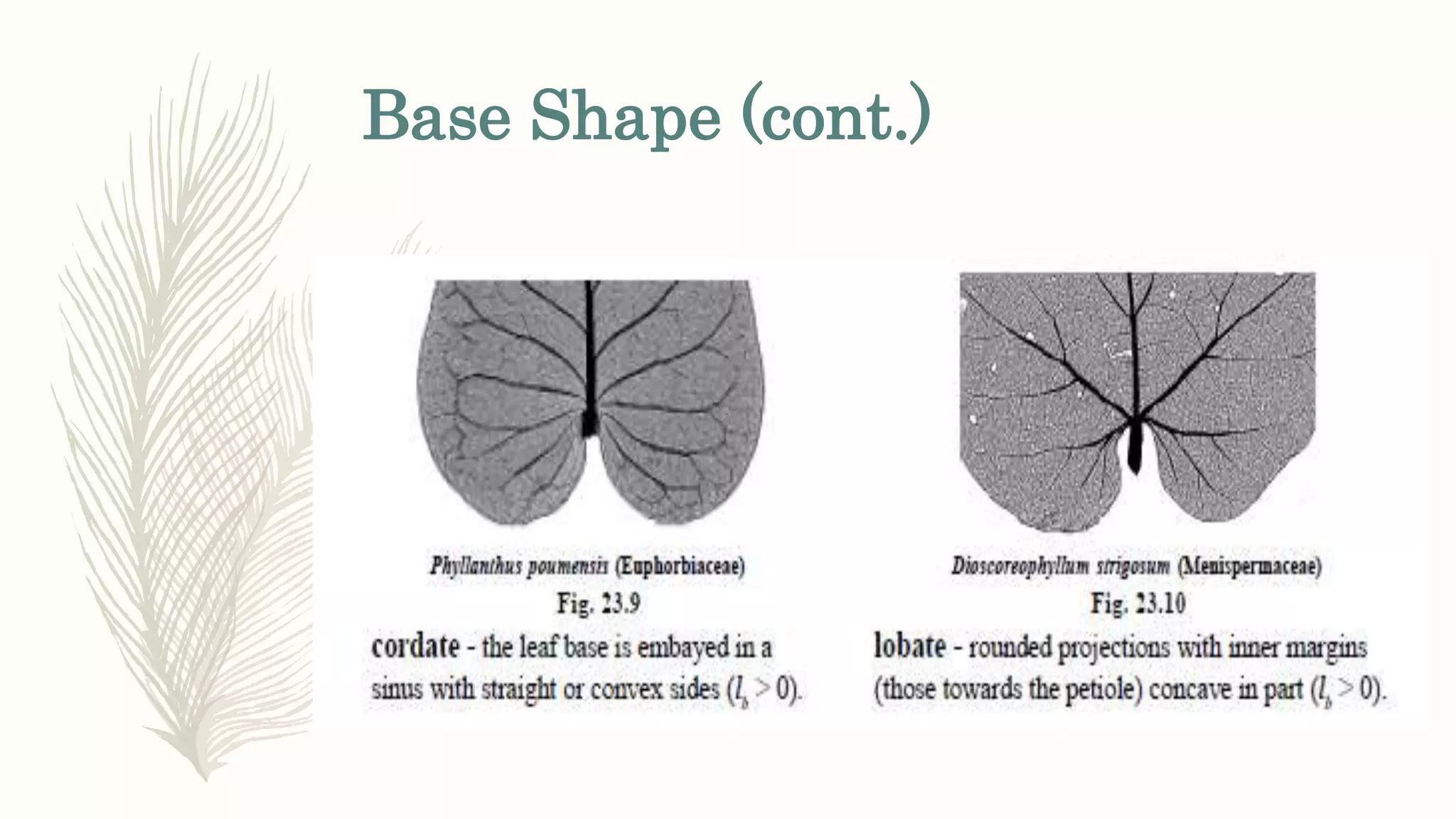
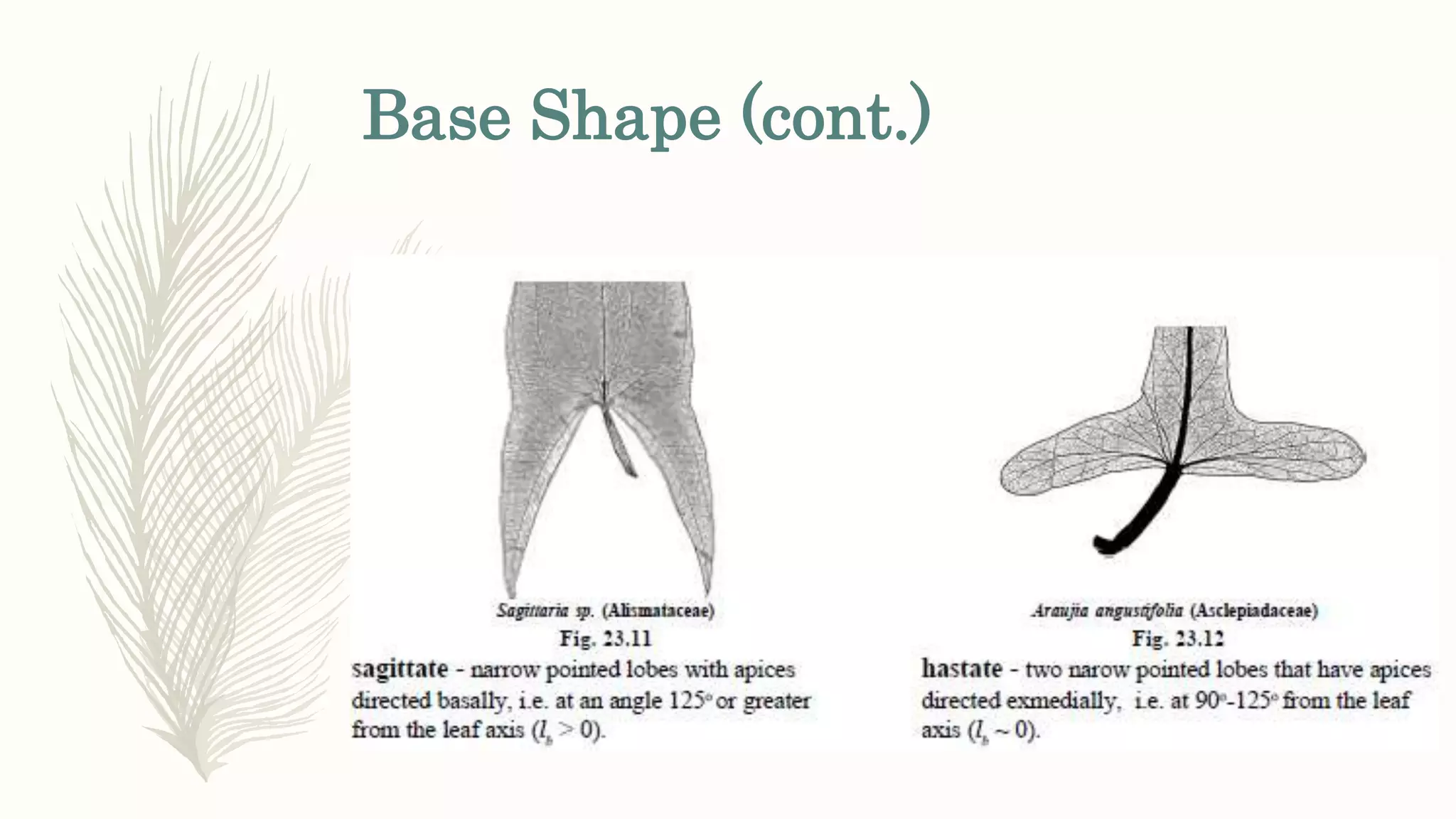
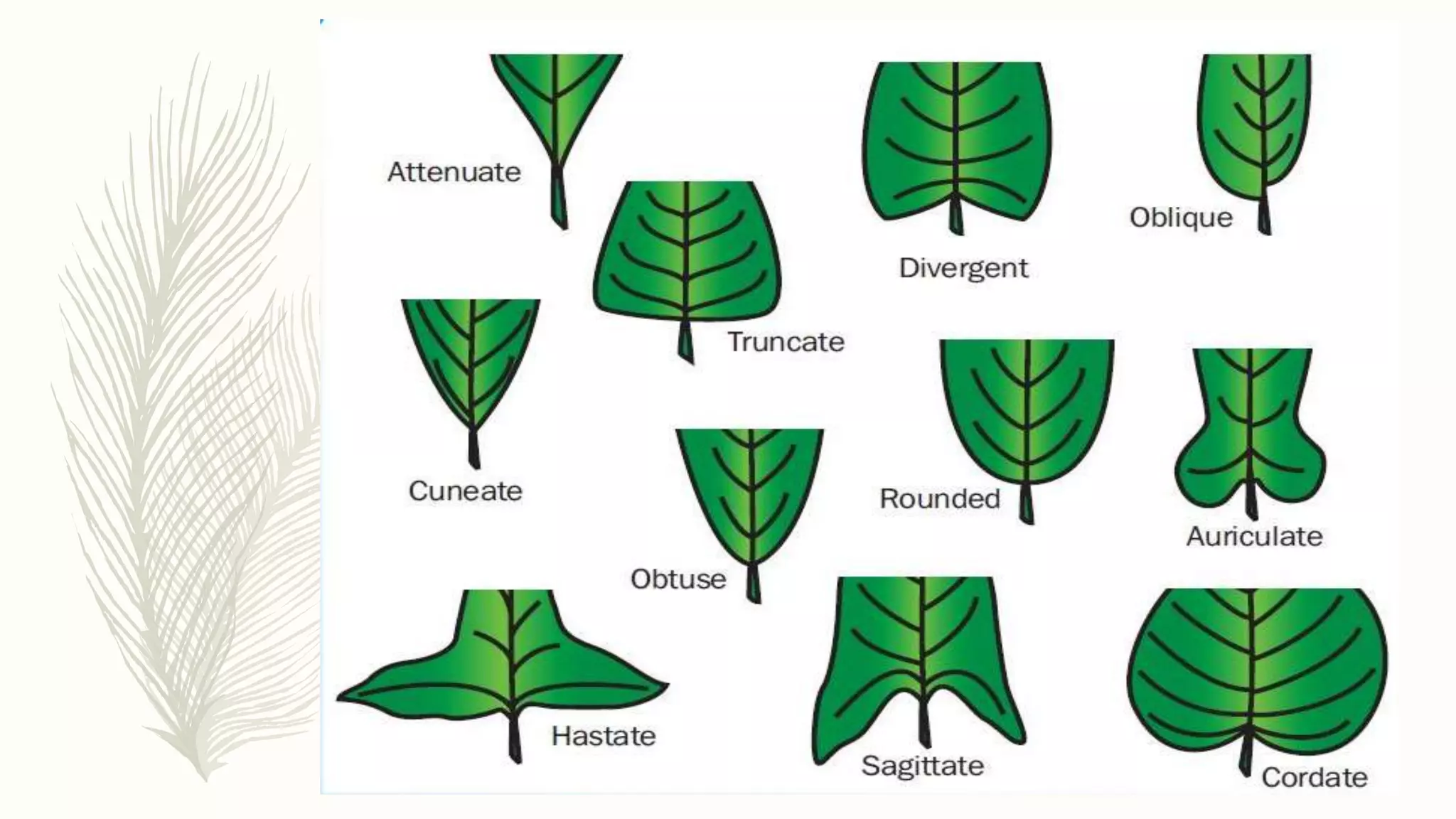
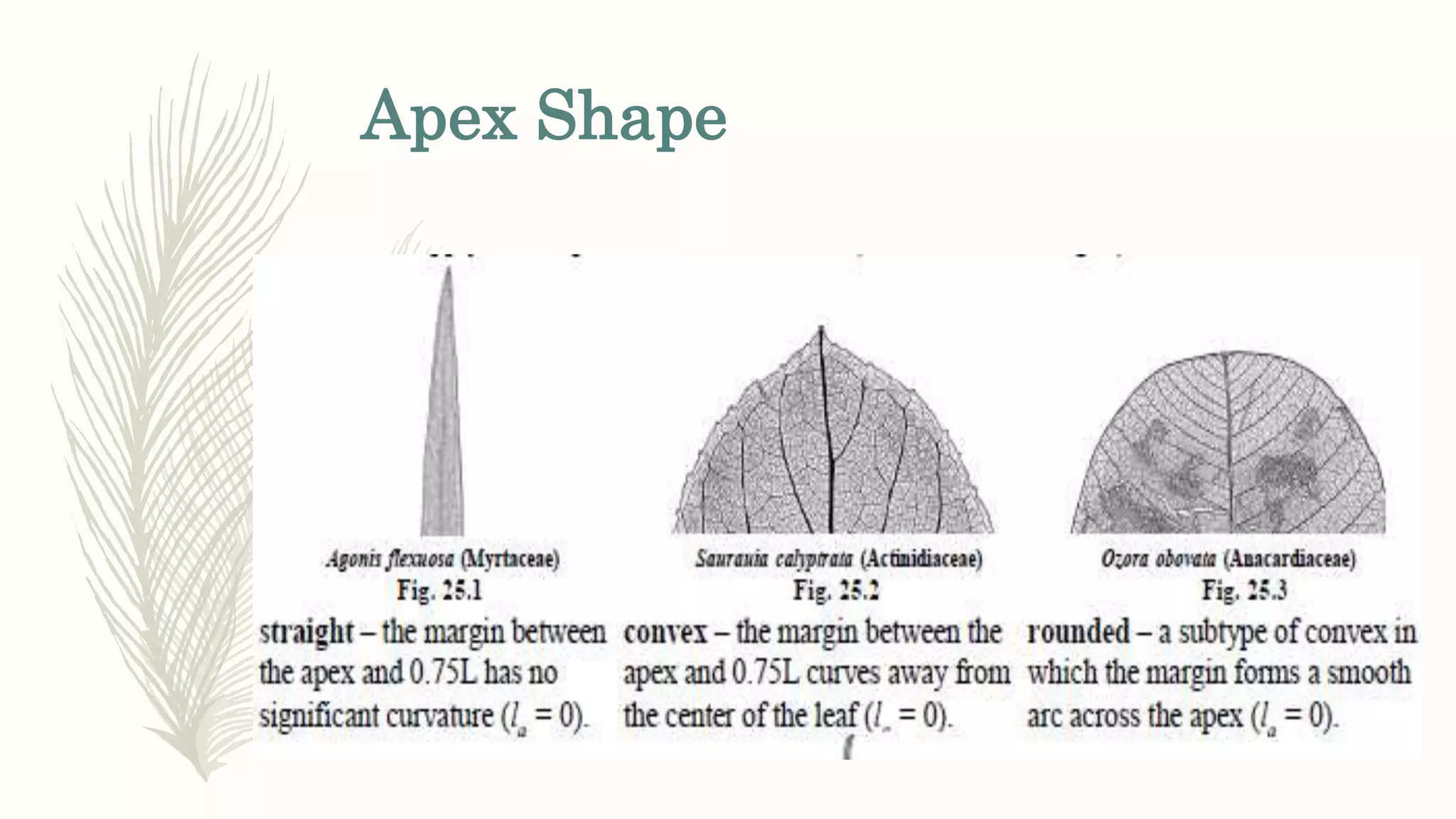
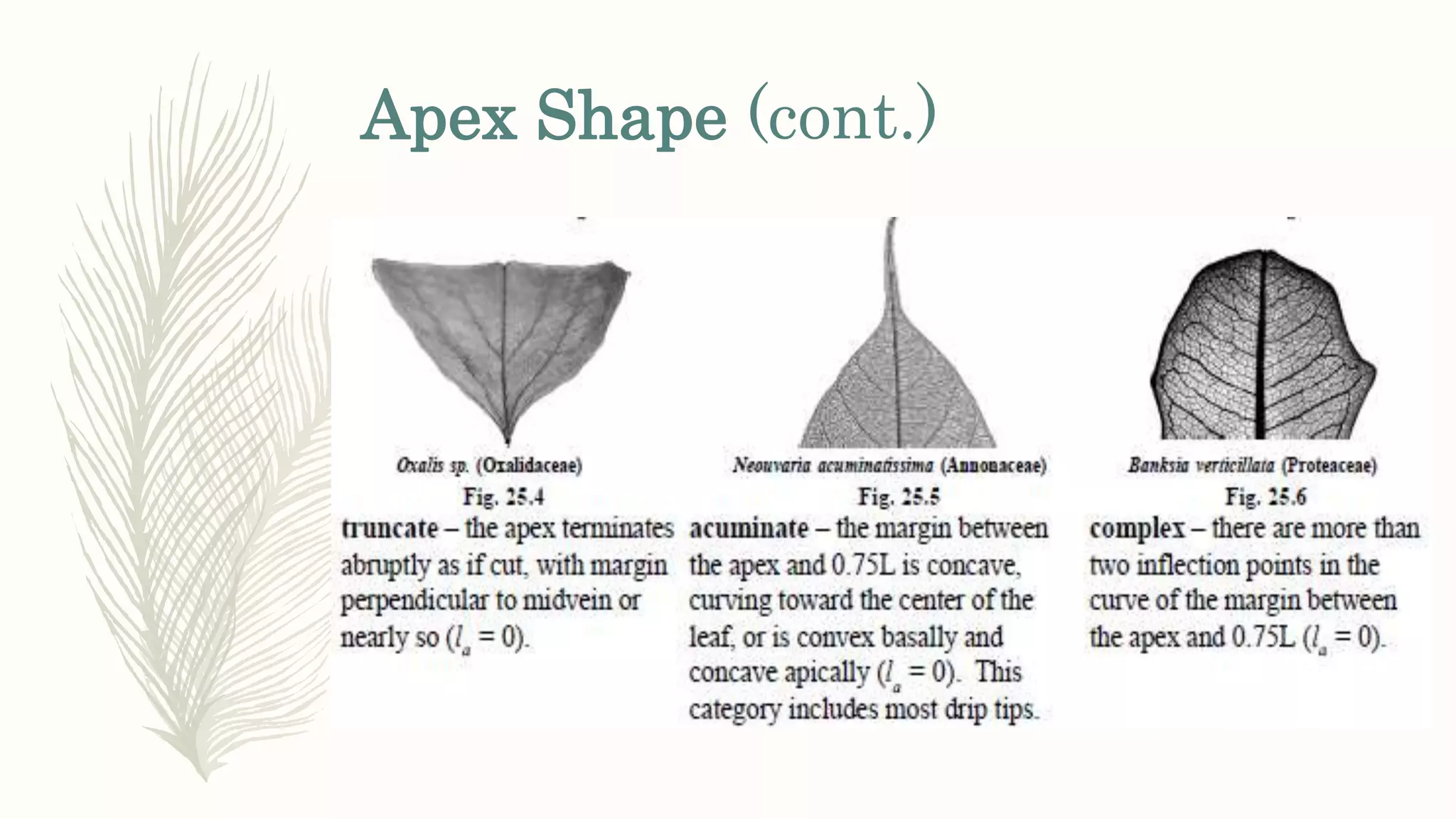
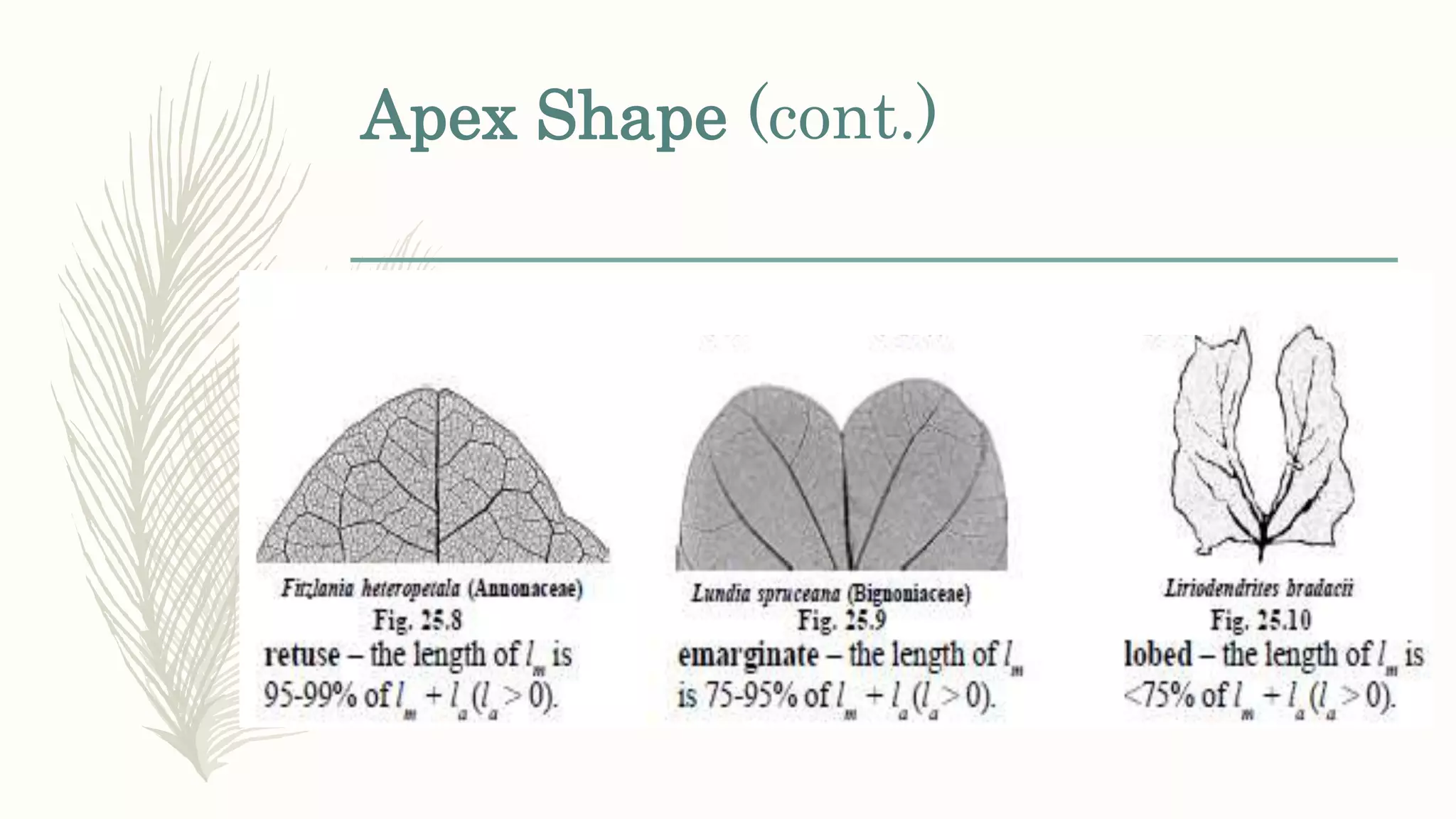
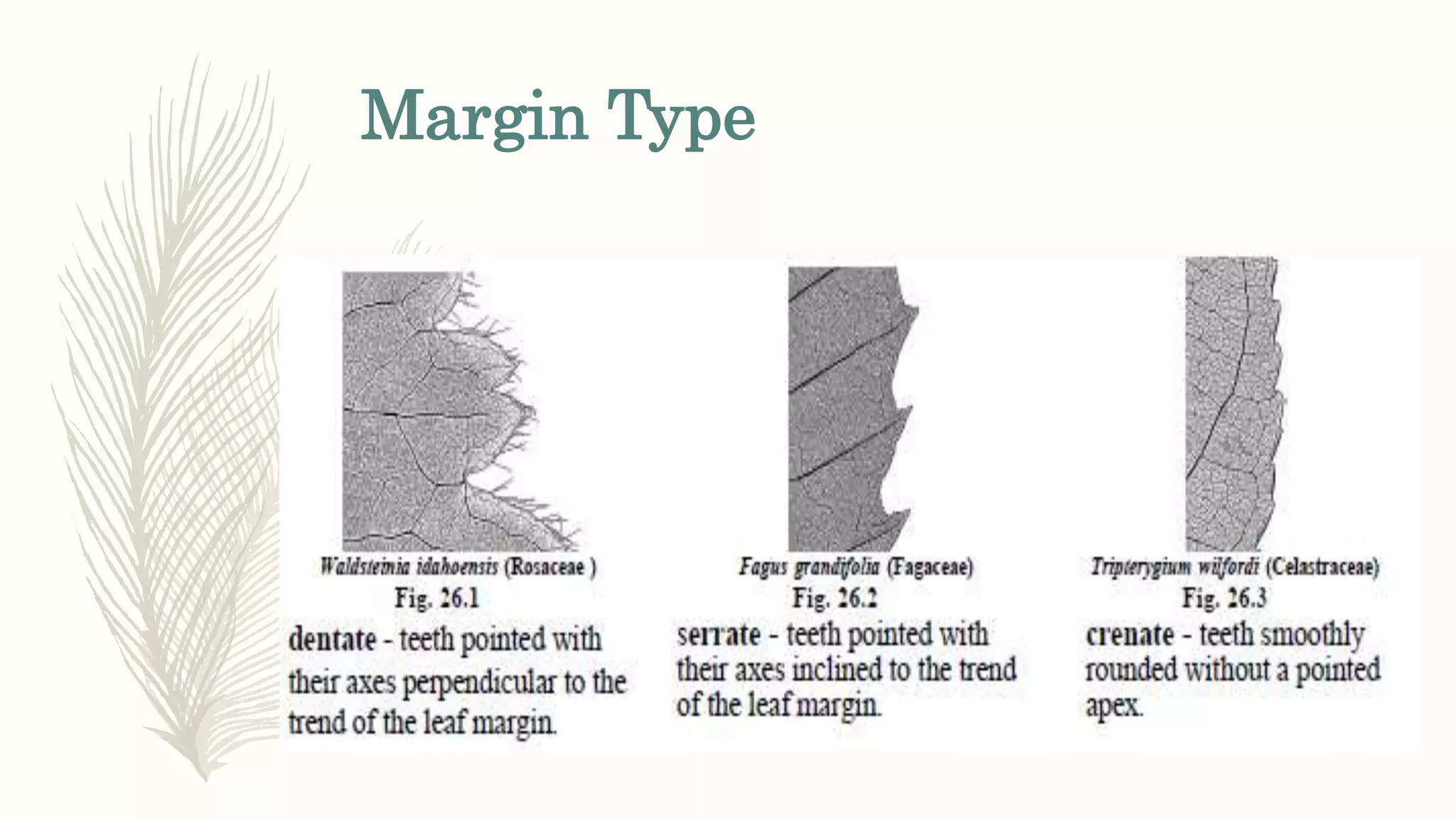
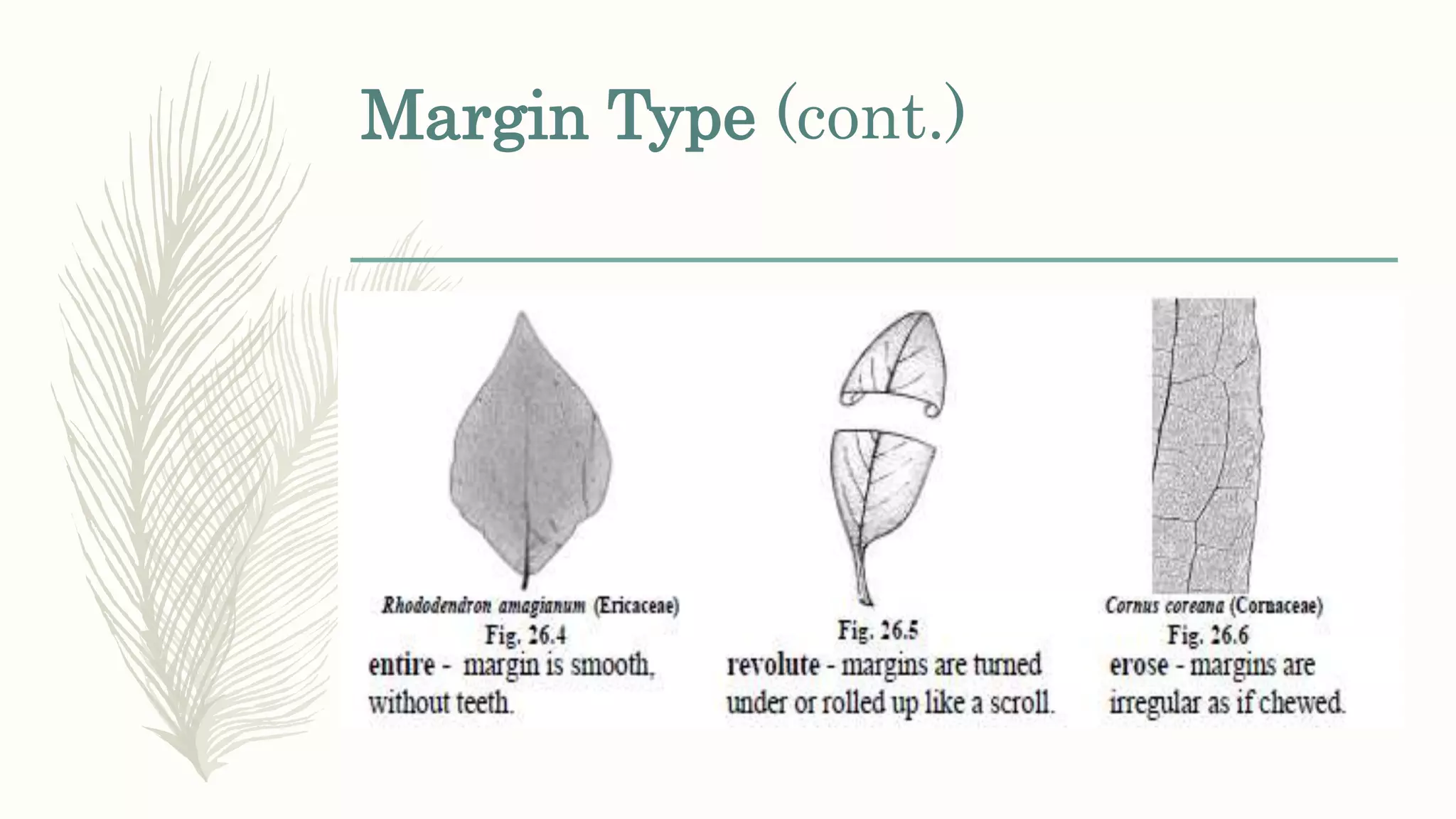
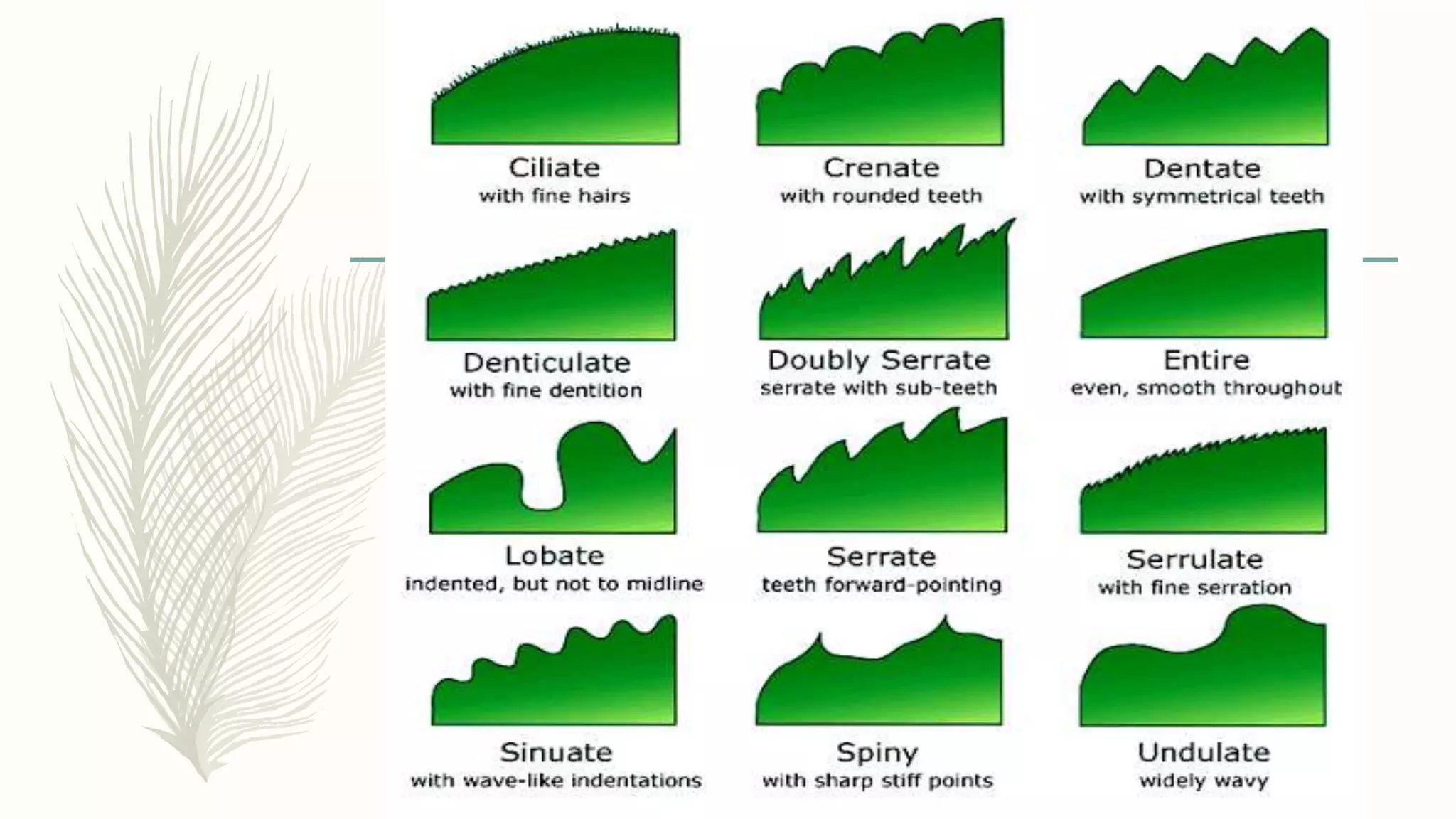
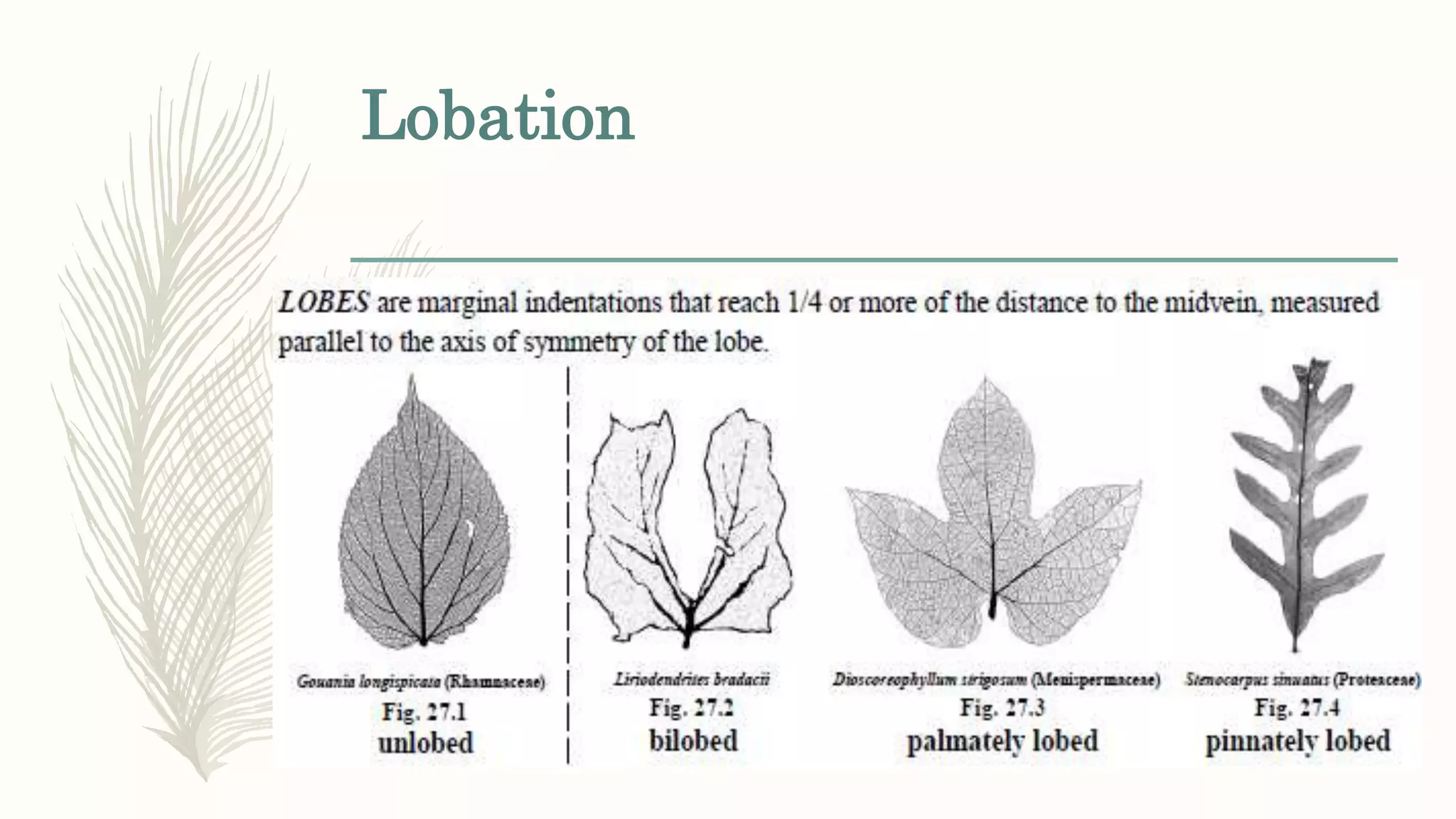
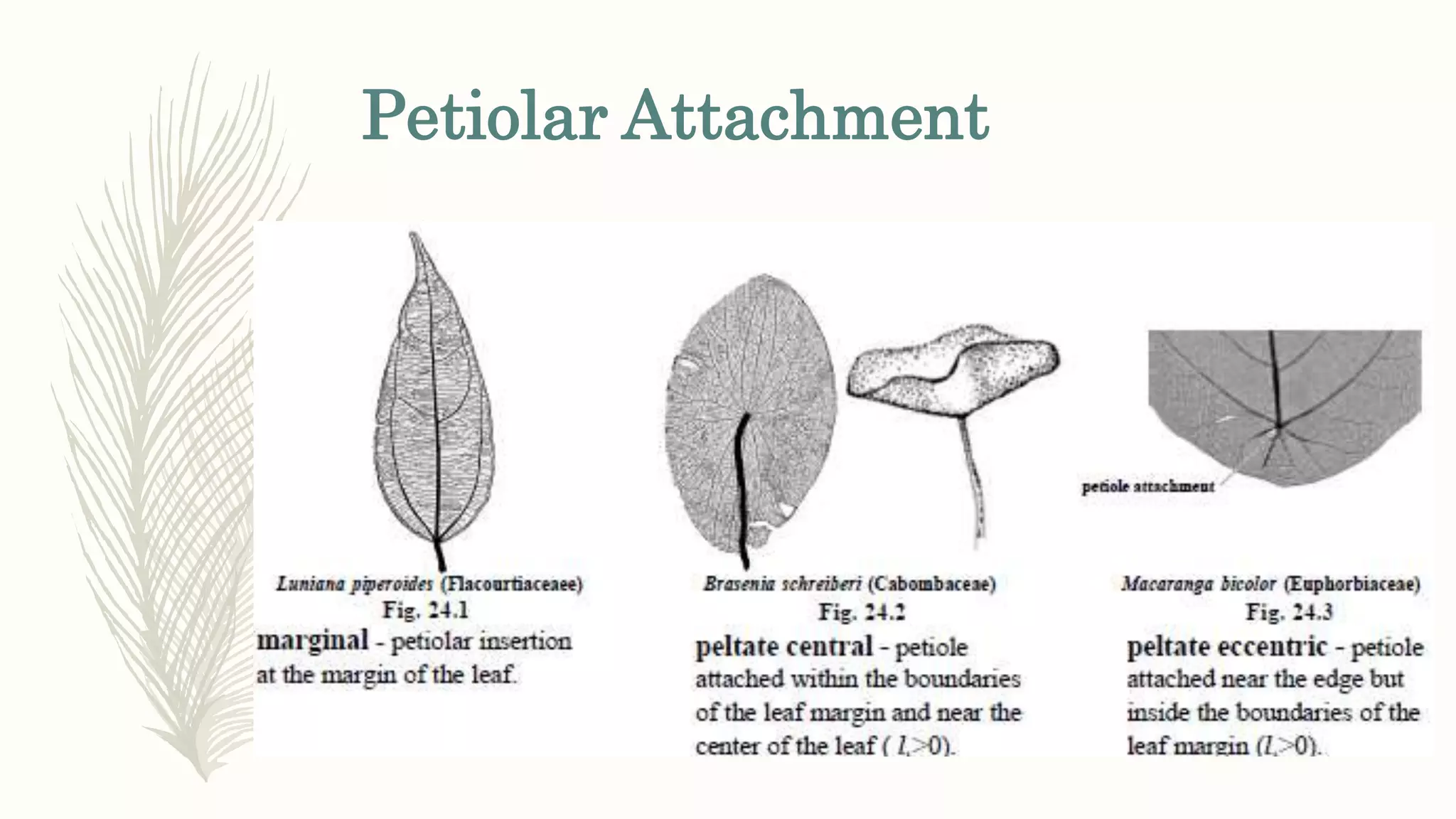
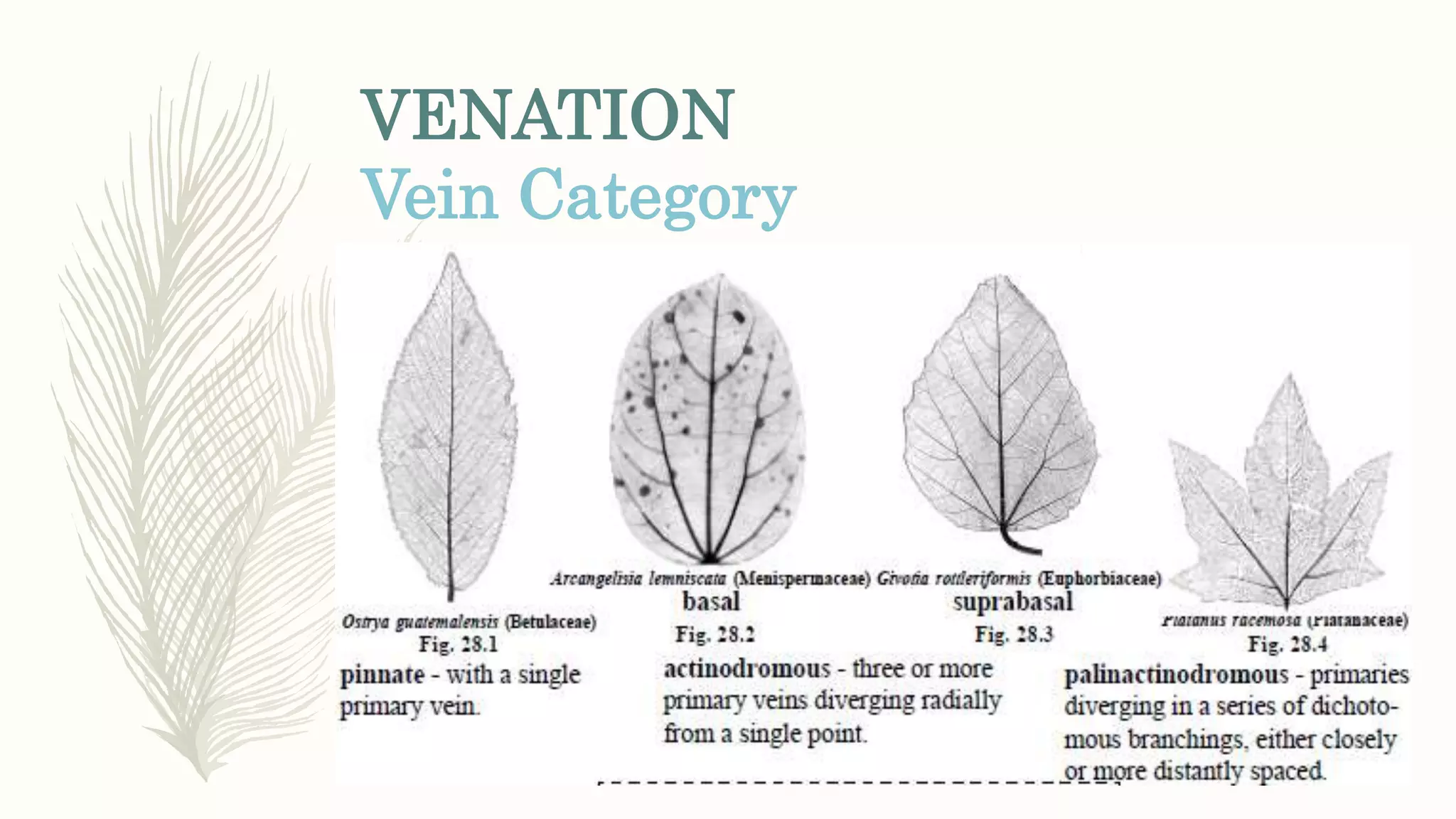
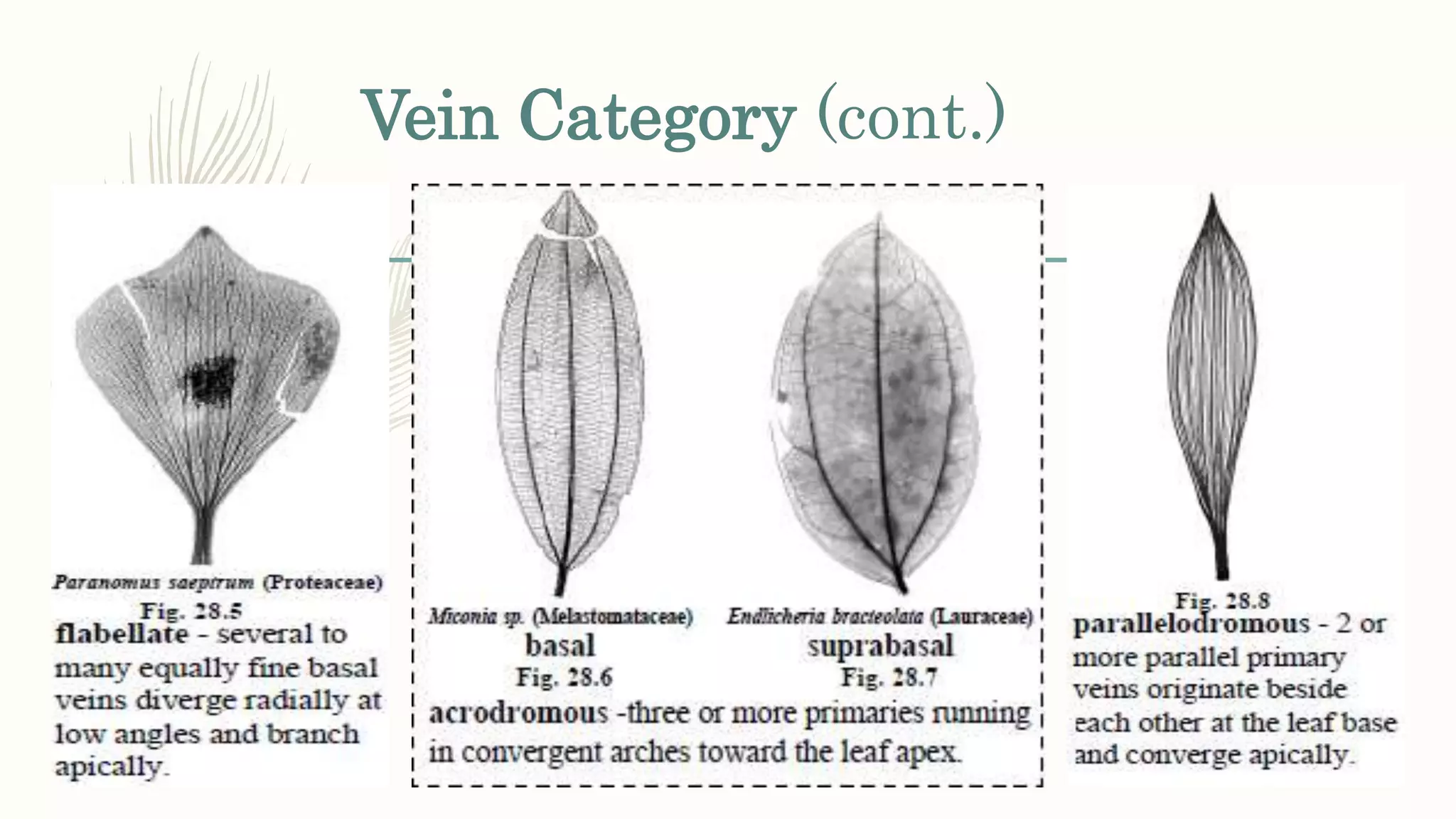
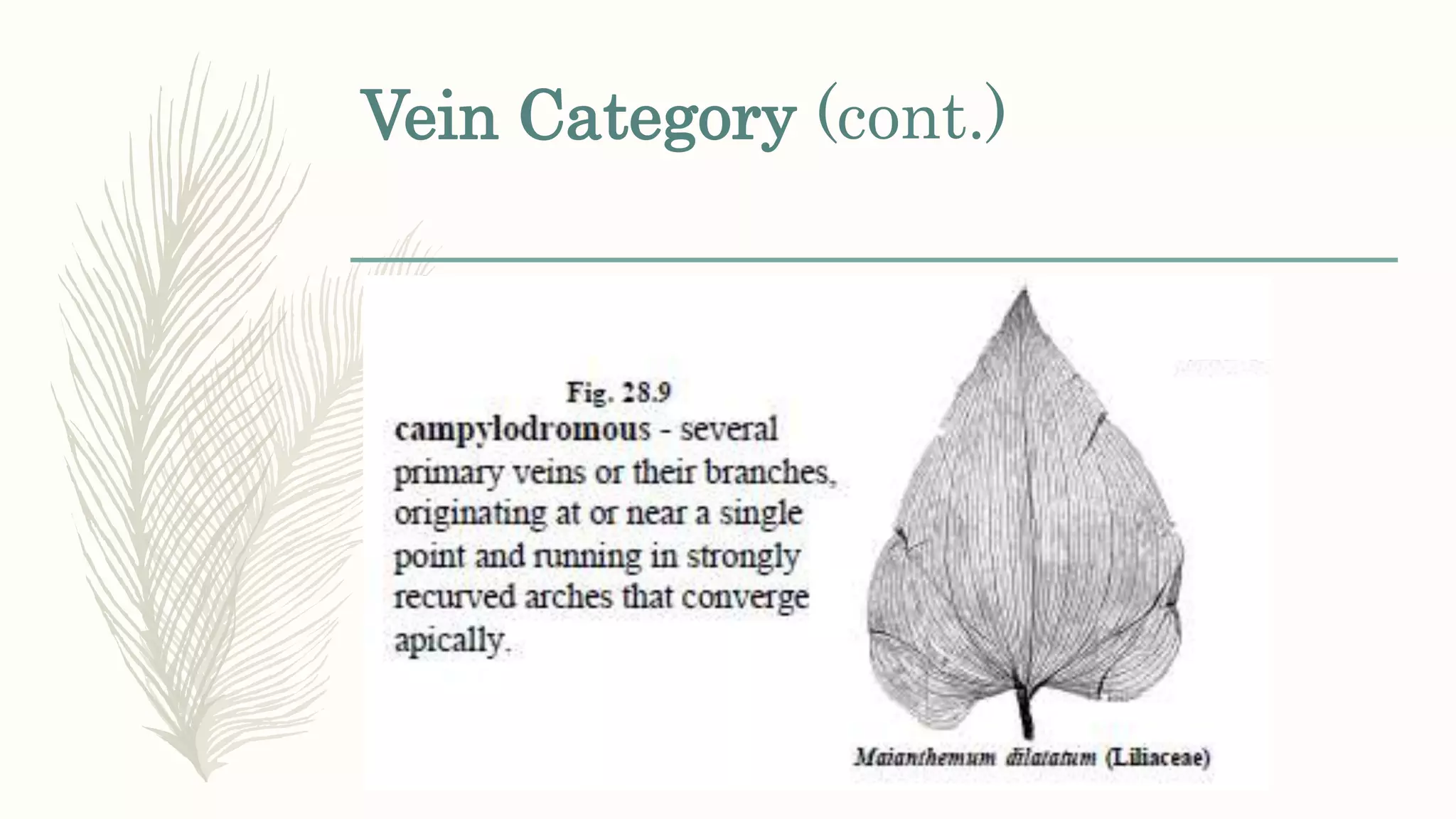
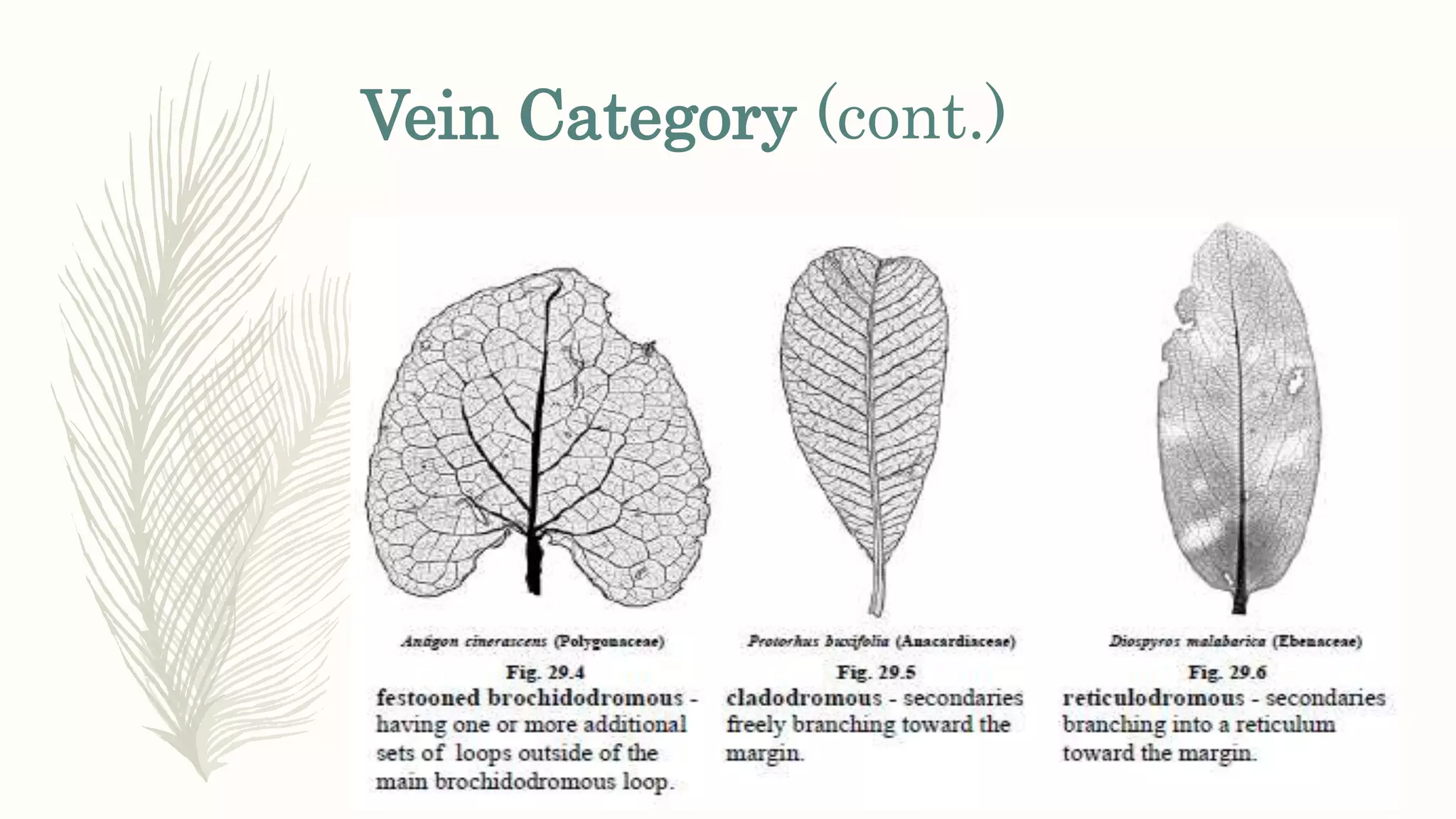
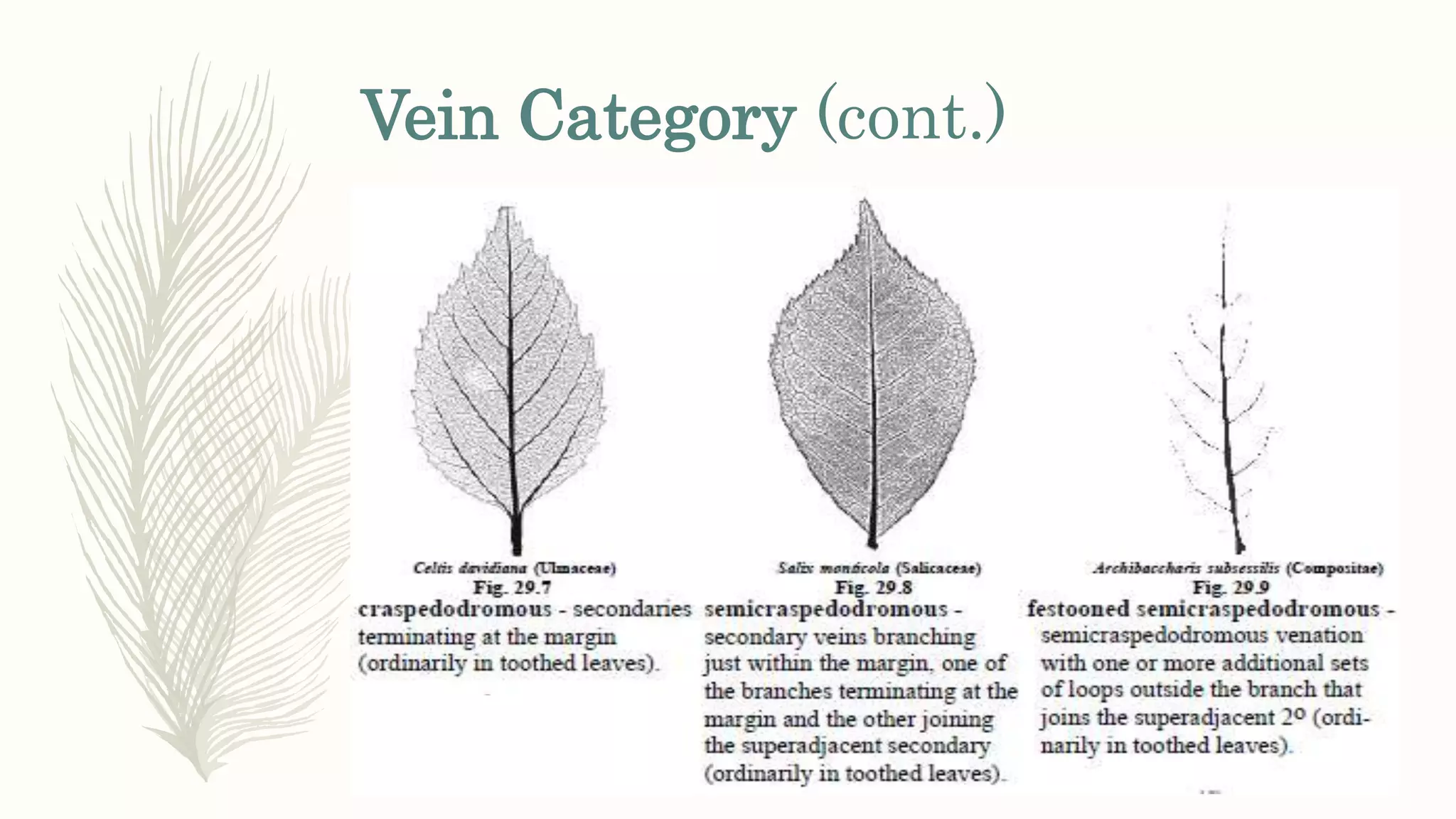
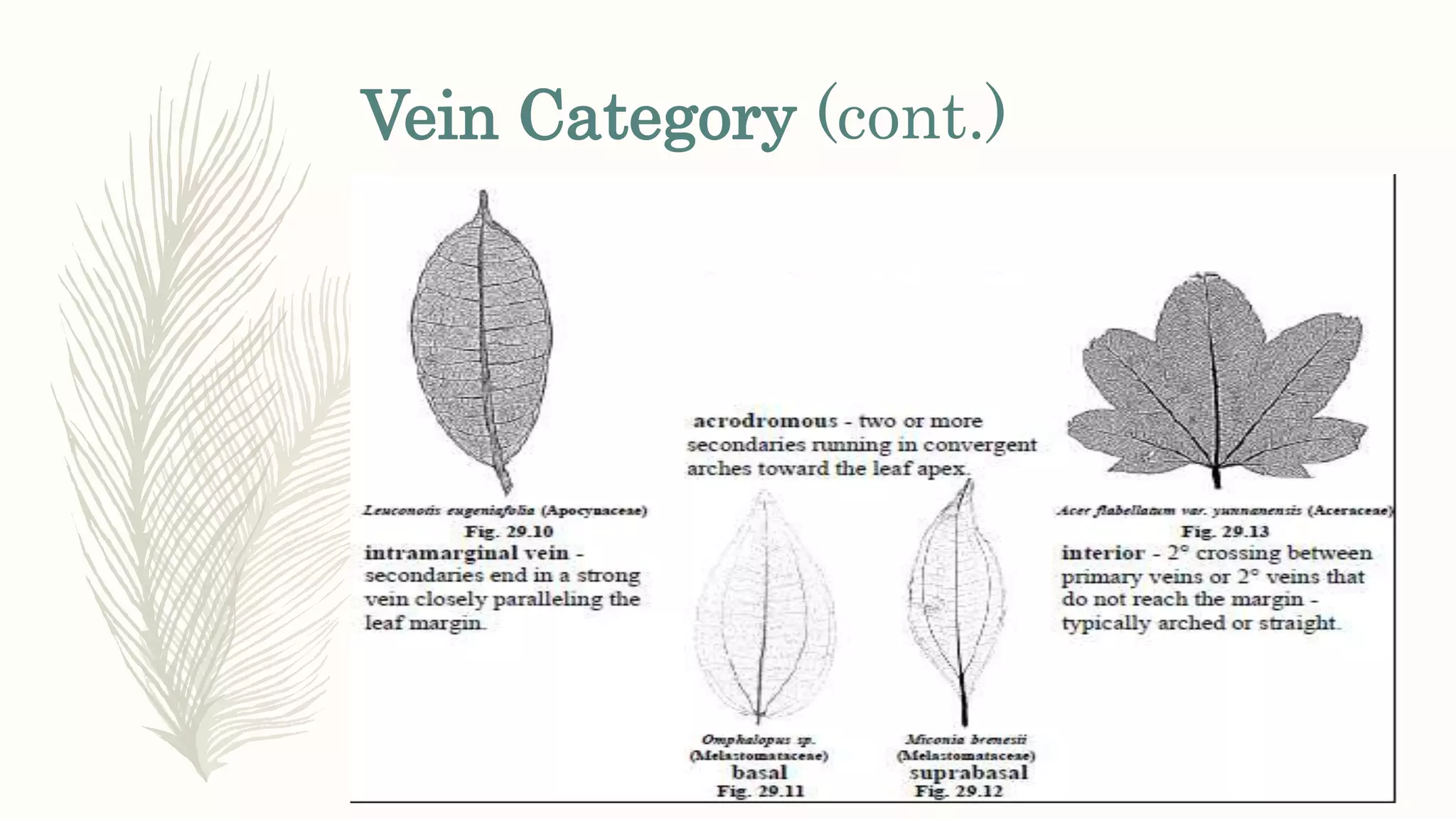
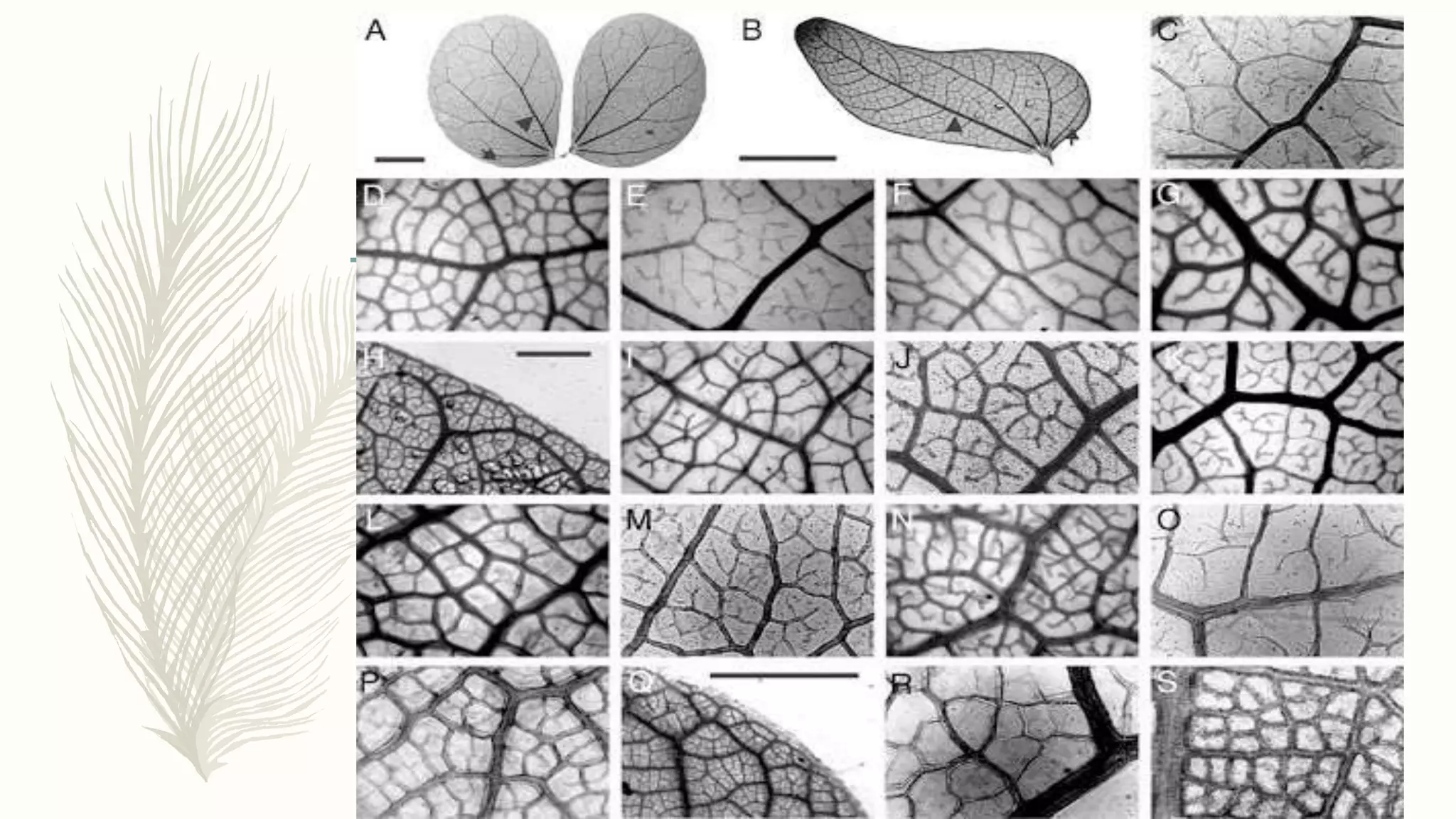
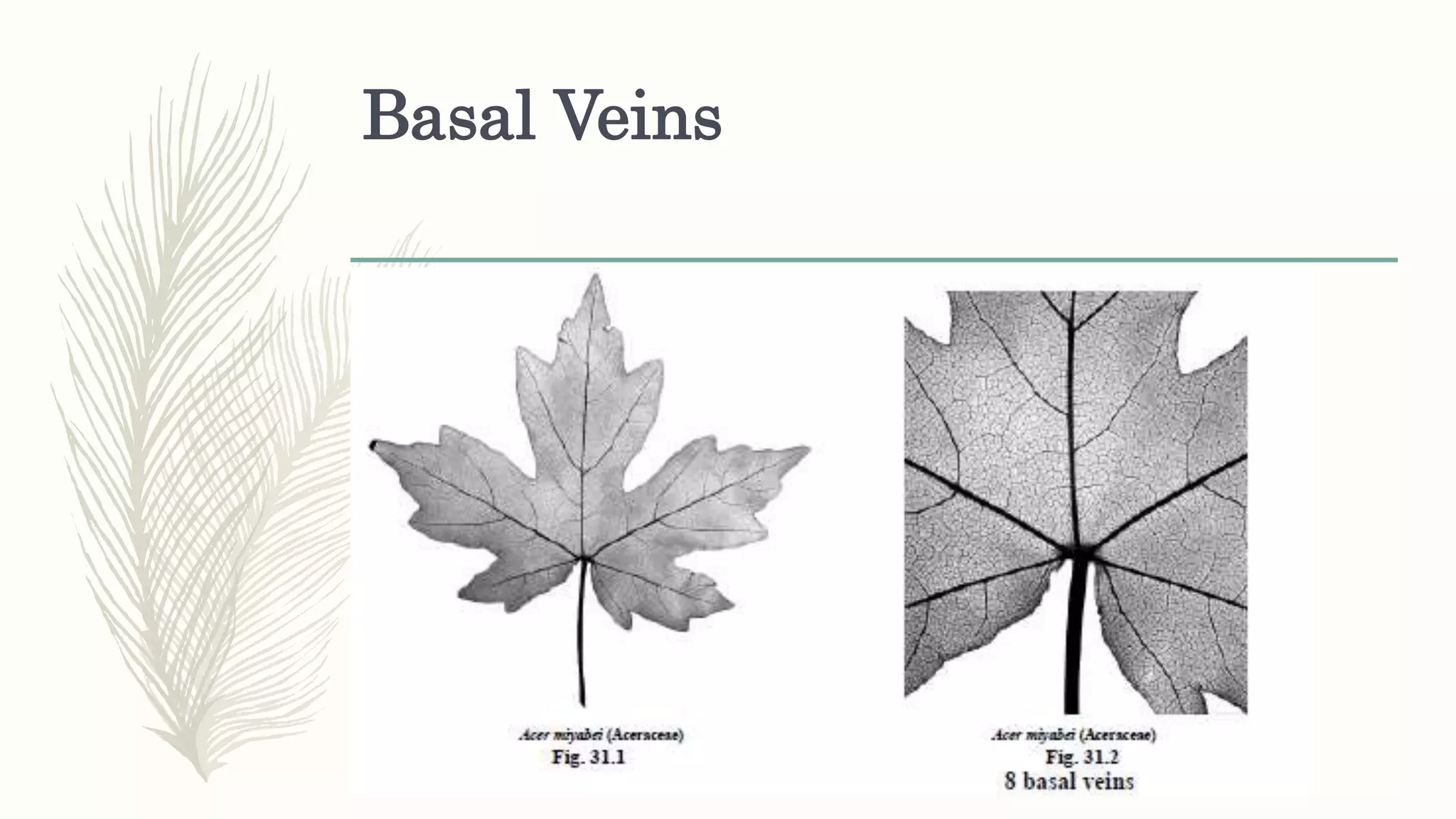
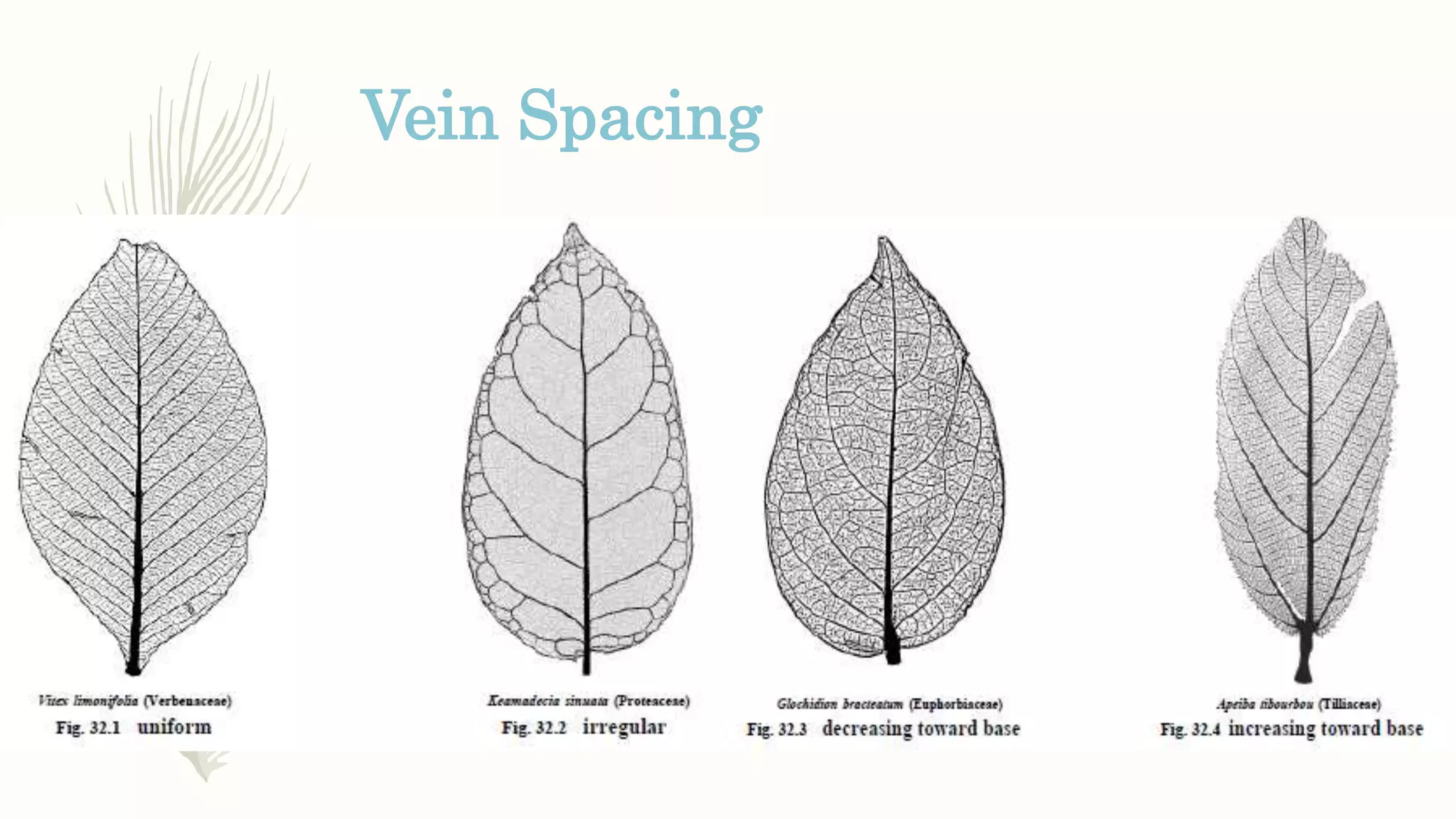
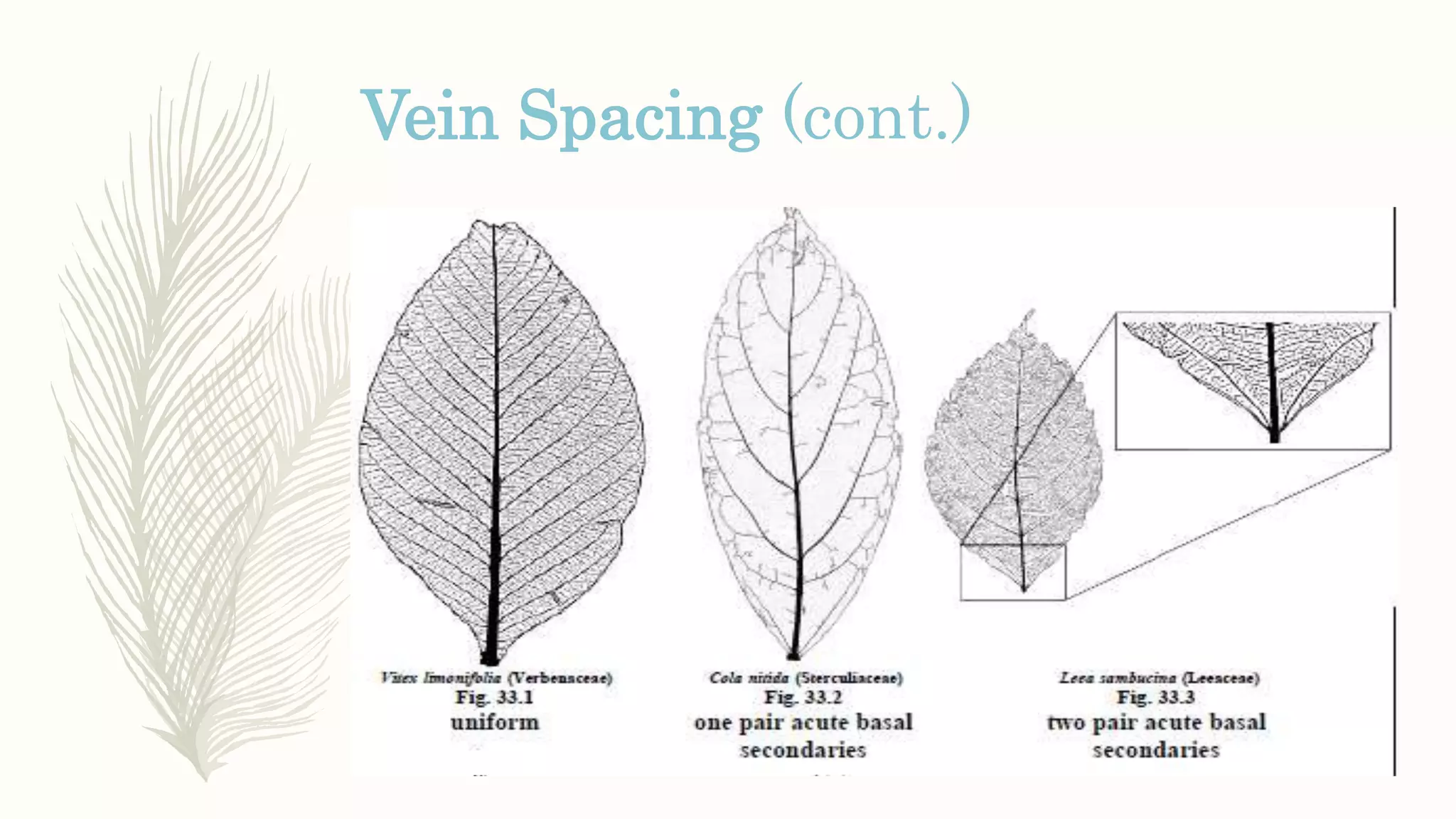
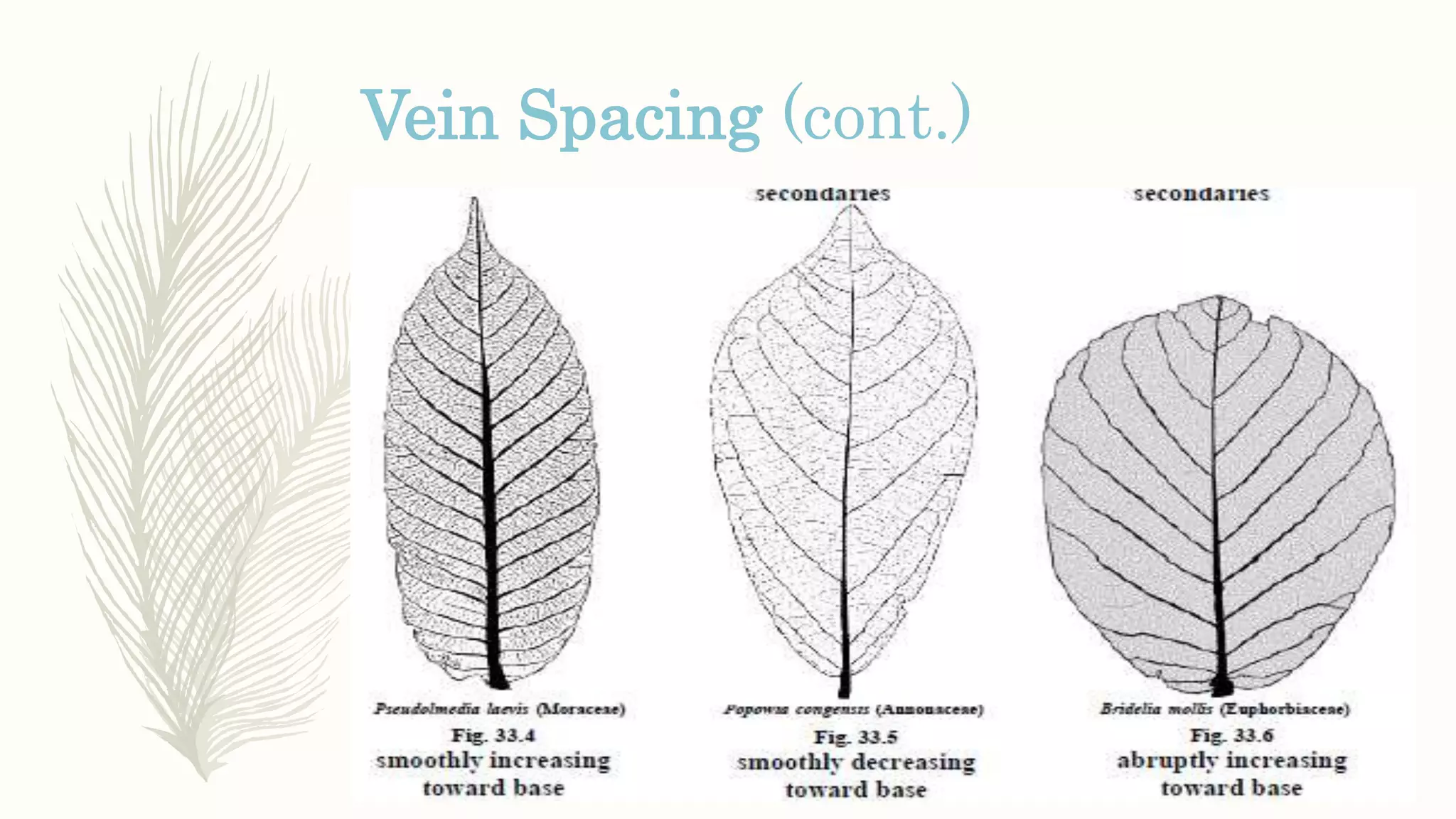
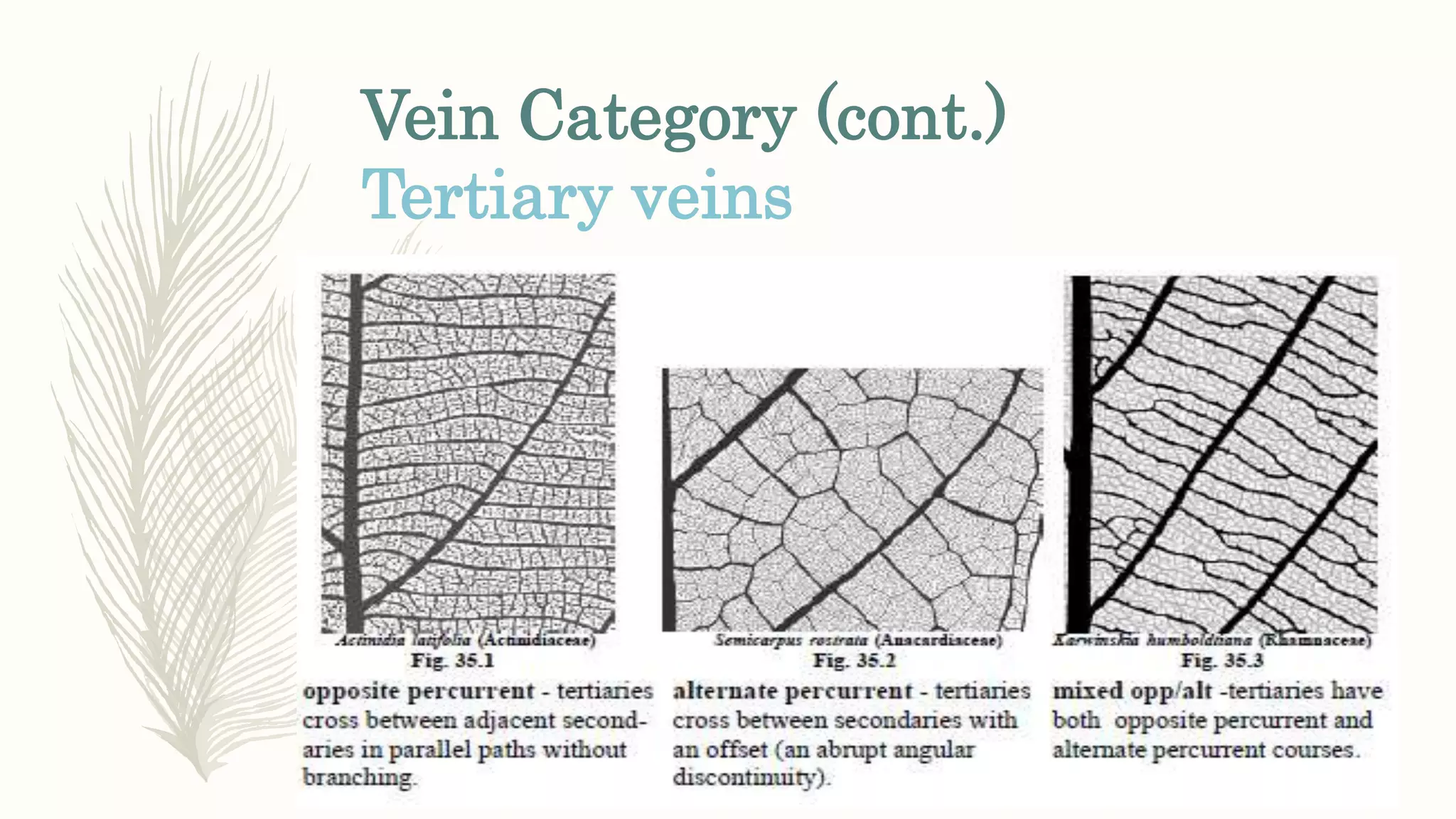
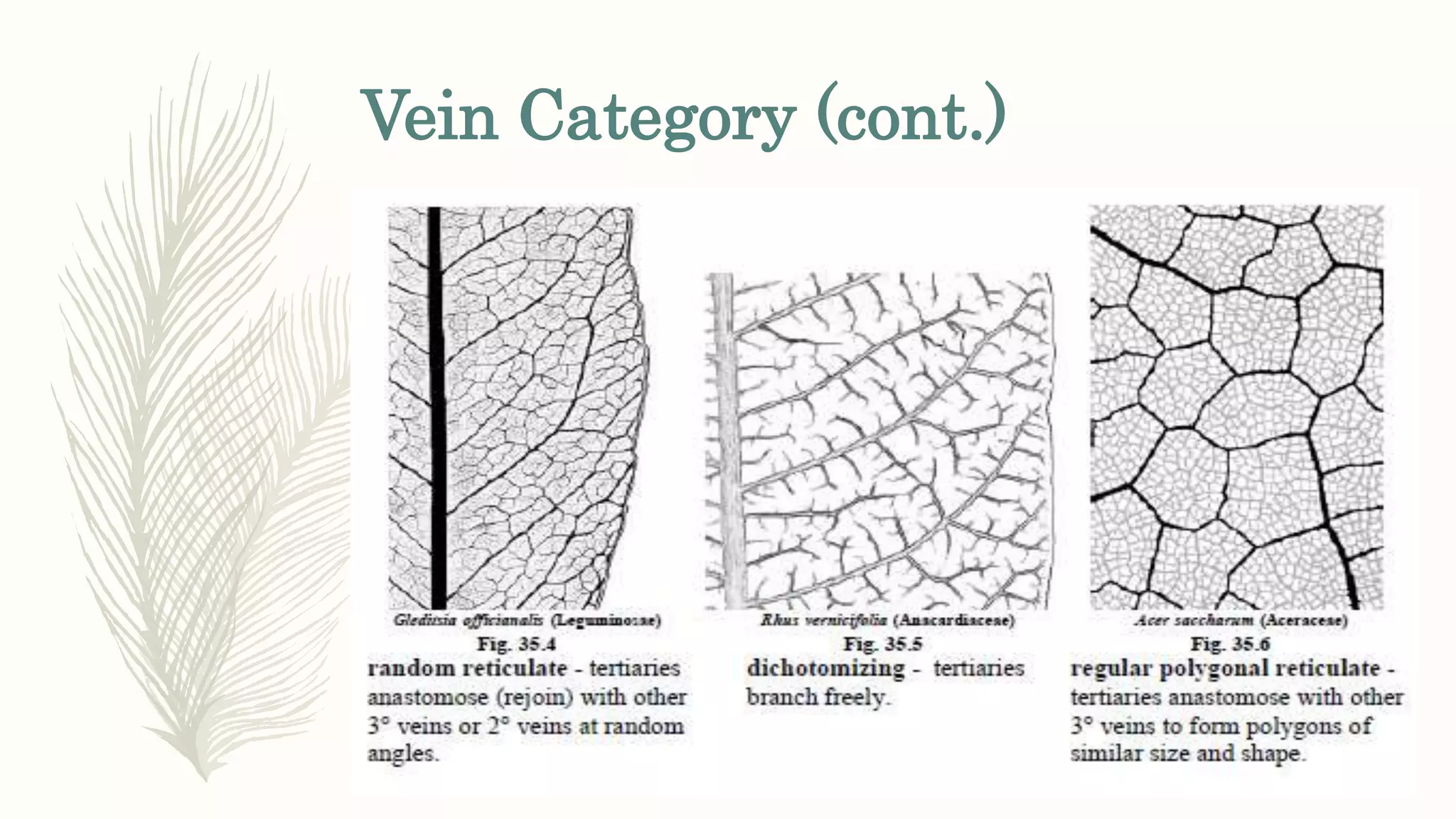
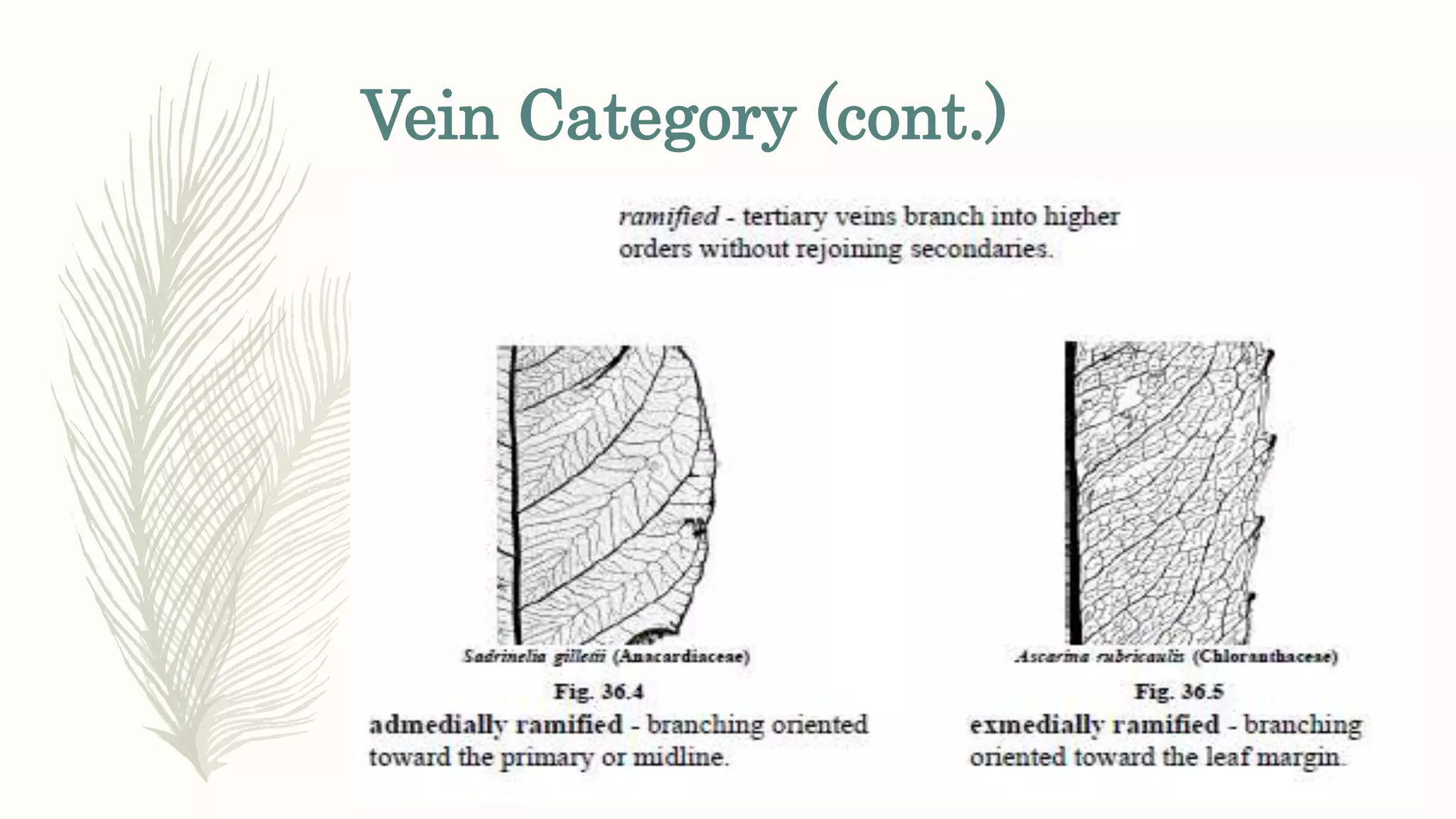
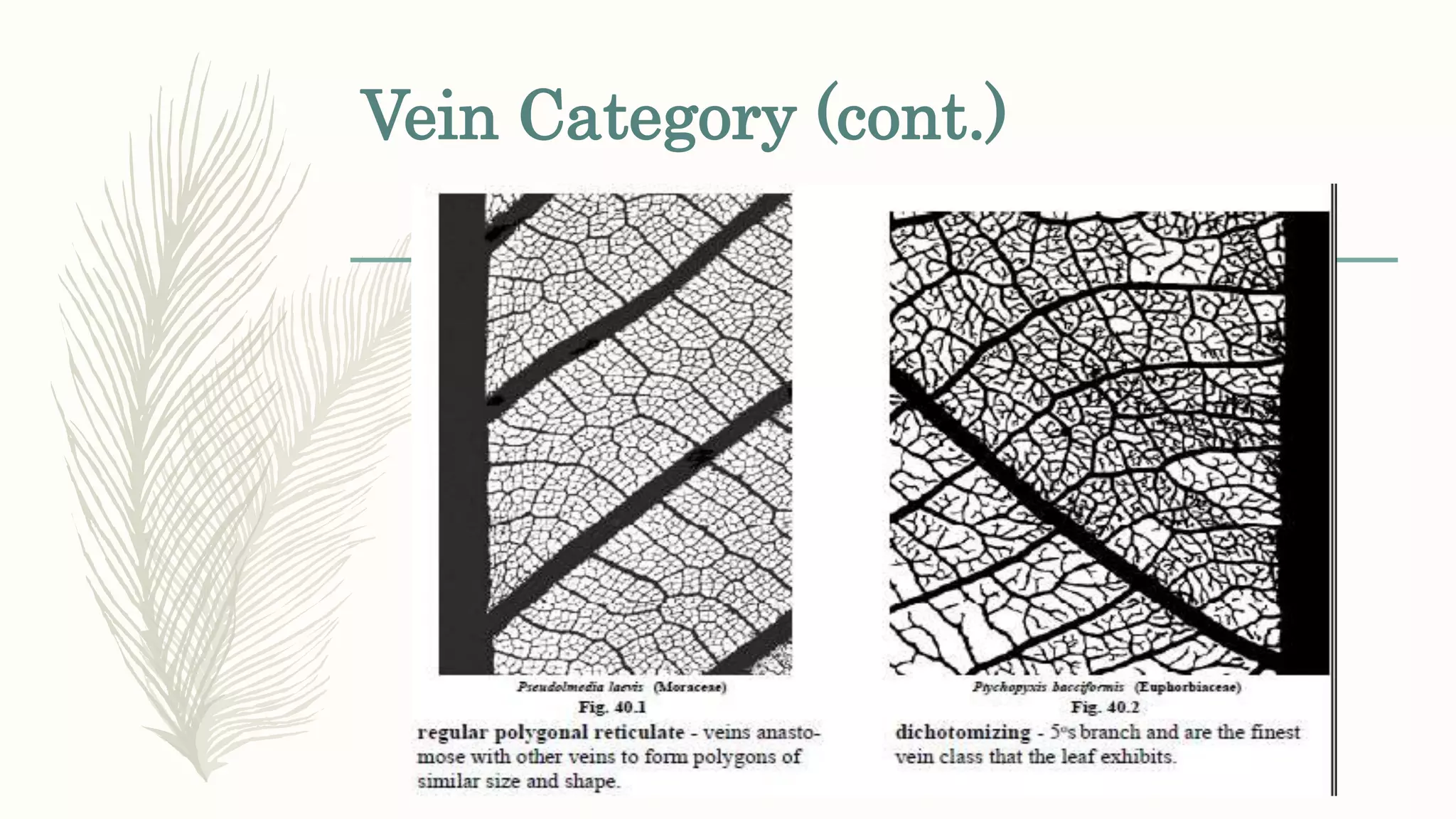
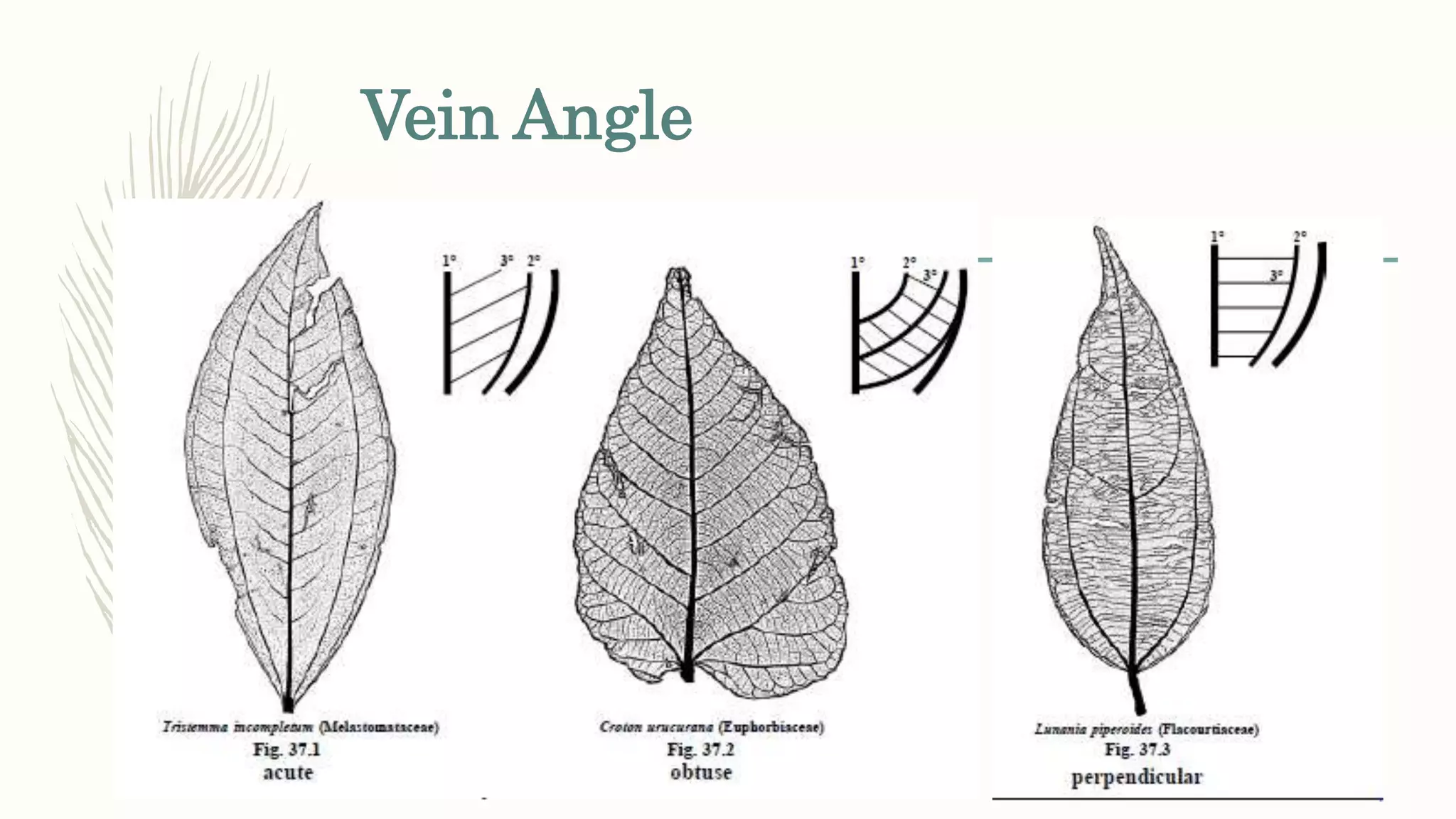
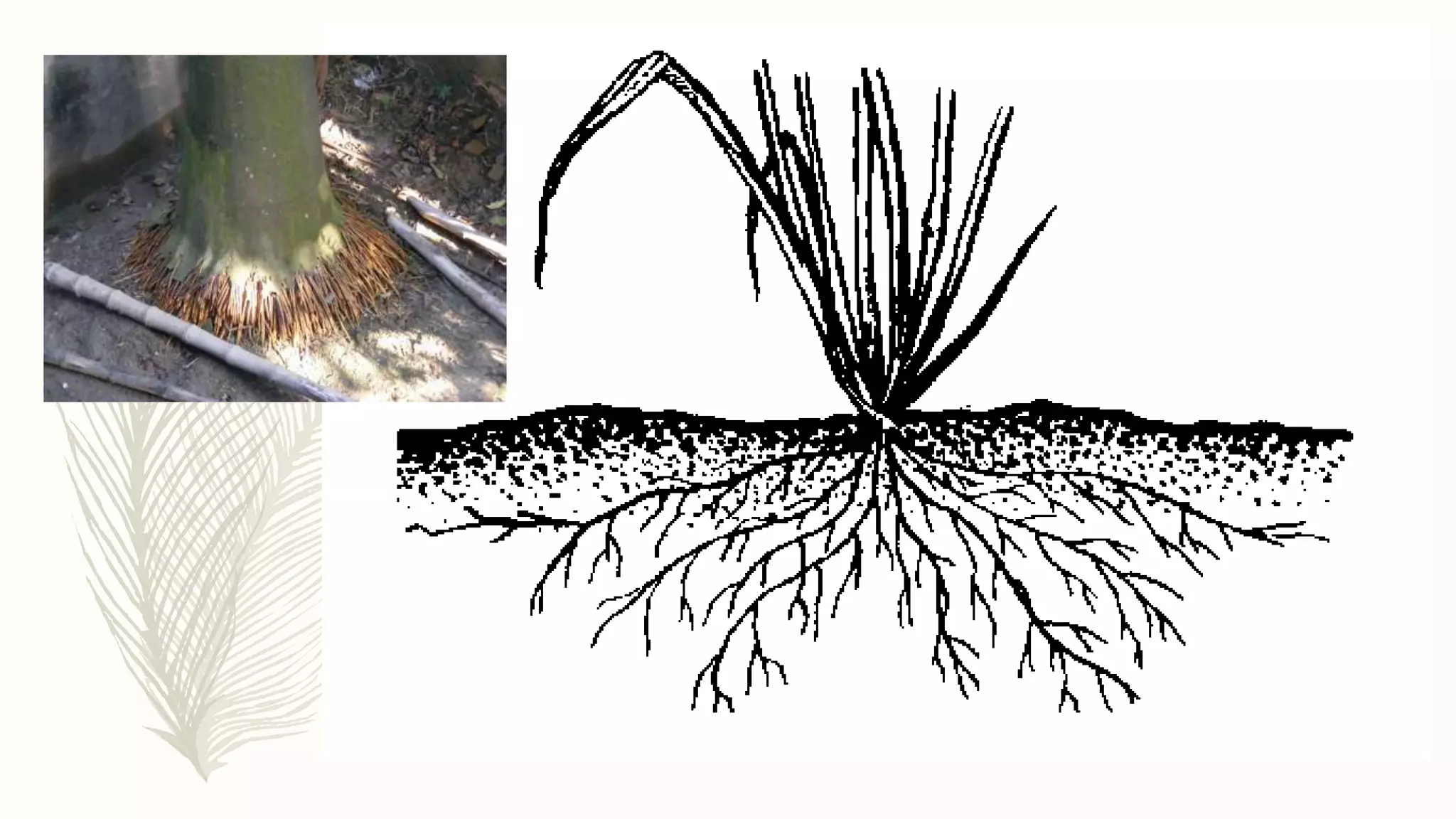
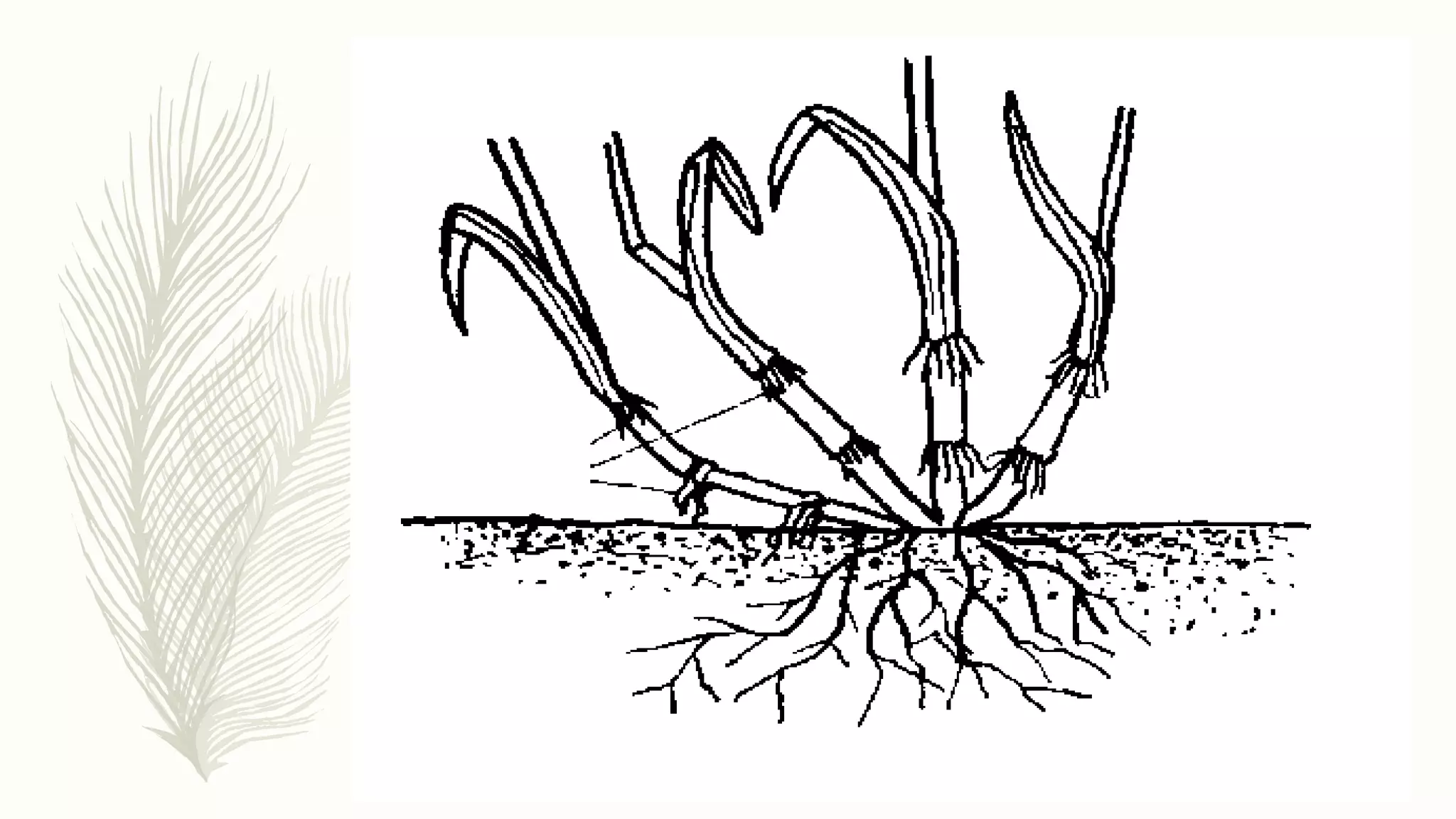
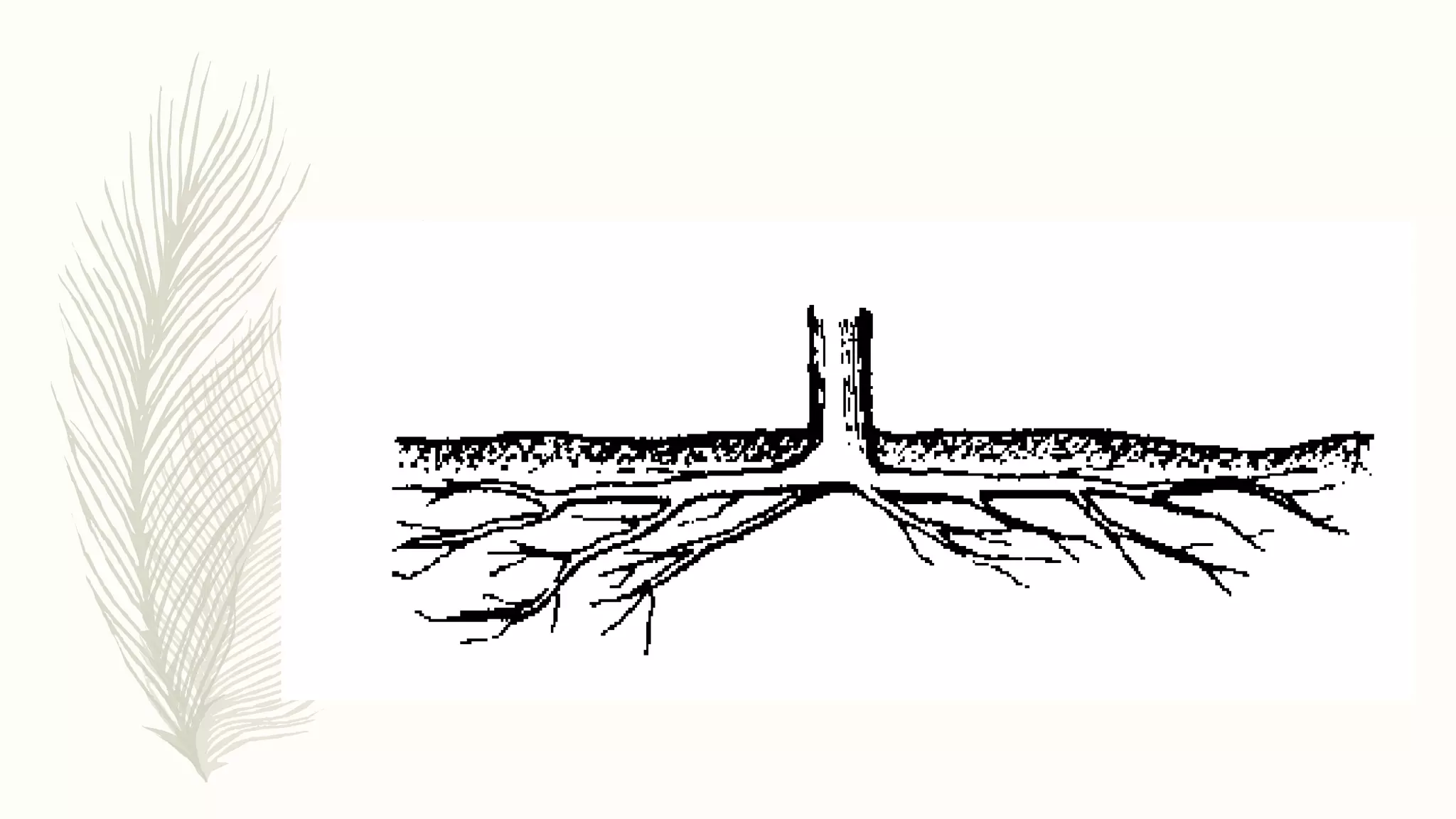
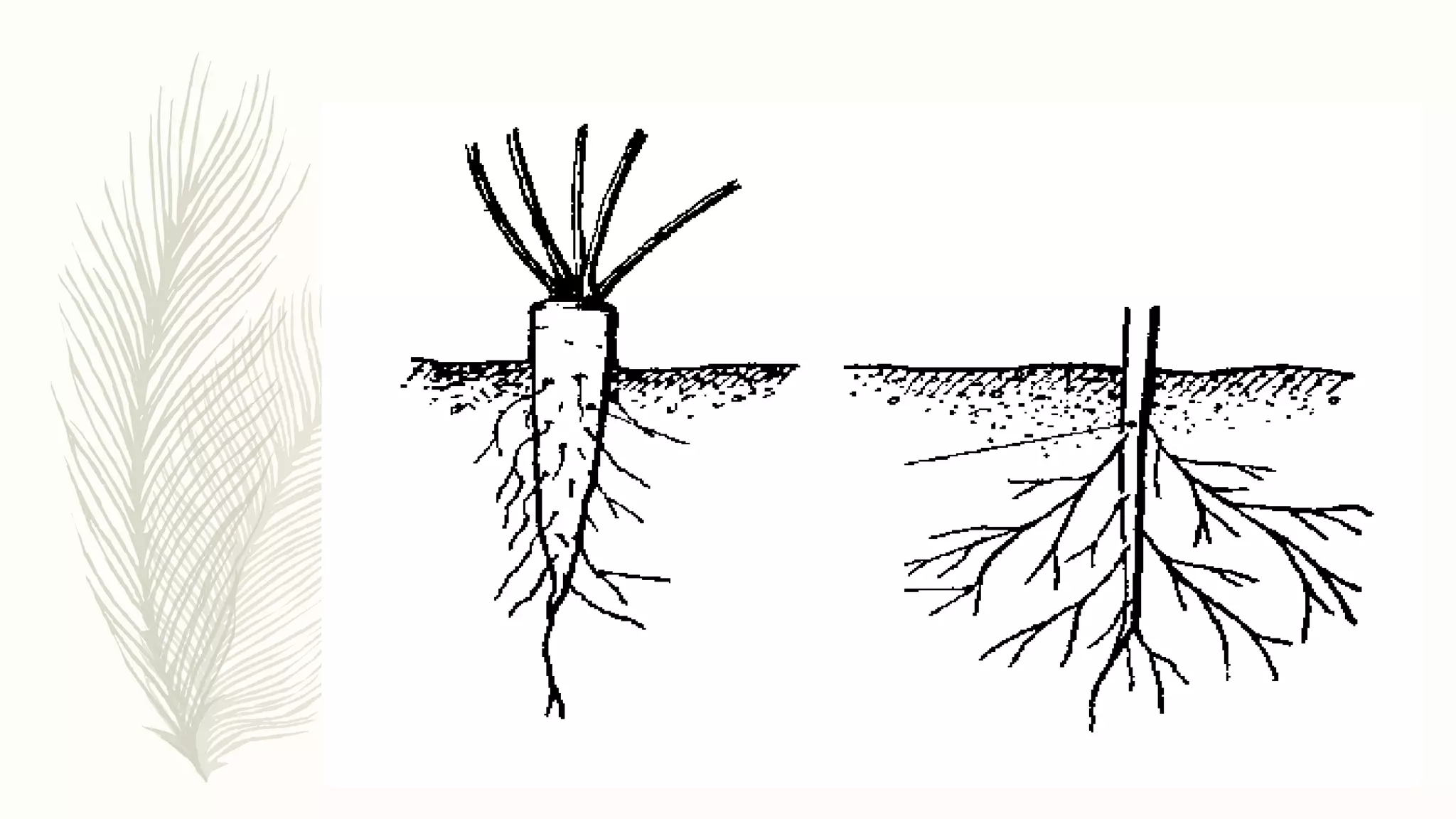
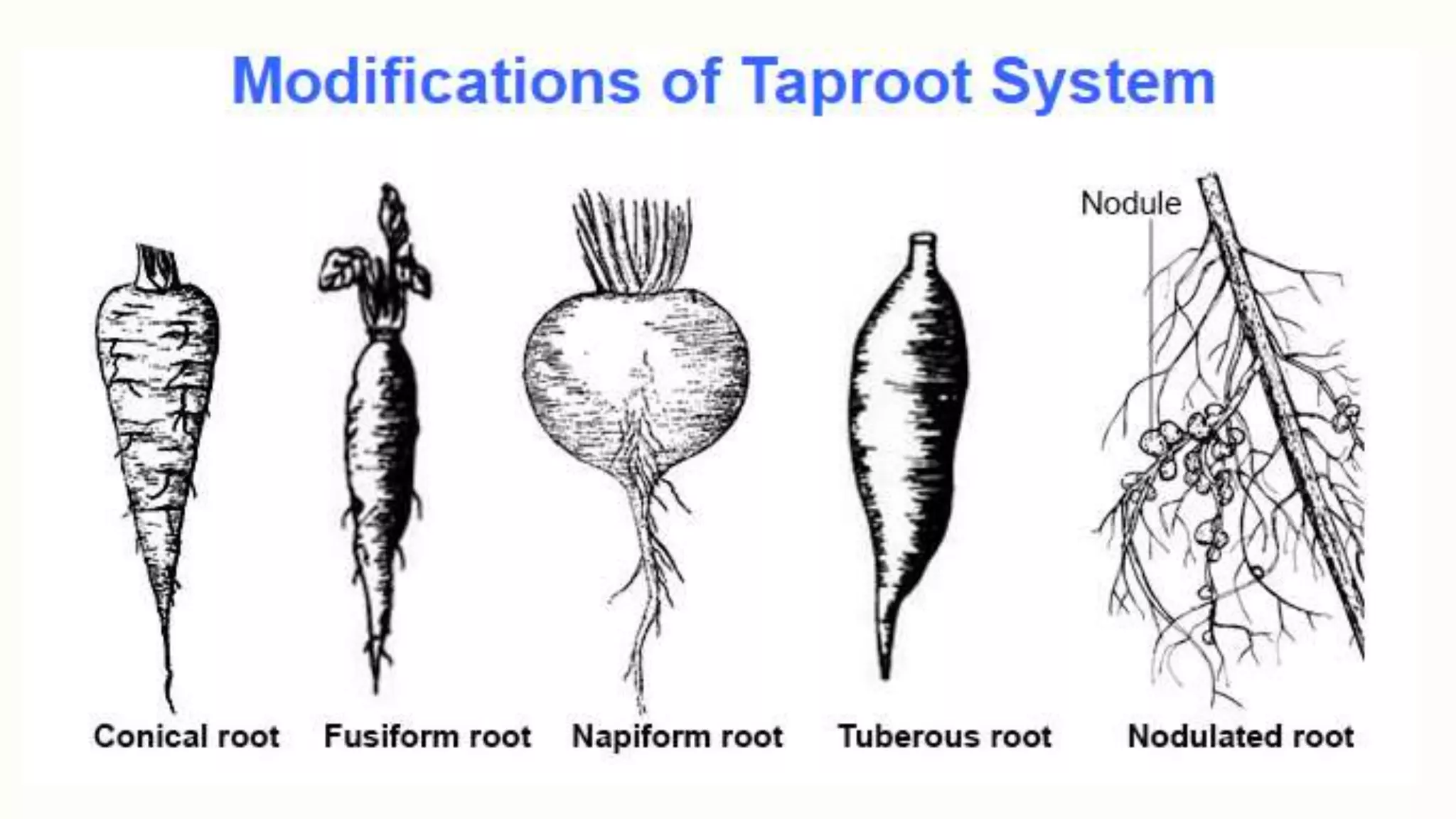
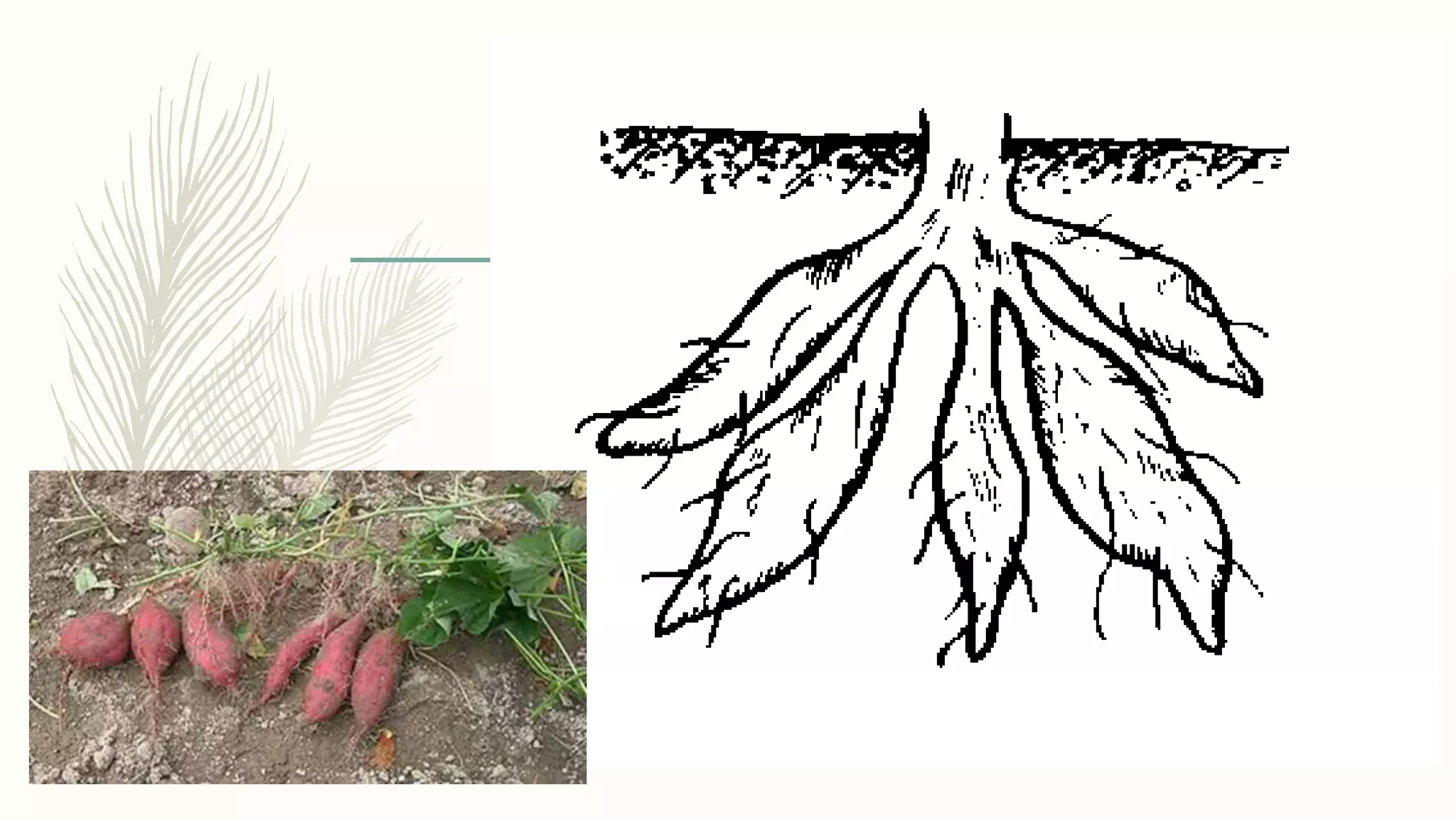
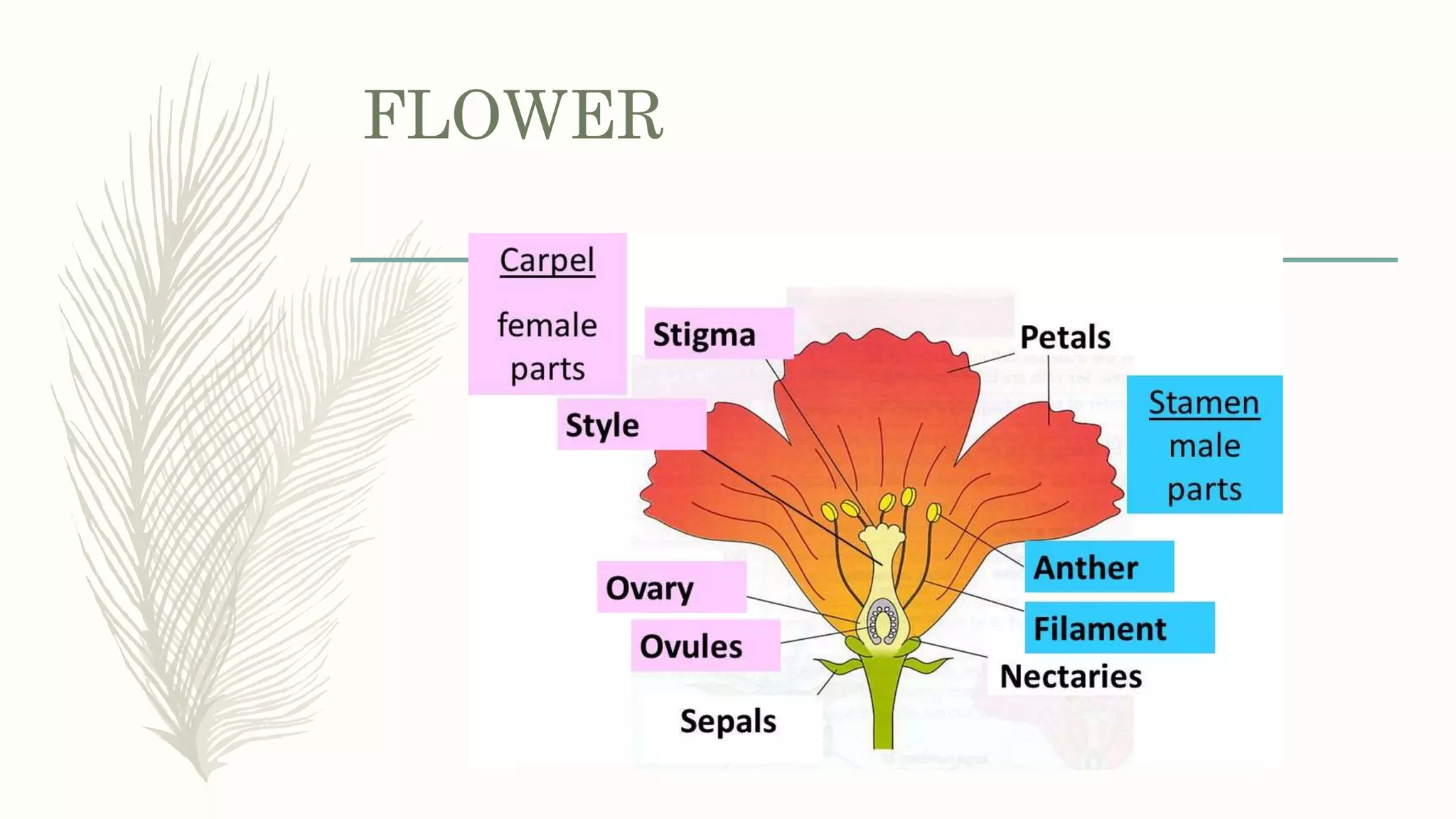
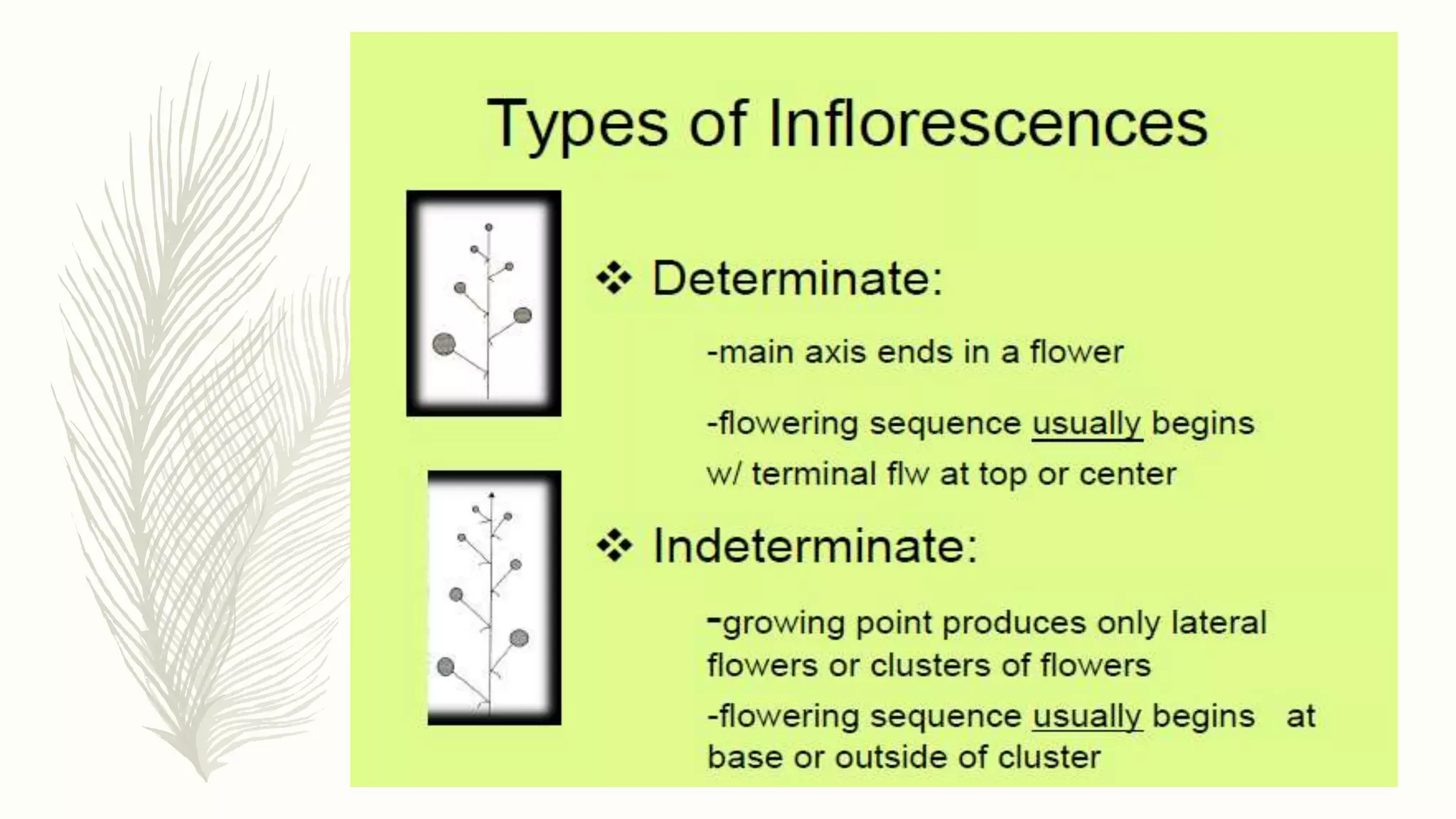
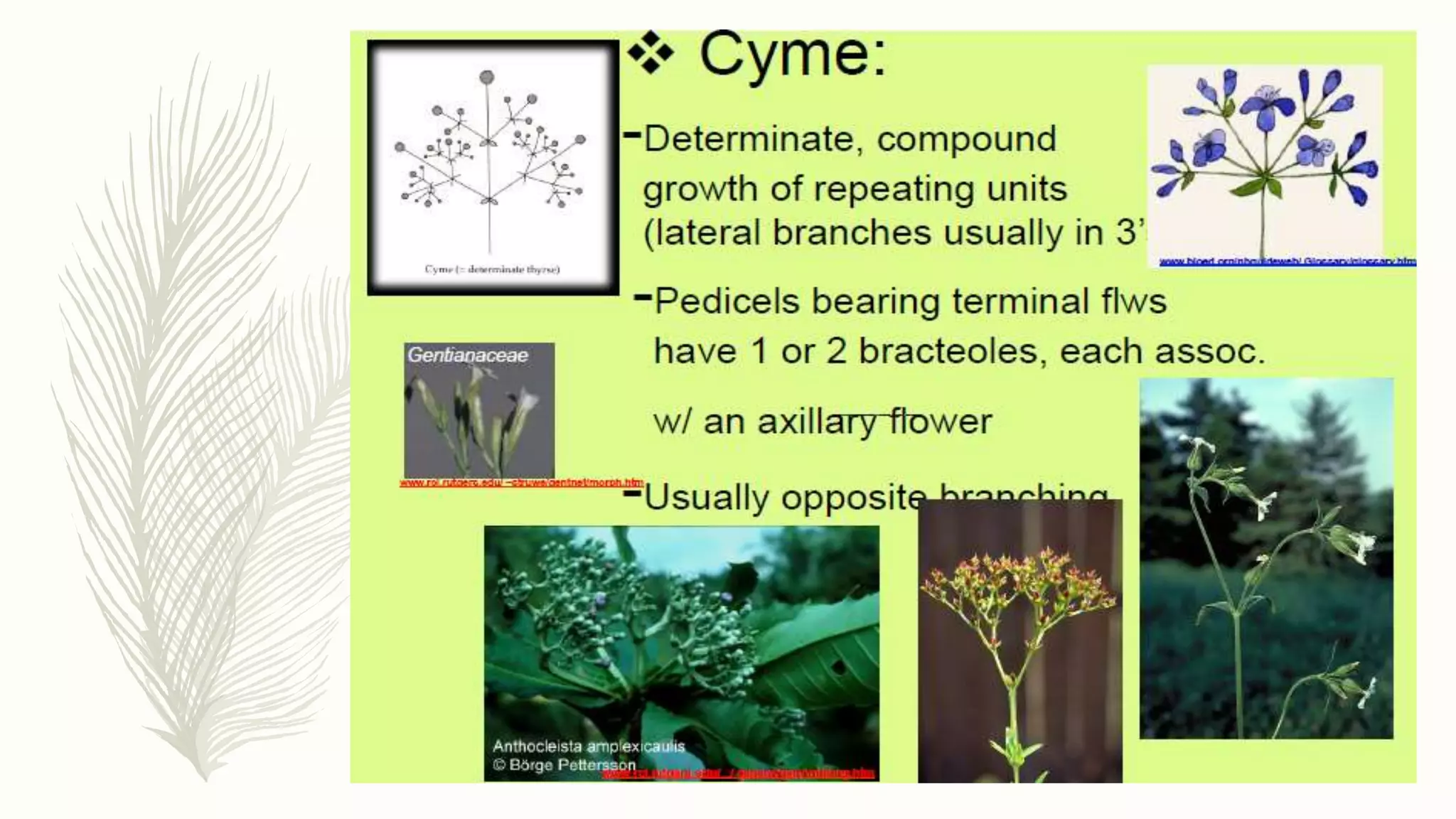
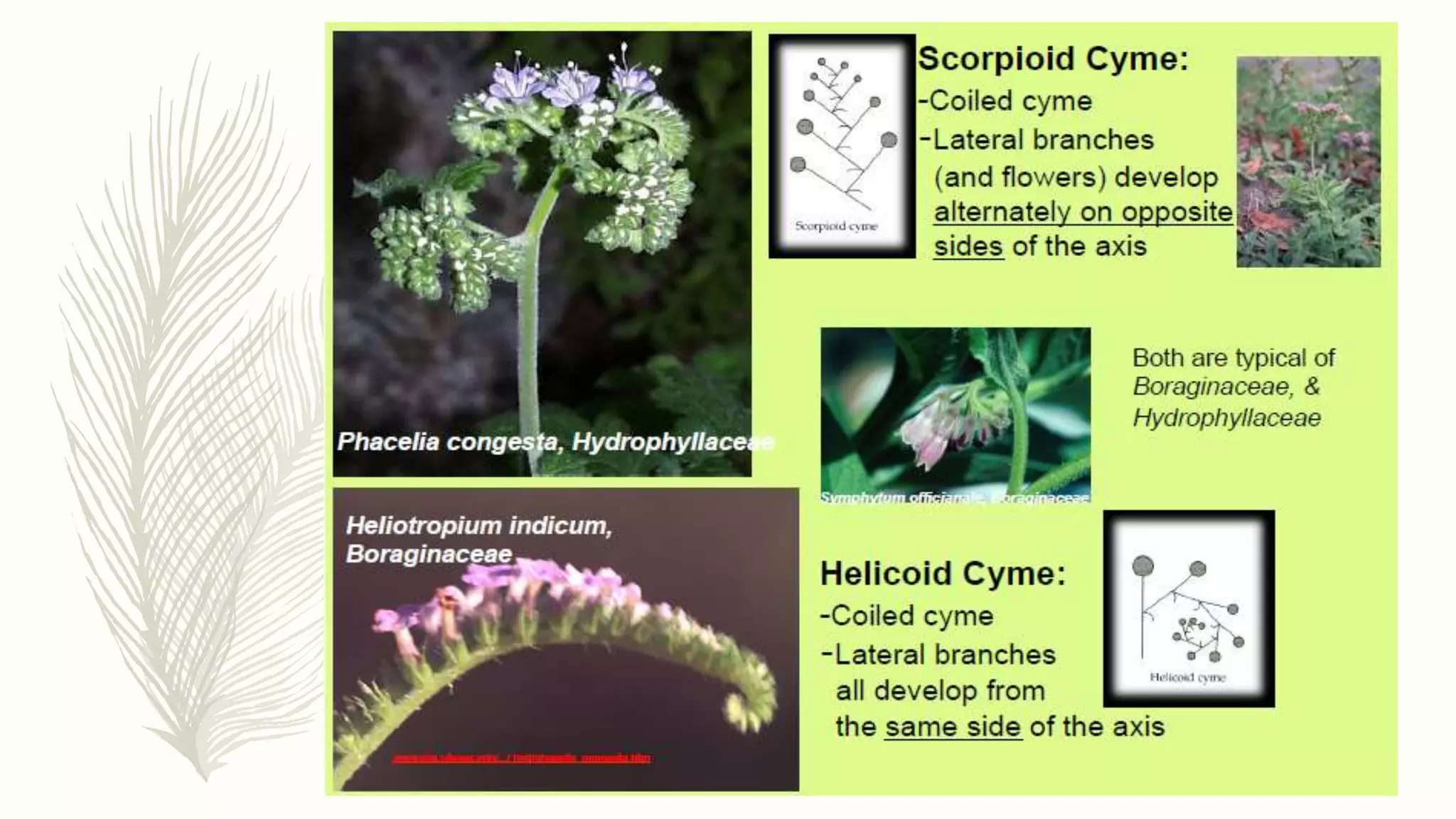
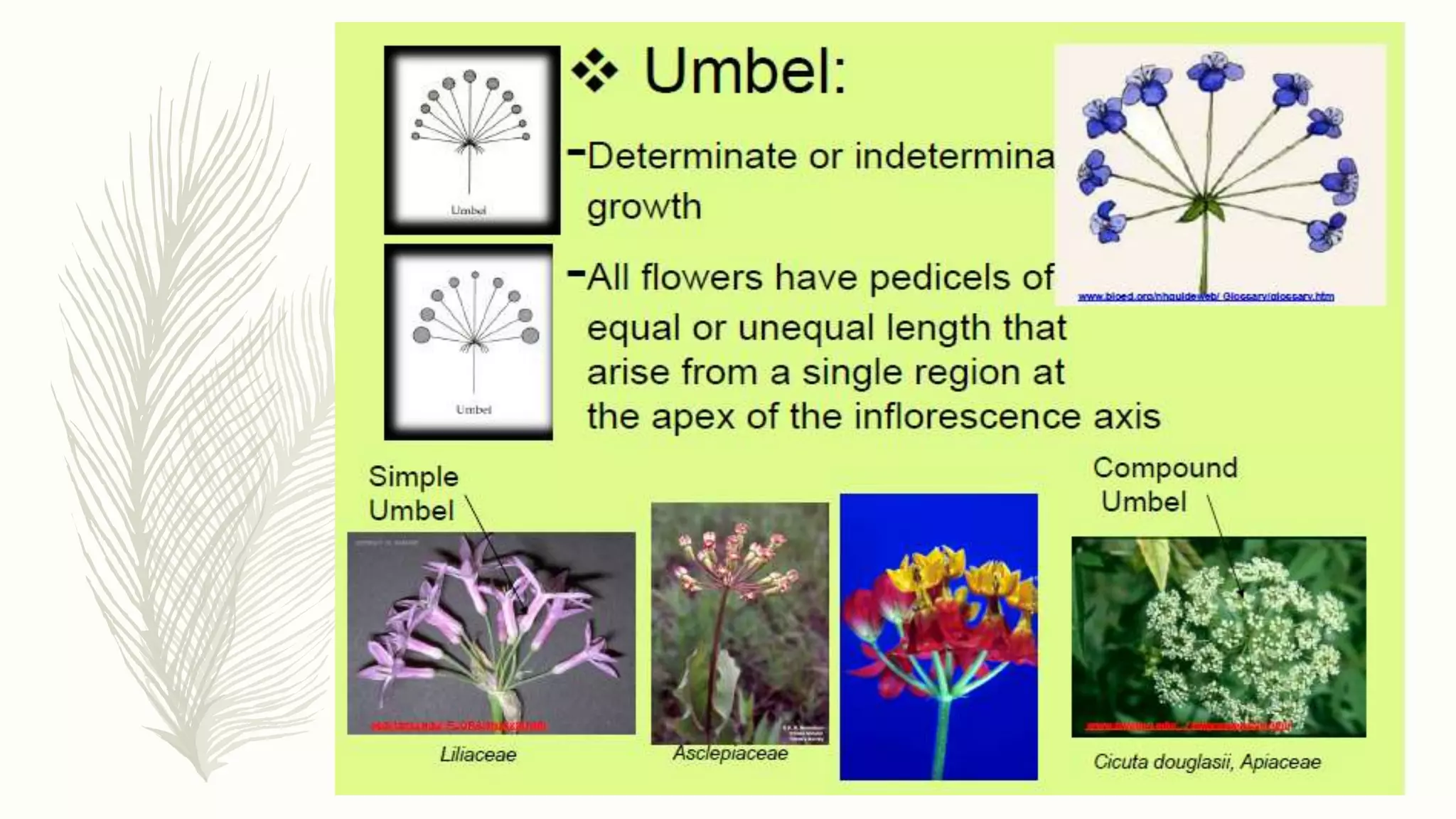
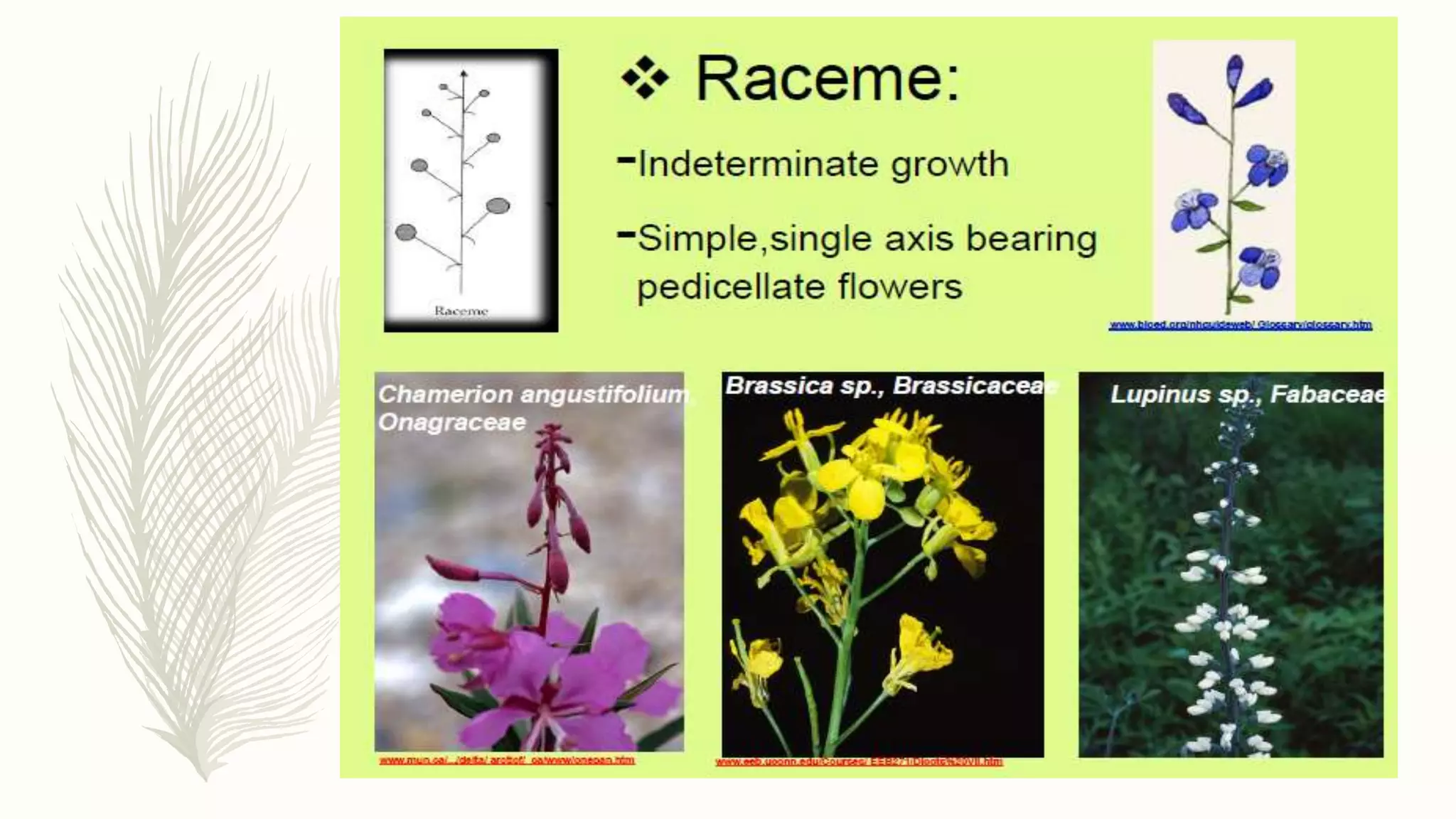
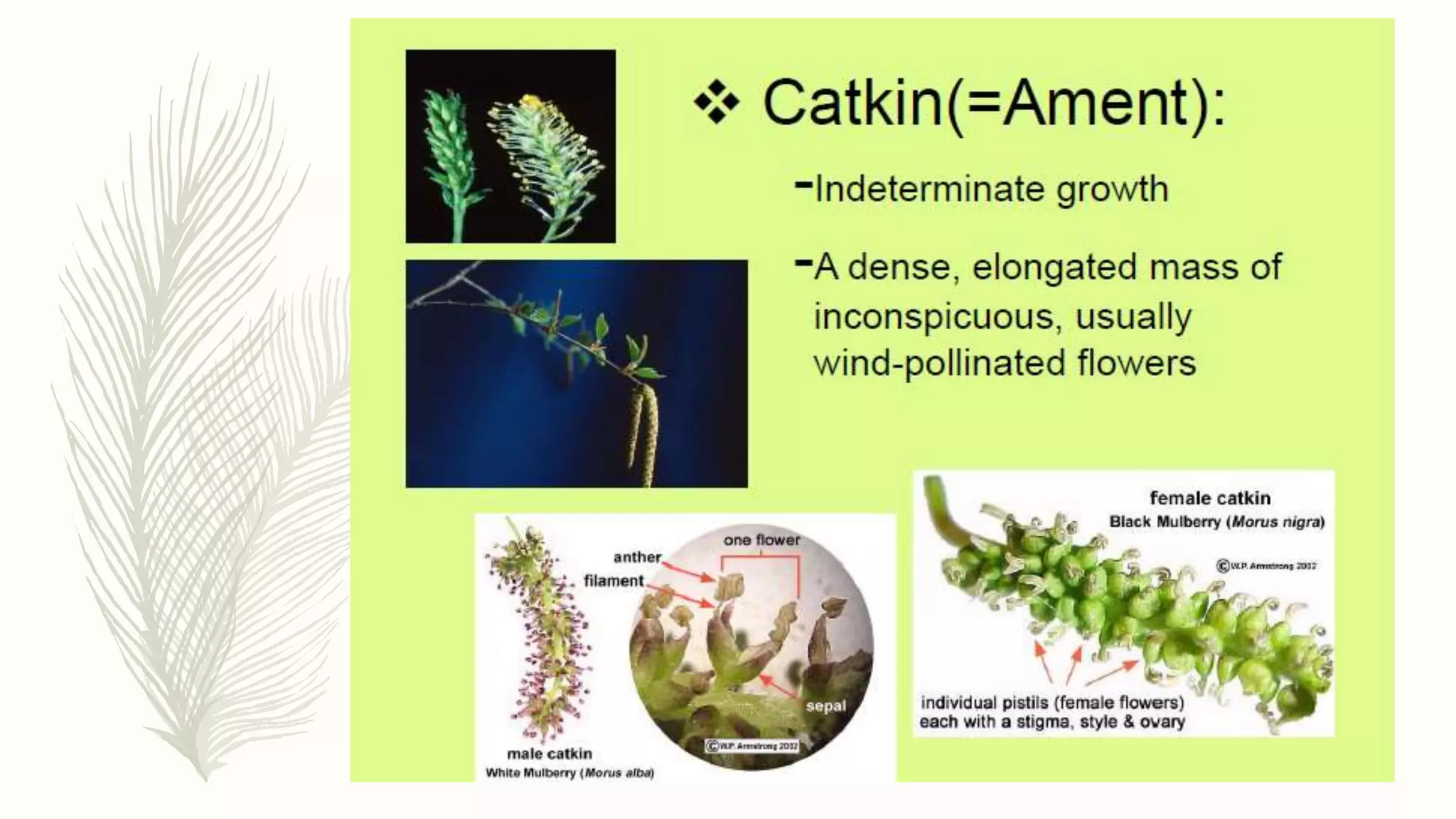
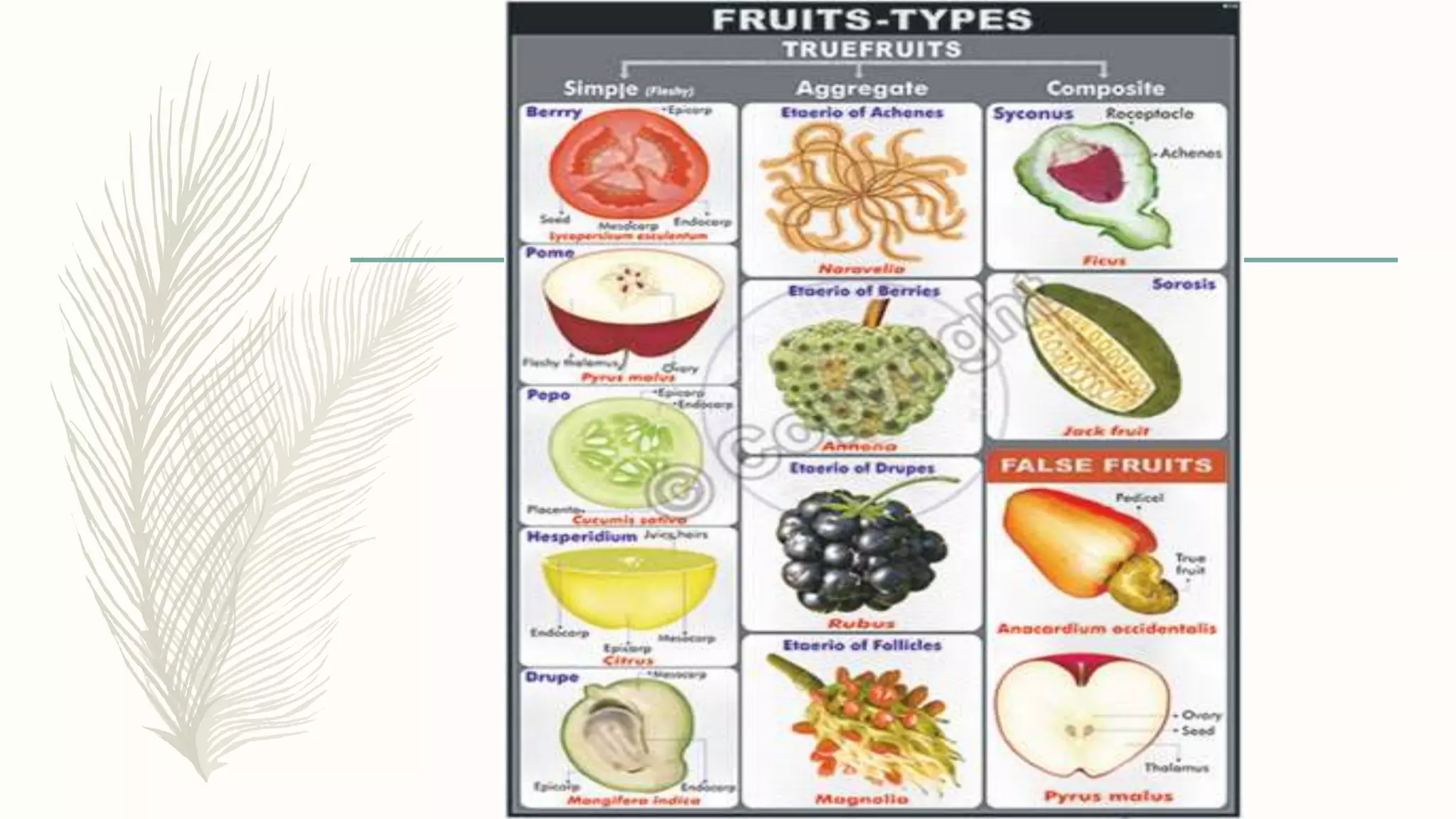
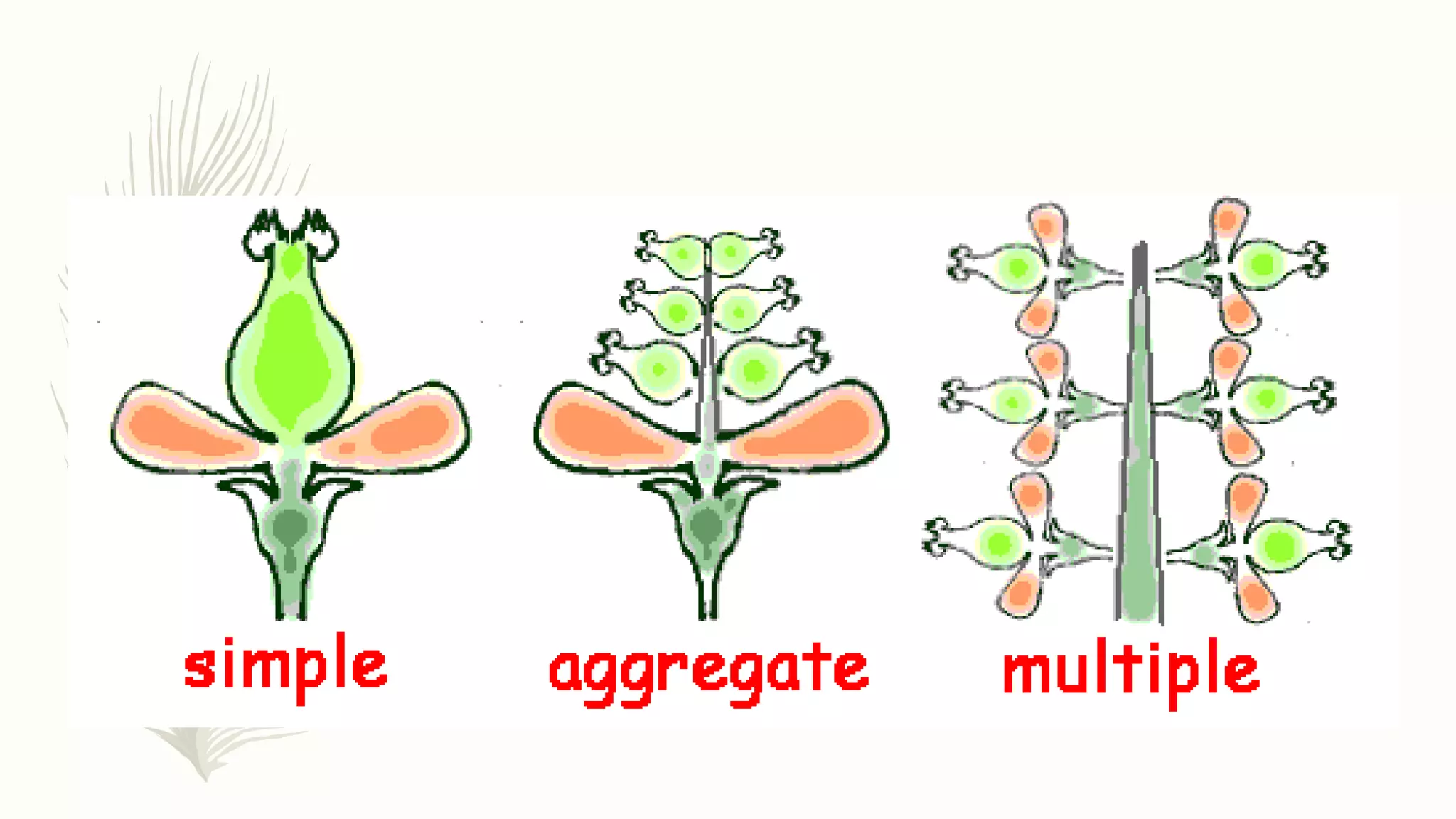
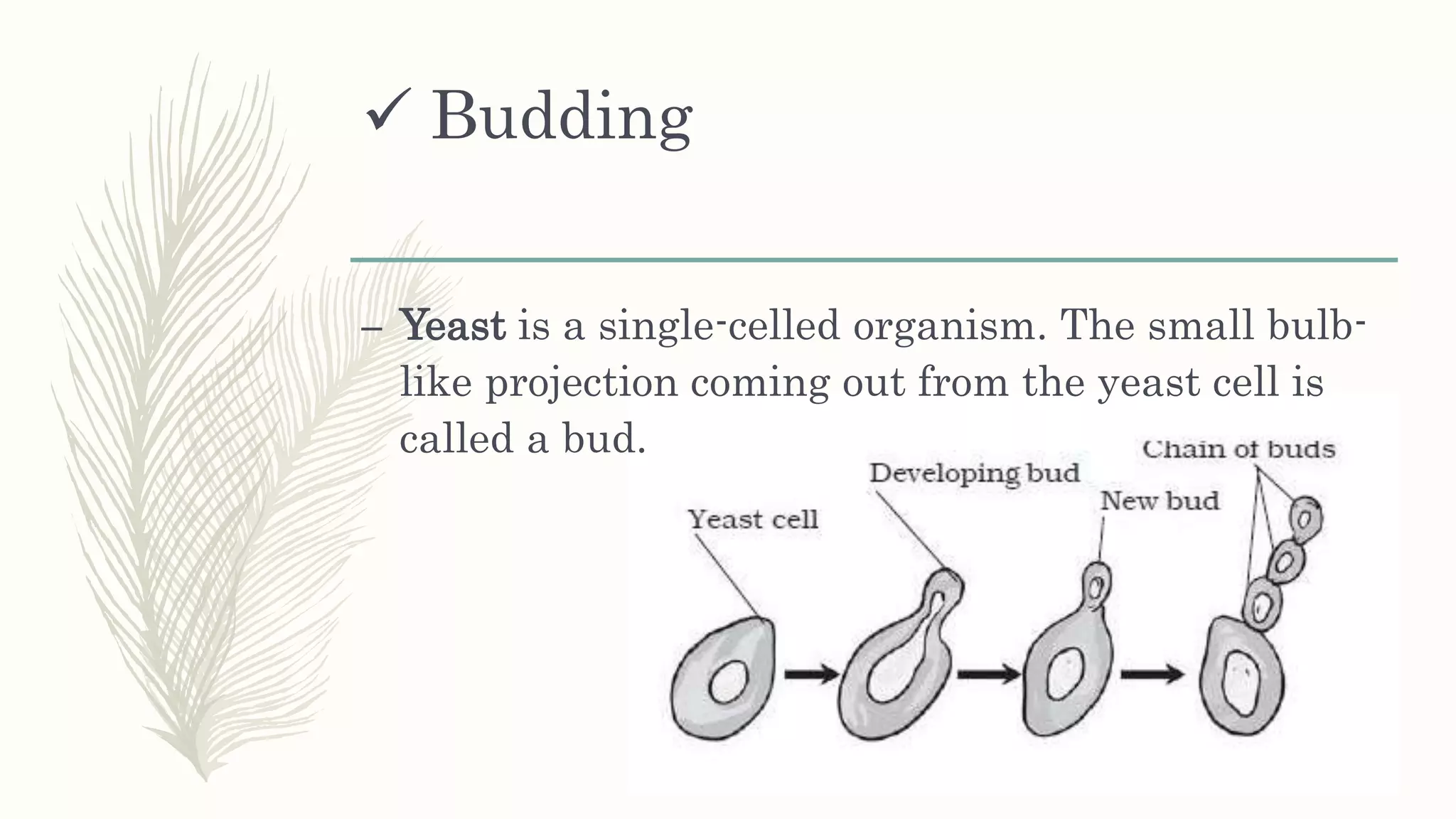
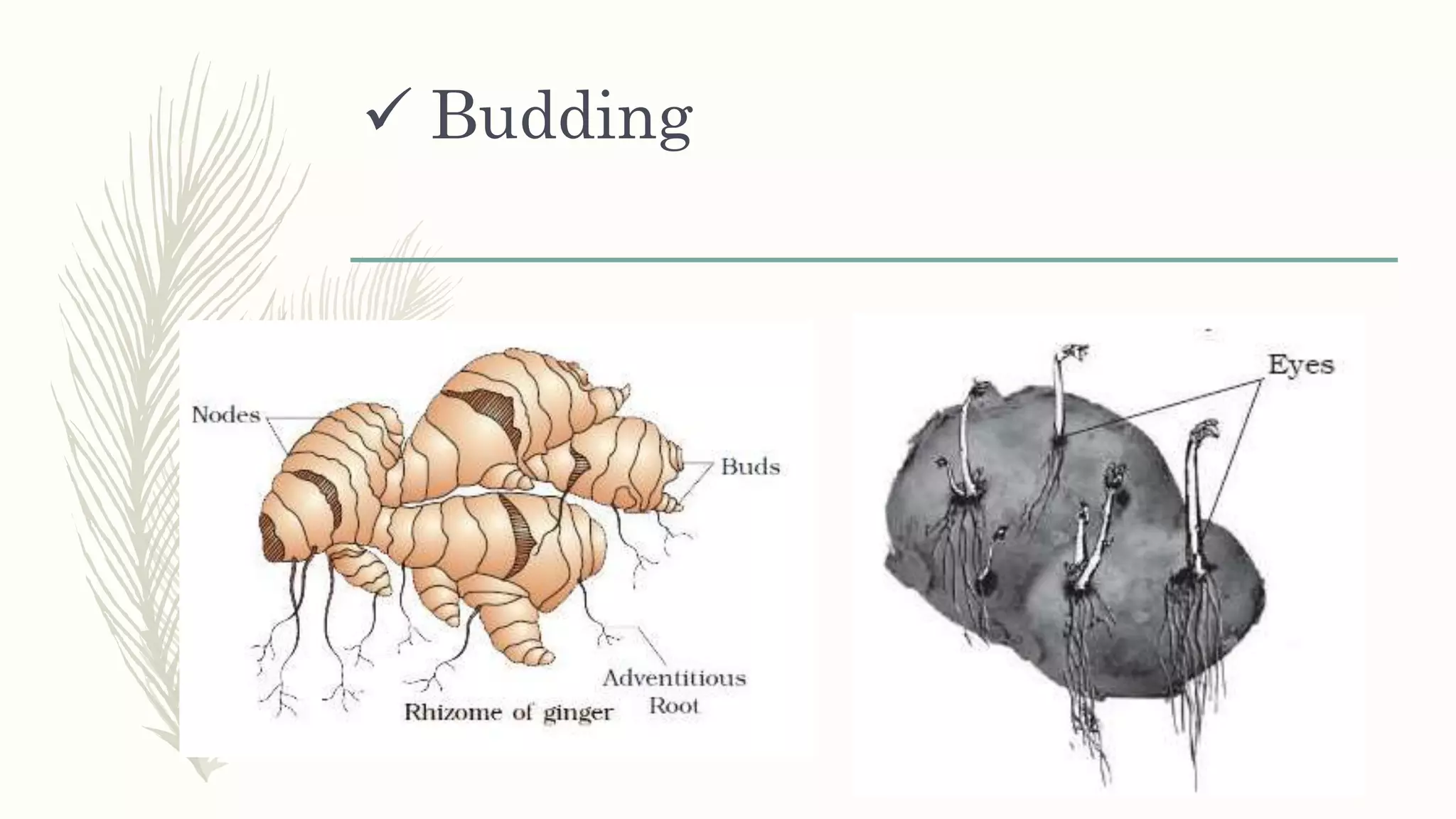
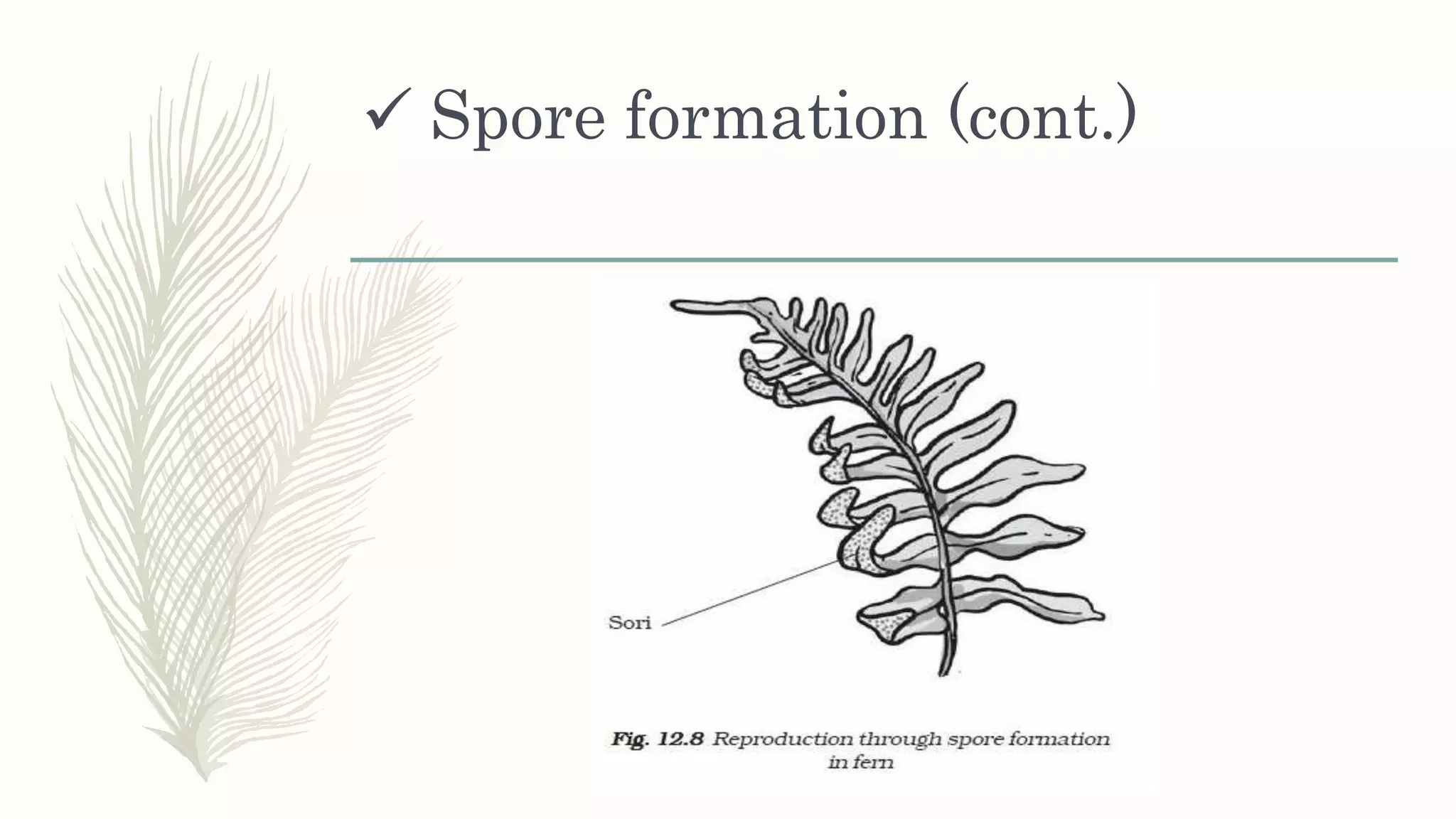
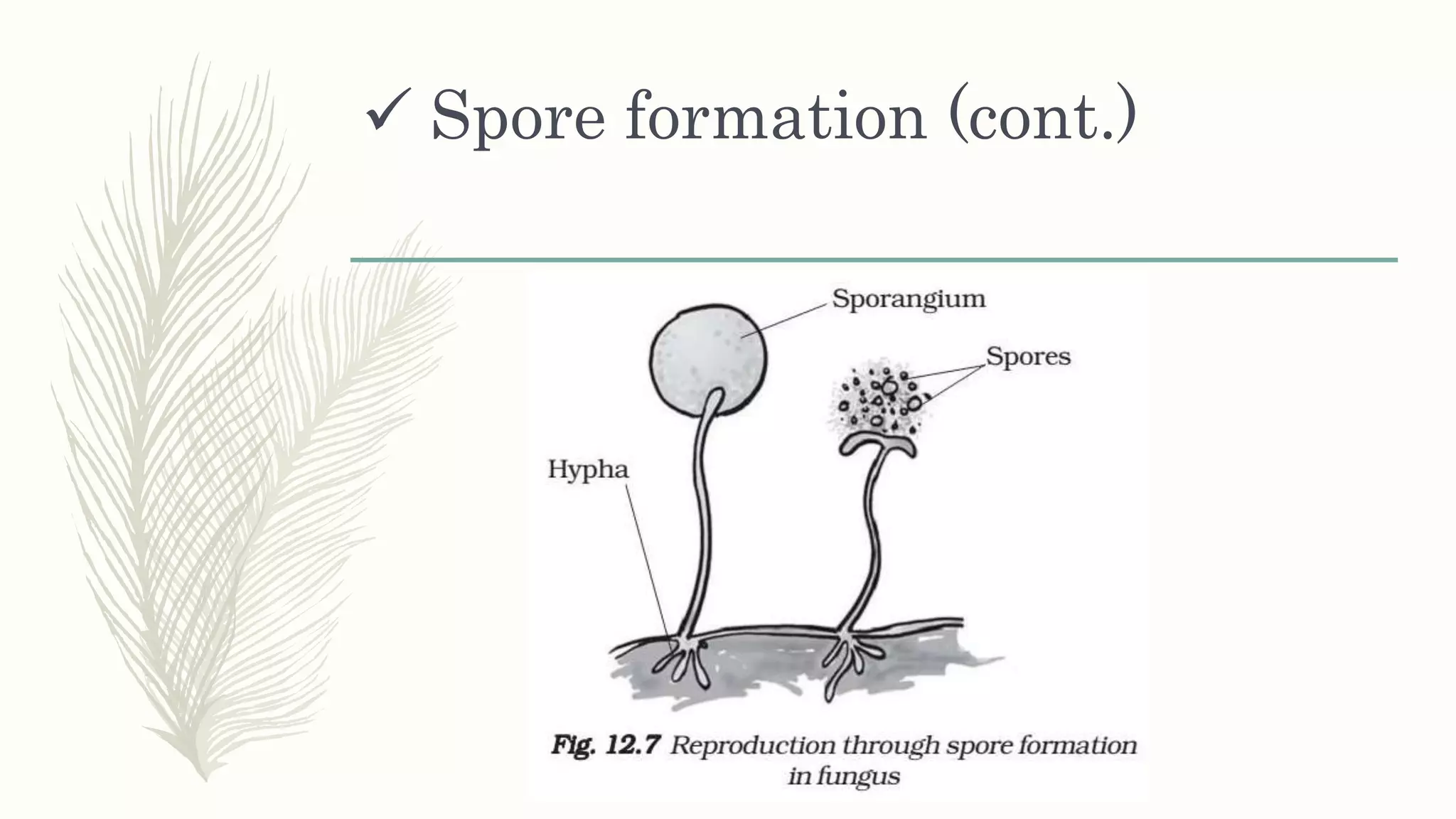
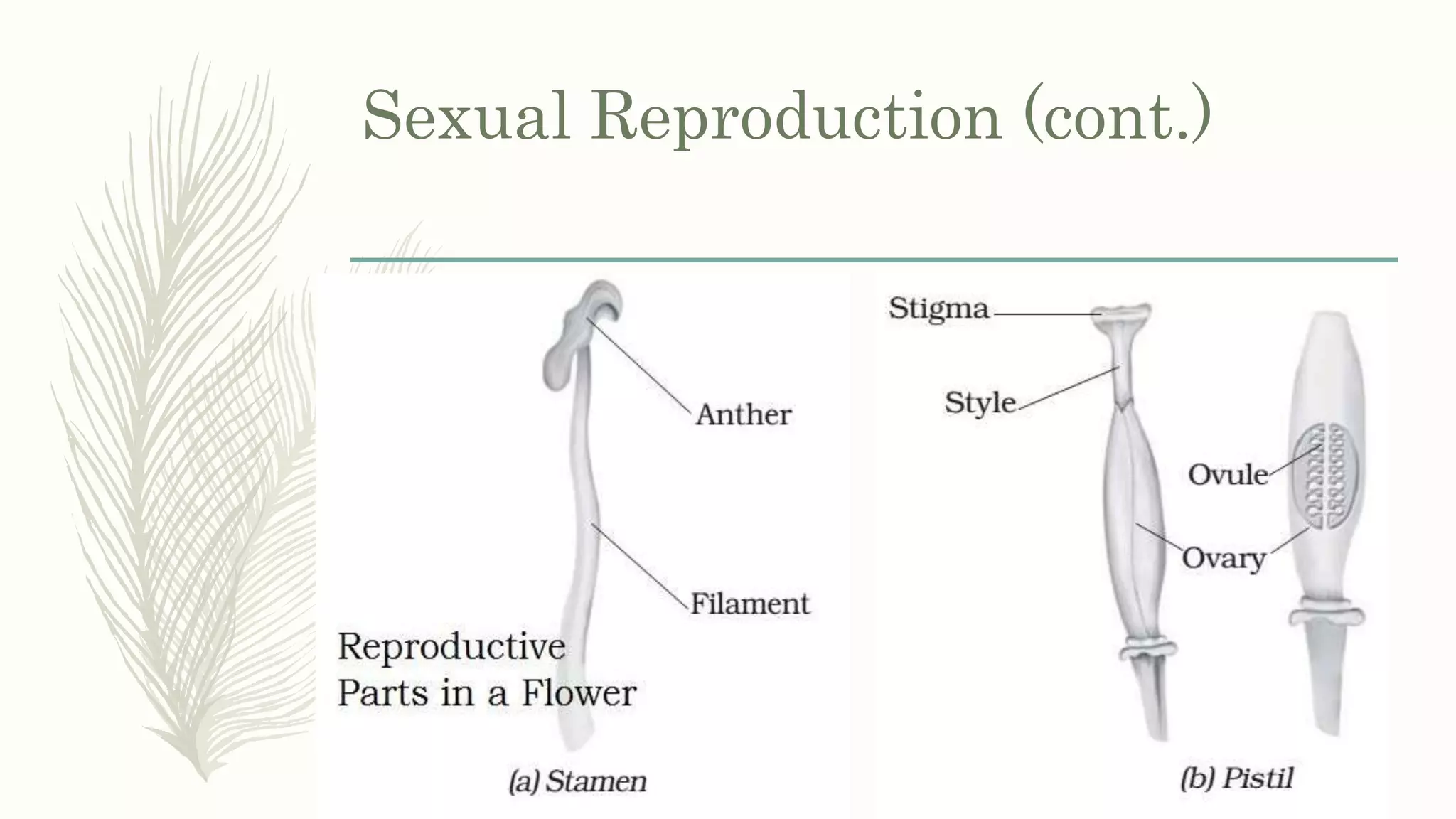
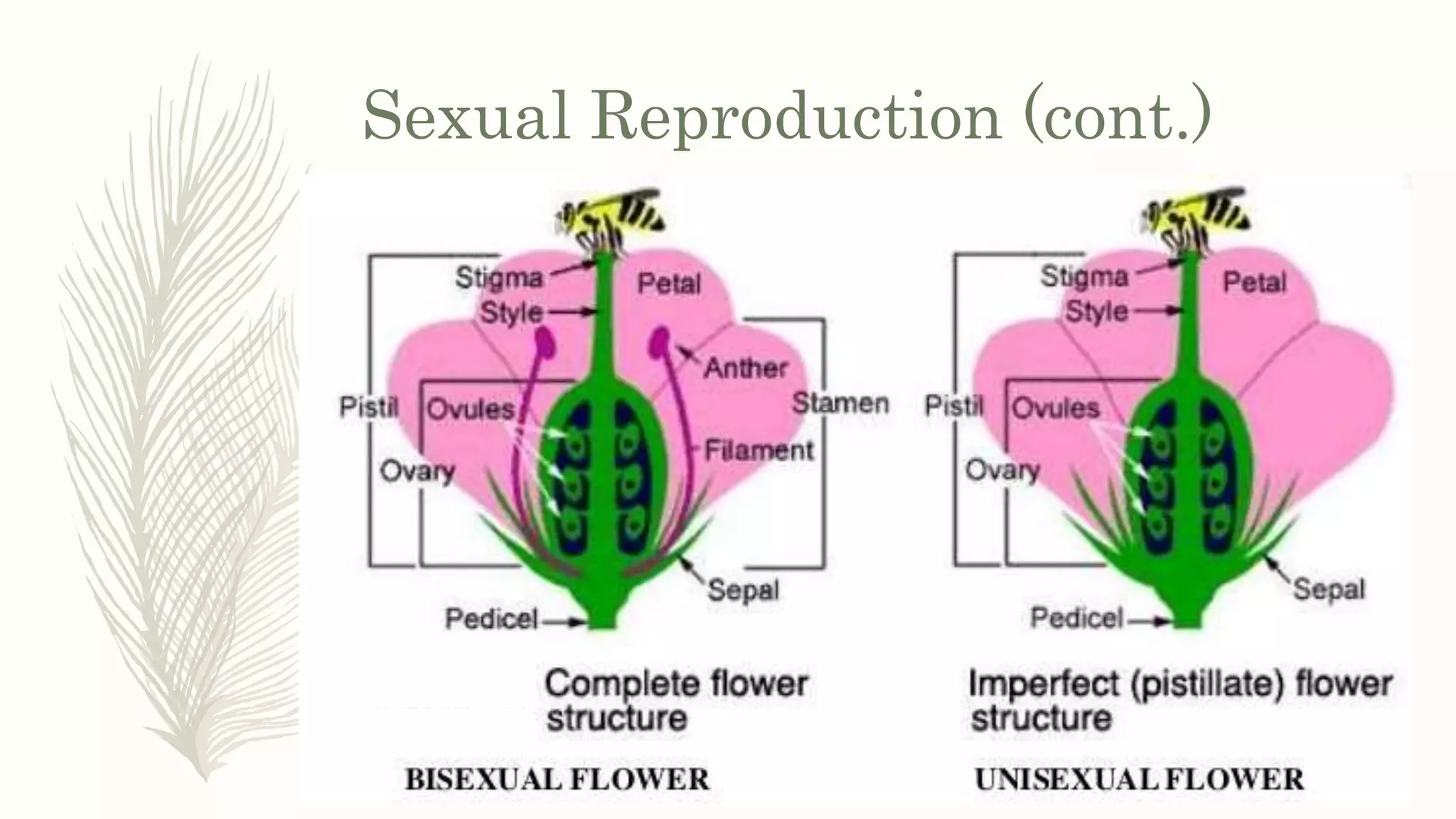
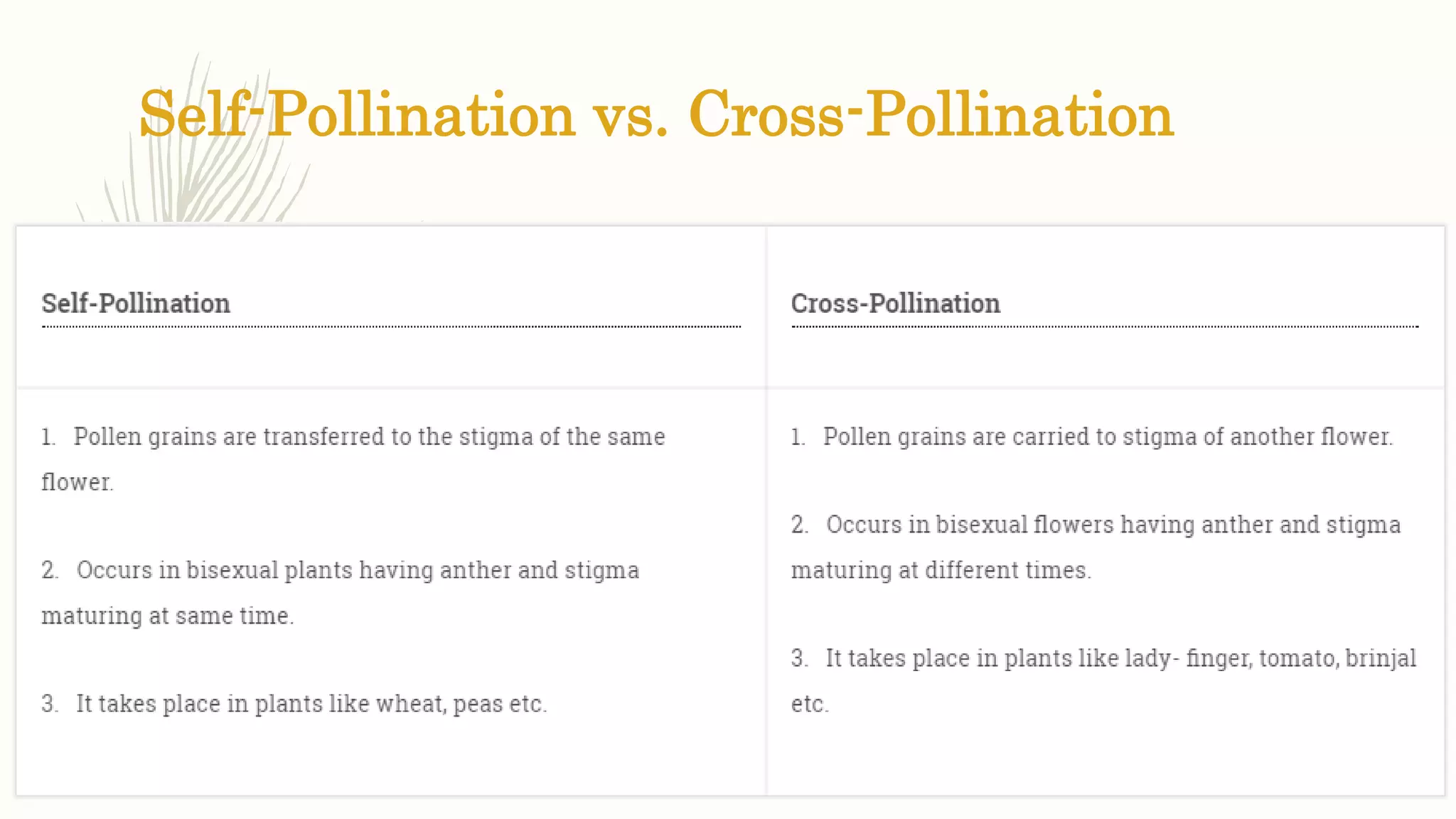
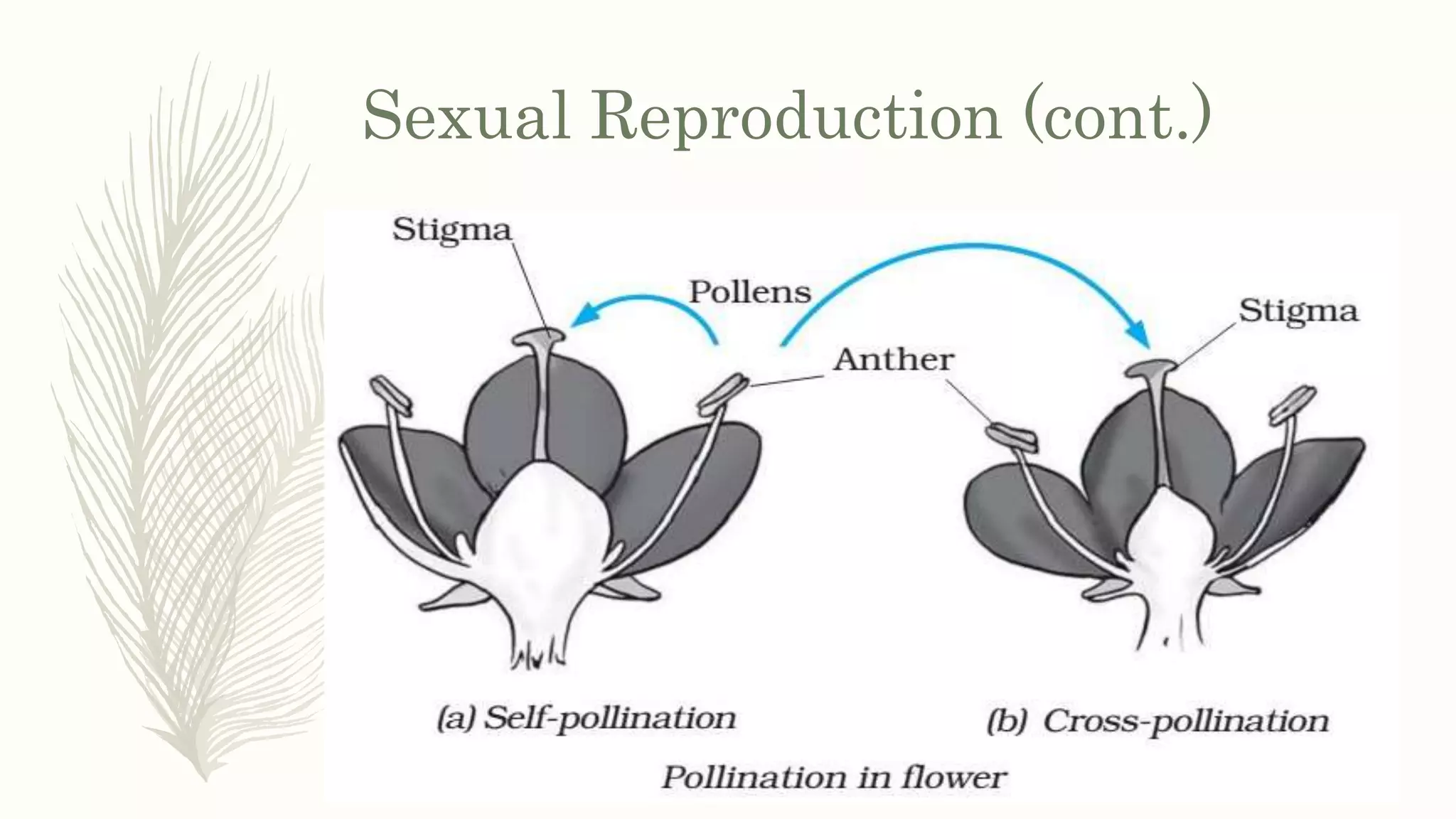
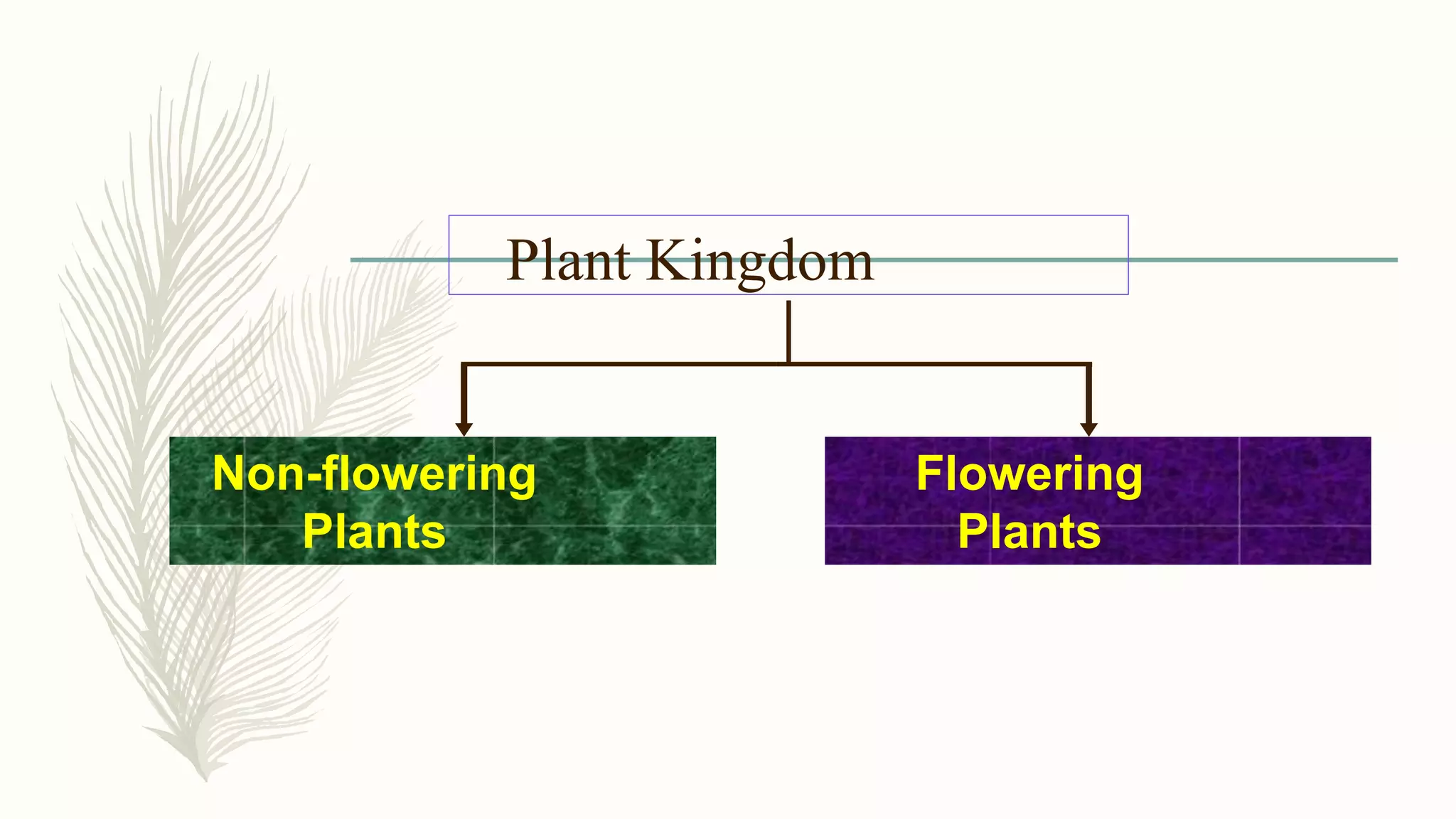
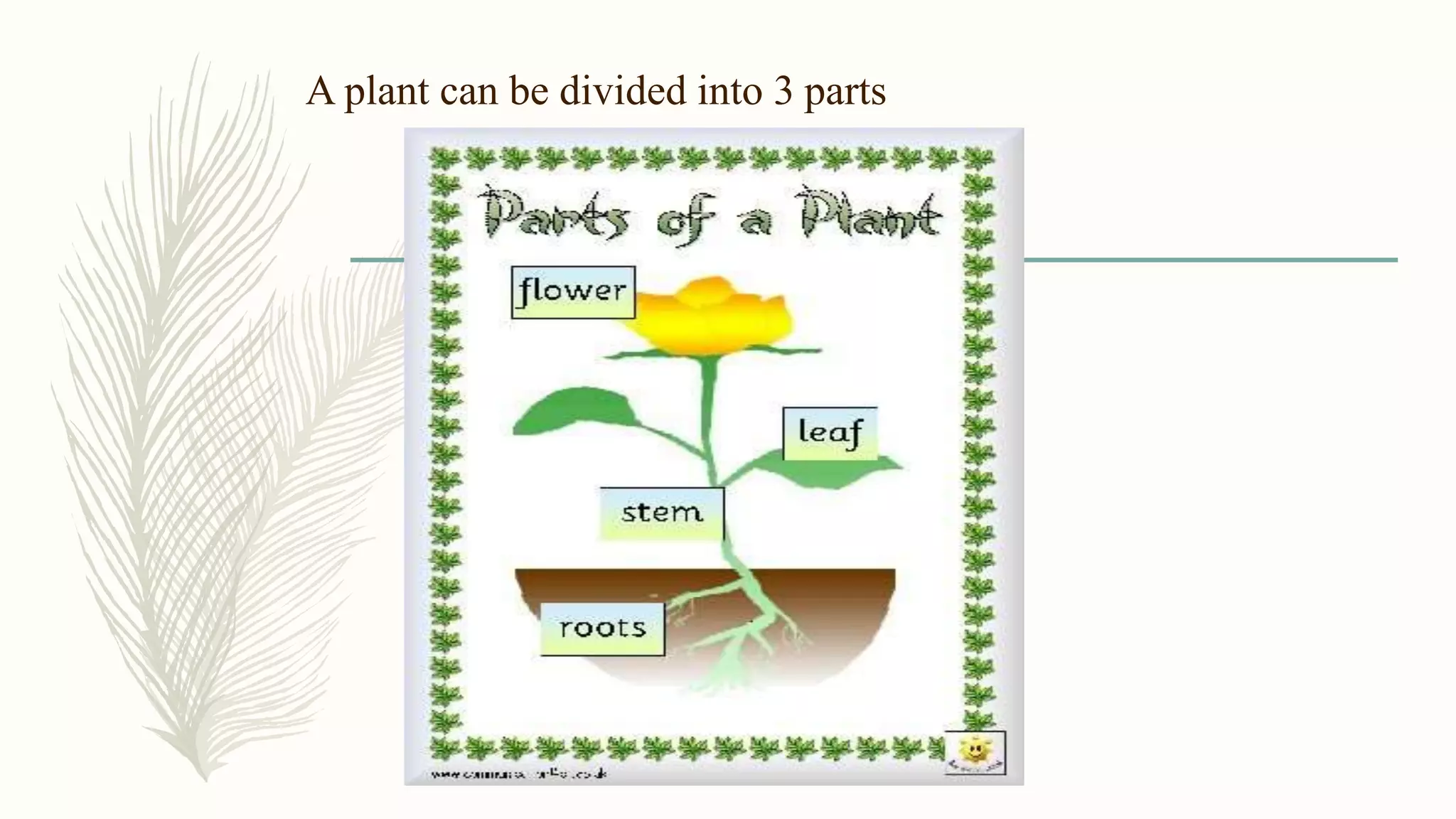
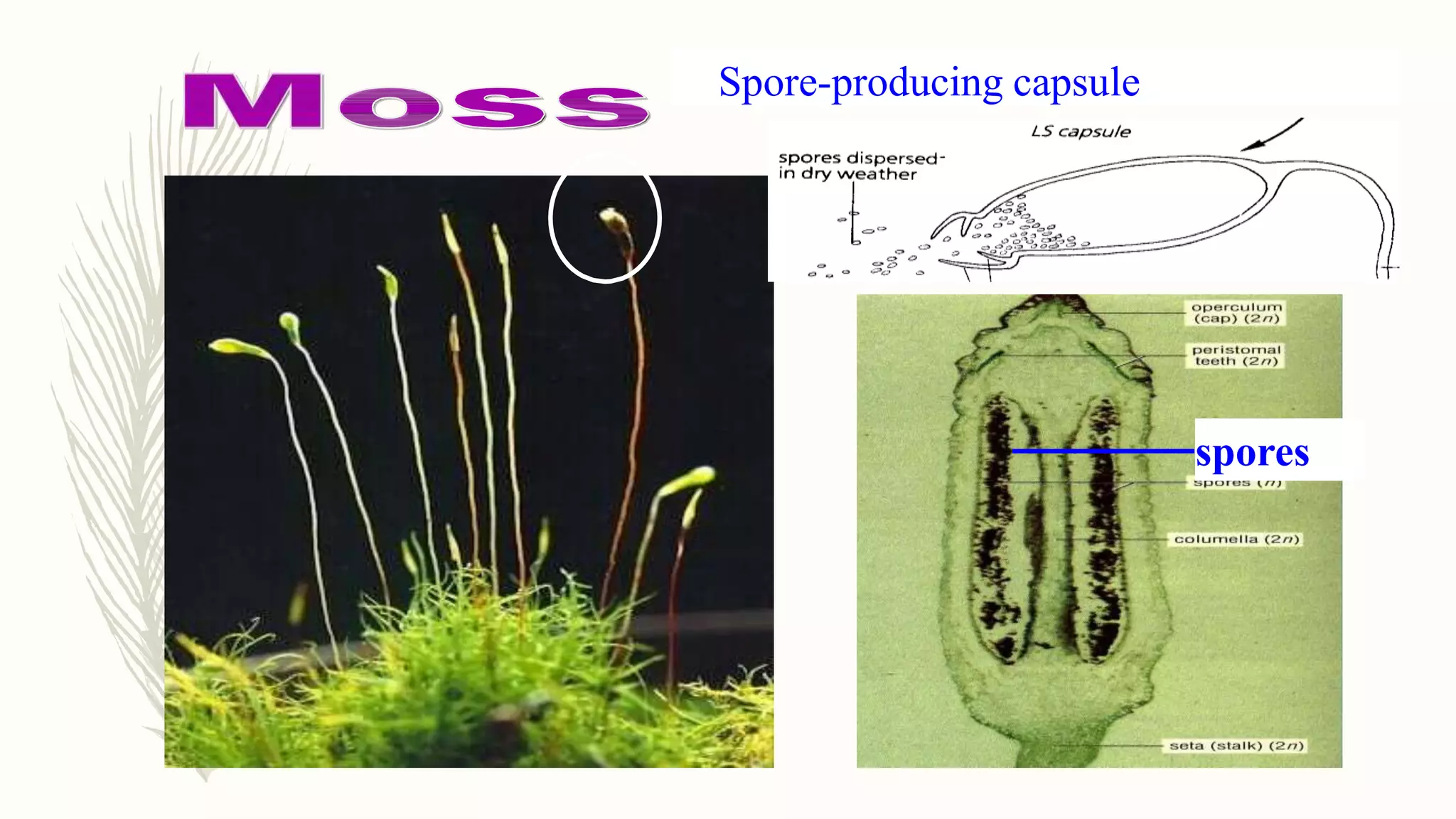
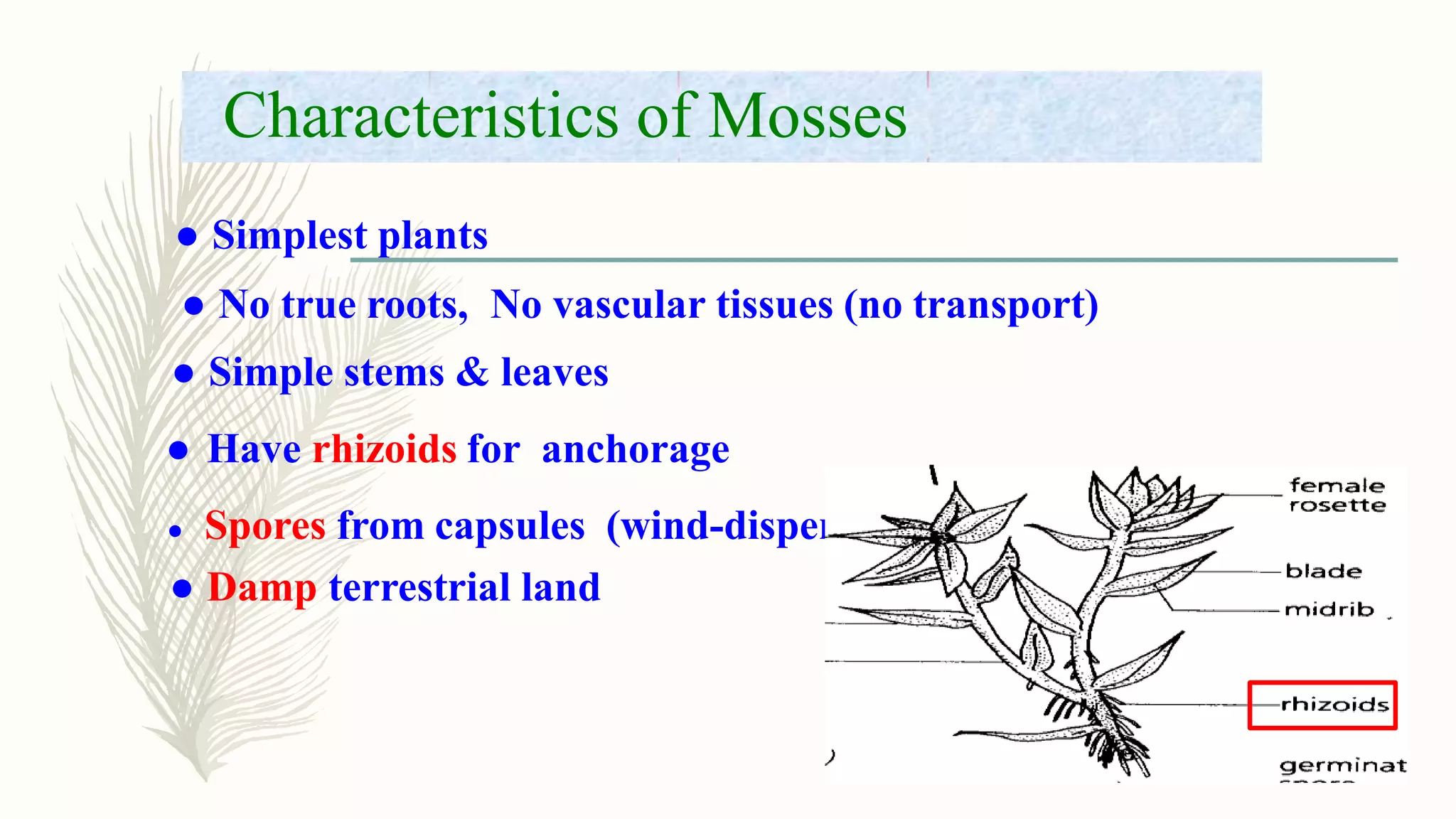
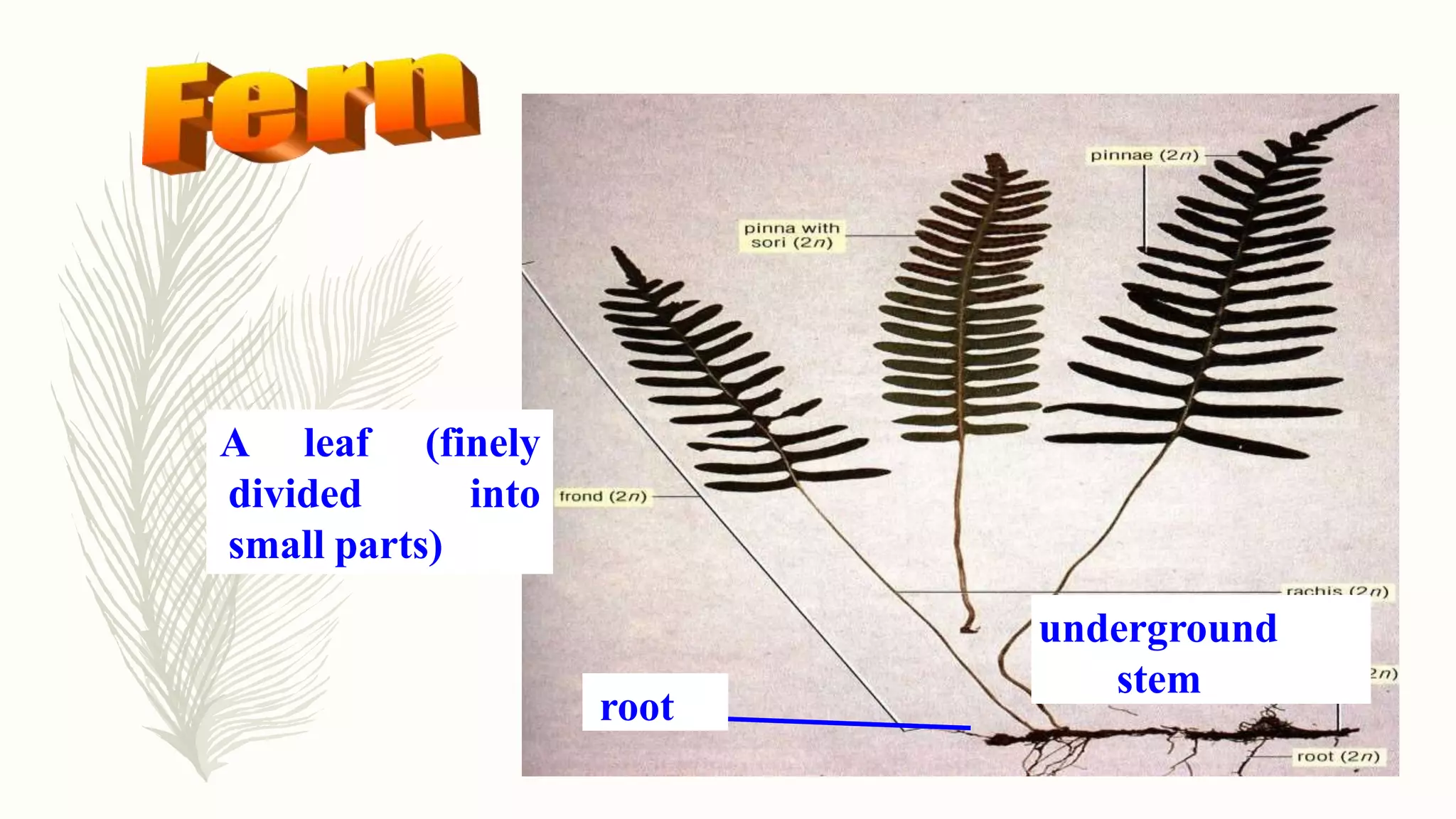
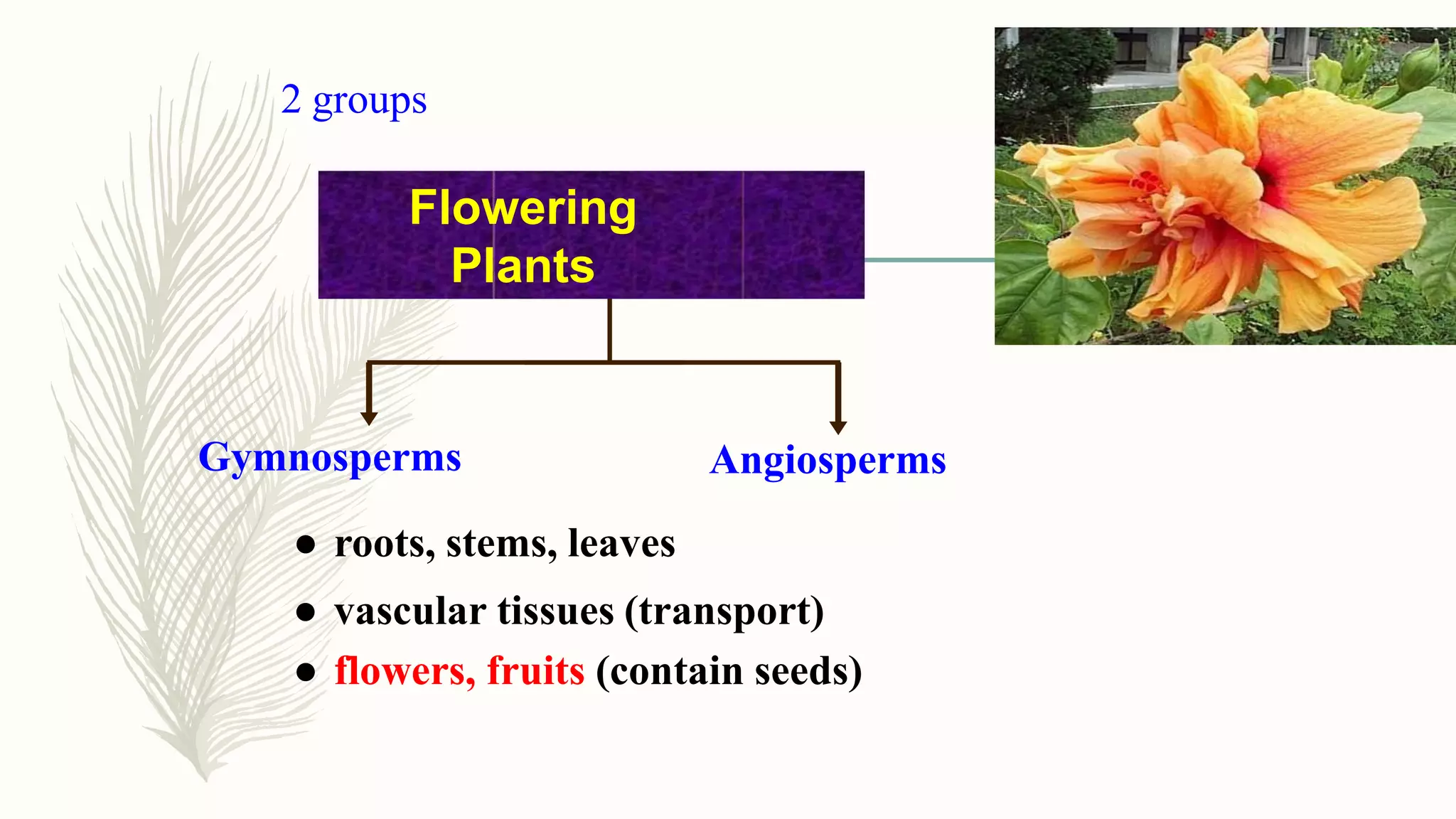
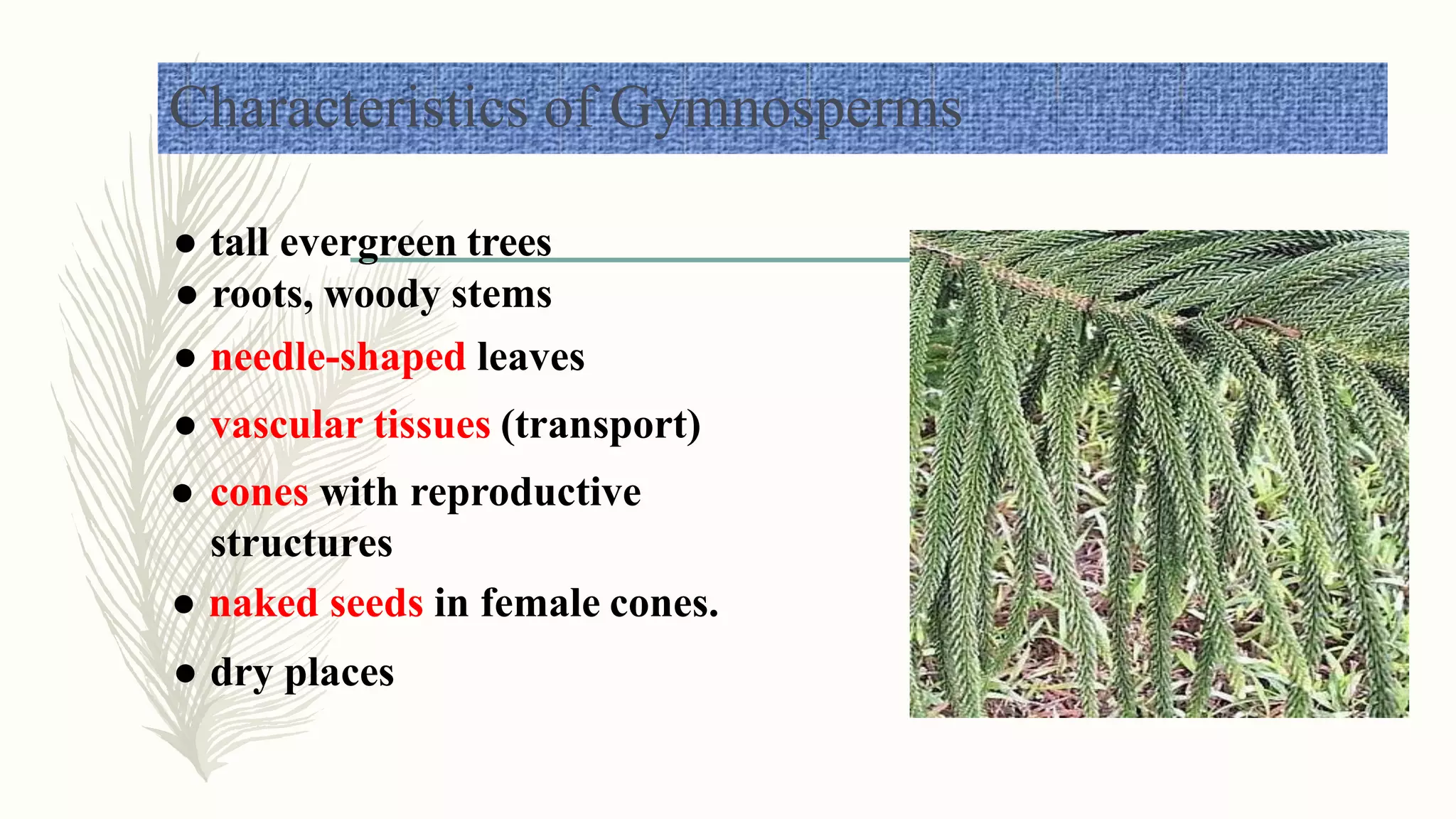
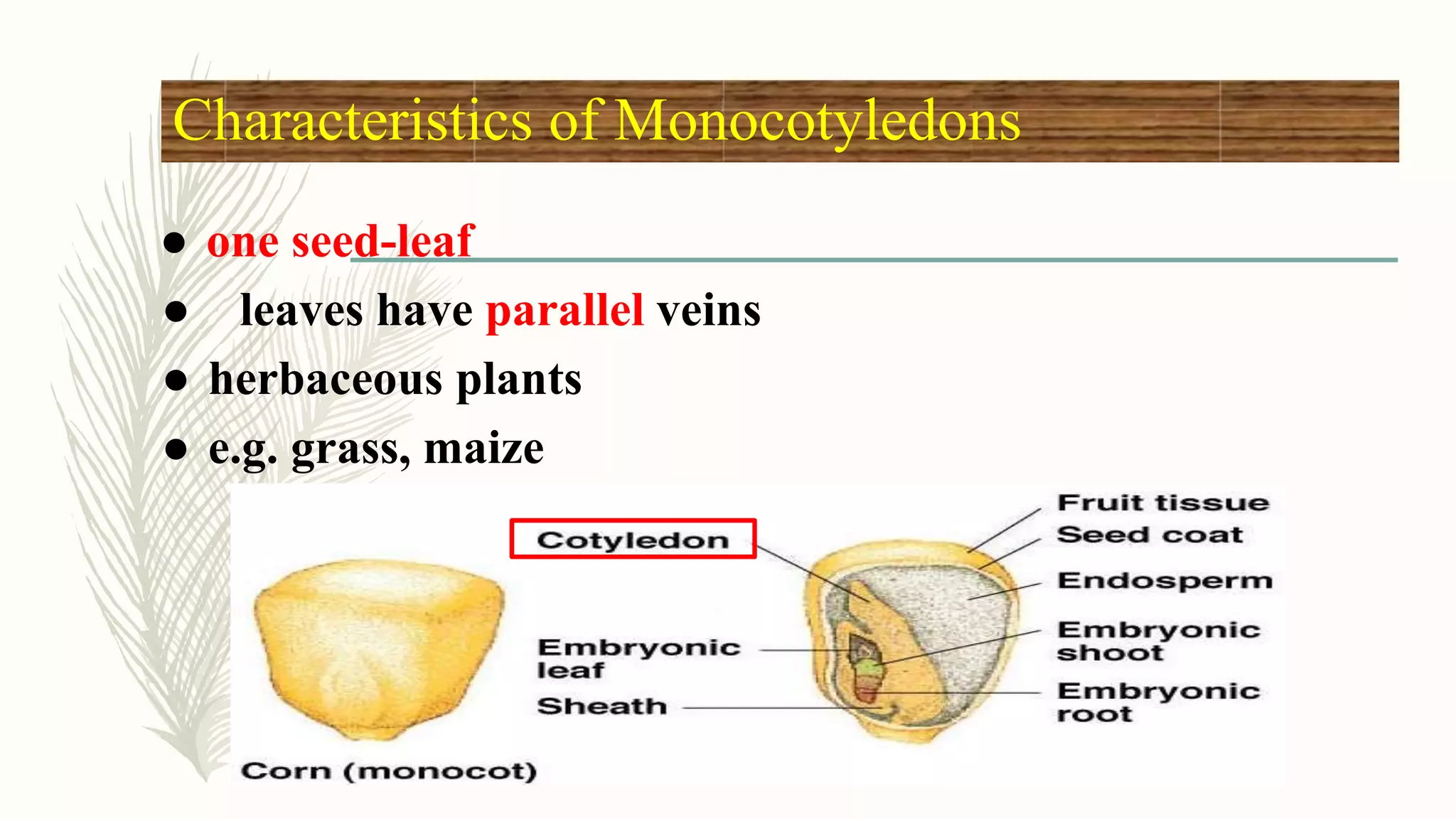
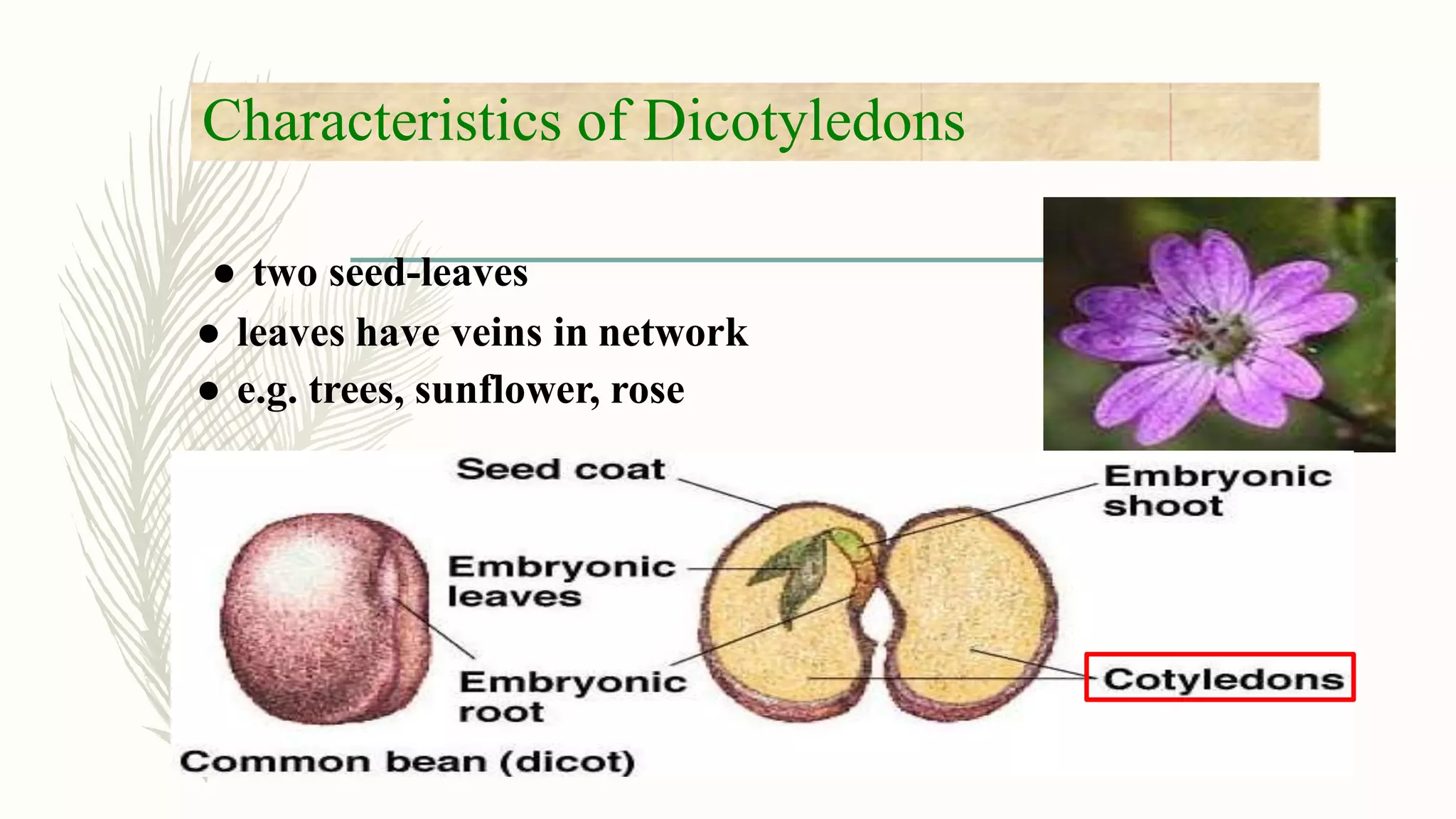
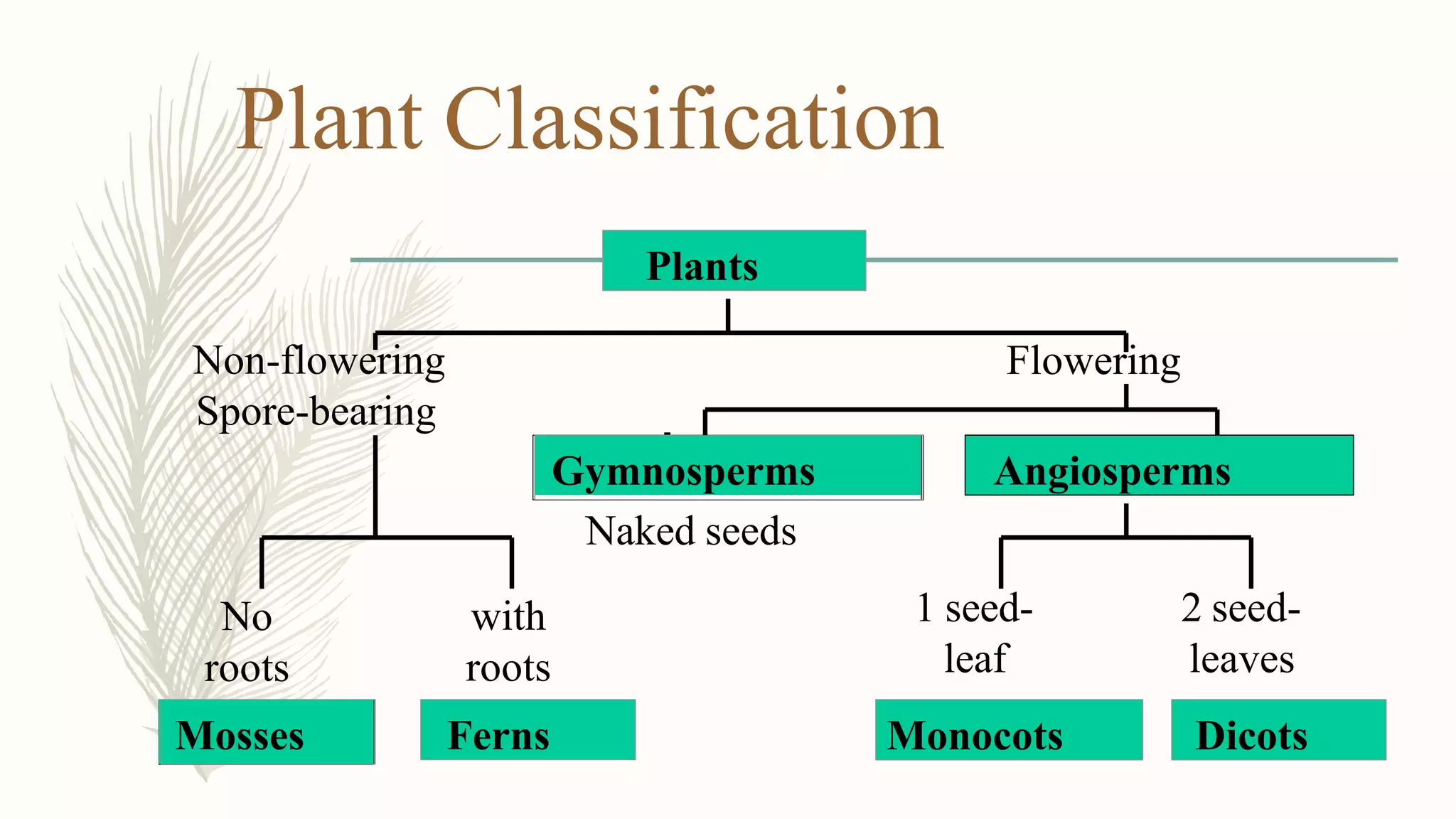
This document provides information about classifying plants based on their physical characteristics and morphology. It begins with objectives to describe plant characteristics and classify plants according to their structure. The activities involve listing plants, categorizing them, and presenting classifications. The document then details plant structures like stems, leaves, and reproductive organs. It describes classifying characteristics like leaf arrangement, shape, margins, and venation. Finally, it discusses classifying plants into groups like mosses, ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms based on these morphological features.