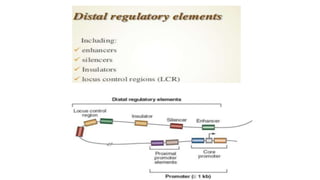
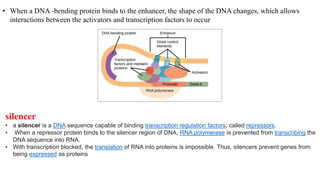
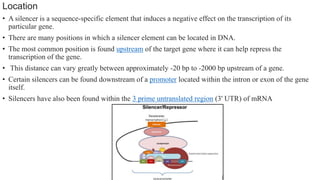
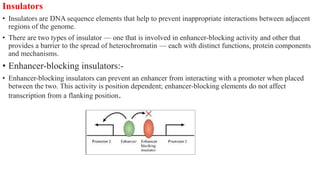
This document discusses cis-acting transcriptional regulatory elements essential for gene transcription by RNA polymerase II, detailing various components such as promoters, enhancers, silencers, insulators, and locus control regions. It explains their structures, functions, and mechanisms of action, emphasizing their roles in regulating gene expression through interactions with transcription factors and chromatin. Additionally, the document describes the positioning of these elements within the genome and their importance in both enhancing and repressing transcription.



![Locus Control Regions
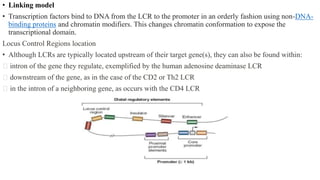
• Locus Control Regions it is bounded by transcription factors coactivators, repressors, and/or
chromatin modifiers. Each of the components differentially affects gene expression, and it is their
collective activity that functionally defines an LCR and confers proper spatial/temporal gene expression.
• A regulatory region first identified in the human beta globin locus but subsequently found in other loci.
The region is believed to regulate genetic transcription by opening remodeling chromatin structure. It
may also have enhancer activity by different mechanisms
• Looping model
• Transcription factors bind to hypersensitive site cores and cause the LCR to form a loop that can interact
with the promoter of the gene it regulates
• Tracking model
• Transcription factors bind to the LCR to form a complex. The complex moves along the DNA helix until
it can bind to the promoter of the gene it regulates. Once bound, the transcriptional apparatus increases
gene expression.
• Facilitated tracking model
• This hypothesis combines the looping and tracking models, suggesting that the transcription factors bind
to the LCR to form a loop, which then seeks and binds to the promoter of the gene it regulates.[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/upstreamcontrollableelements-210202160926/85/Up-stream-controllable-elements-12-320.jpg)