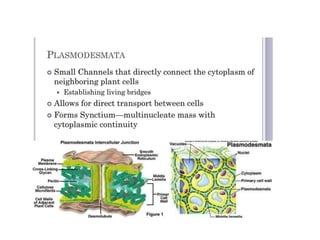
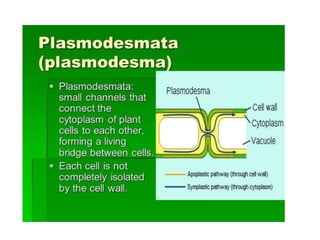
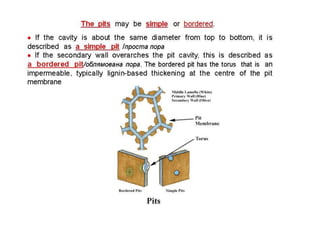
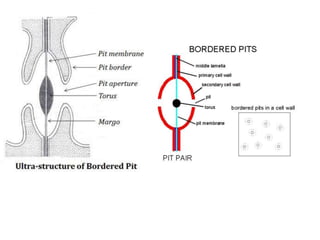
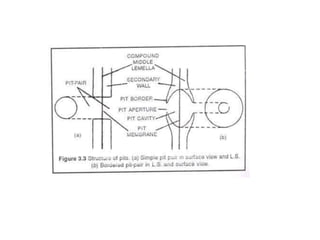
Plasmodesmata and pits allow communication between plant cells. Plasmodesmata connect adjacent cells and transport molecules, proteins, RNA and more to regulate processes. Pits are thinner areas of the cell wall that allow fluid and communication between neighboring cells. Pits have a pit chamber, aperture and membrane and come in variations like simple, bordered, half-bordered and blind pits. Both plasmodesmata and pits facilitate intercellular transport and communication in plants.