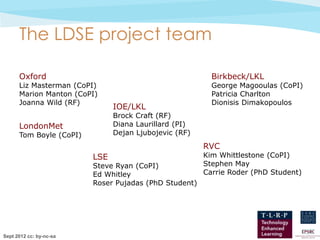
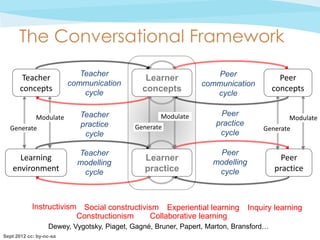
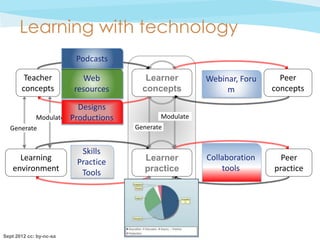
The document discusses the conceptualization of teaching as a 'design science' that fosters collaborative professional learning among educators, enabling them to share and improve teaching designs. It emphasizes the importance of computational support for learning design and proposes tools like the 'Learning Designer' and 'Pedagogical Patterns Collector' to help educators articulate and enhance their pedagogical practices. Furthermore, the document outlines a theoretical framework for analyzing teaching methods and their outcomes, aiming to streamline and optimize the teaching process.





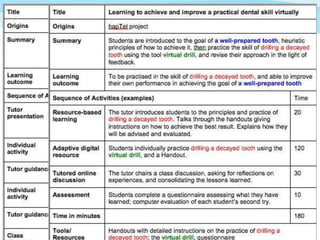


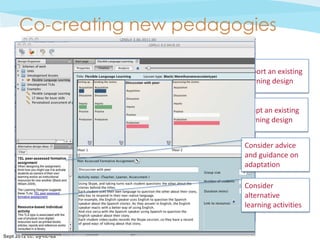
![Adopt/Adapt a teaching pattern
Export to
Read, Watch, Listen Word
Investigate Check the feedback
[Moodle]
Discuss
Add link to an Practice
on the overall
OER, e.g. a digital Share distribution of
tool for practice Produce learning activity
Represent the
teacher as Adjust the type of
present or not learning activity.
Edit the
Adopt – Adapt – Import resources - Test and re-design – Share what works
instructions.
Sept 2012 cc: by-nc-sa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cde-ride-dl-121024040558-phpapp02/85/Teaching-as-a-design-science-in-learning-and-technology-10-320.jpg)
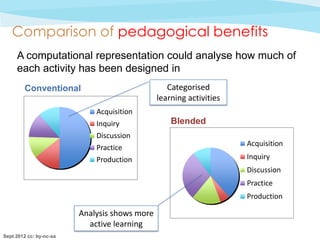
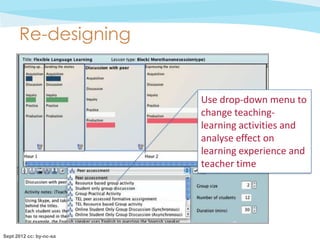
![Comments on the PPC
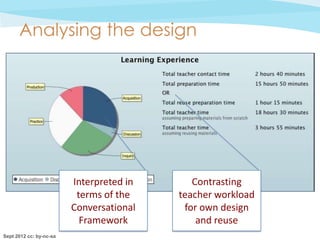
• [The pie-chart] is one of the most useful features … it
gives a good overview of the balance between different
learning experiences
• I rarely consider how the students' time is apportioned …
it's good to be made to think about this.
• Seeing how the sessions are shaping up in such a visual
medium …. would probably make me think more
carefully about providing a mix of activities
Sept 2012 cc: by-nc-sa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cde-ride-dl-121024040558-phpapp02/85/Teaching-as-a-design-science-in-learning-and-technology-11-320.jpg)

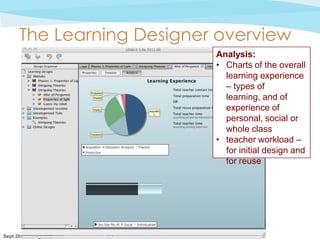




![What issues must the Learning
Designer also address?
• Complexity
“It’s very overwhelming … there’s a lot going on and to
• Potentially a not sure what all the terms mean. I mean I
think about. I’m tool of management control
don’t understand the difference between production and
• Interpretabilityaof analysis OKDesigner]Itturnssee a
“My only worry is that it [the Learning
practice. Let’s have look *…+ Yes – an–option. Yes I
an institutional requisite rather than
into
I get it. becomes
• Thedifference.tool,have pie charts, it'syoufocusI wouldwithit
the
measurement Probably we needusefulmore*...+ here tool
“I think it's cute to rather than a
a bit help
need for a topic-orientedorganisationaltool
explanations and examples. But once
neat
get into the
go
that allows some critical self reflectionmy time because I
on practice. I know
back problem withmy stuff, is that the pedagogy is neutral of
“My thedifficult” the tool reorganise once out there, can
and squidge
isn’t so goal is the latter, but software,
that know that it would be a good thing to have a mix of
would while the approach to teaching and learning
the topicso seductive to gather information for
become
all of these things (i.e. forms of learning). But that's with
requires a topic approach and this tool doesn’t help because
departments, policy makers, etc, and the information that is
I think it's a good thing. If I didn't believe that this was a
this approach”
produced is then you woulduseful for individual that was
good thing, probably ONLY show me a pie chart
teachers, not education ministers, etc” ok”
90% of one thing I would still think it's
Sept 2012 cc: by-nc-sa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cde-ride-dl-121024040558-phpapp02/85/Teaching-as-a-design-science-in-learning-and-technology-30-320.jpg)