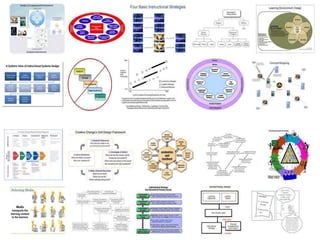
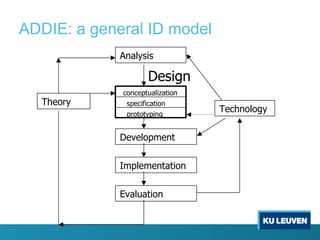
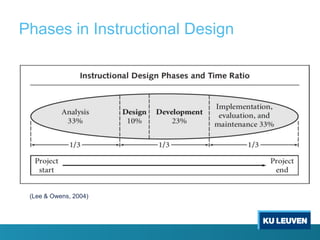
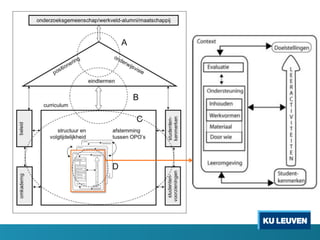
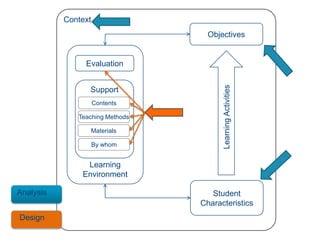
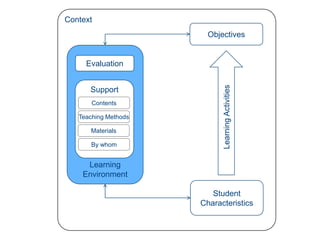
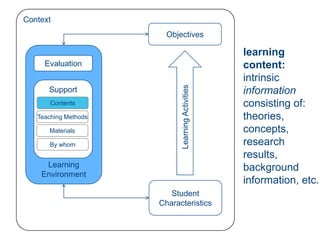
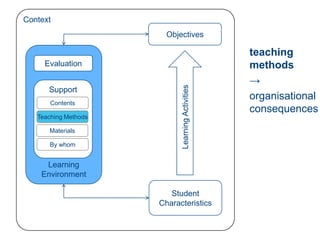
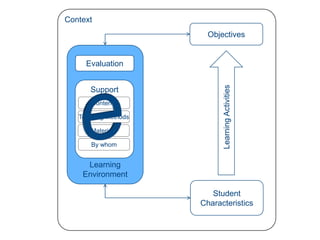
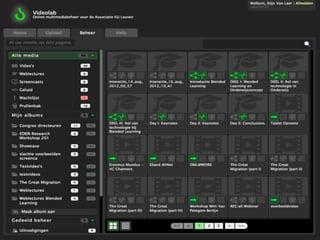
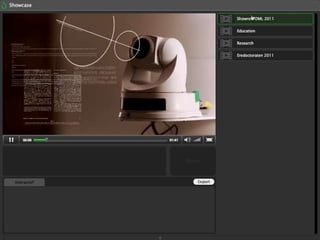
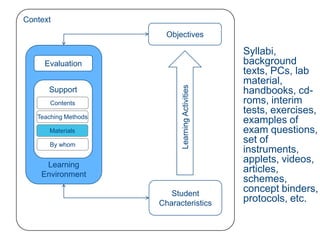
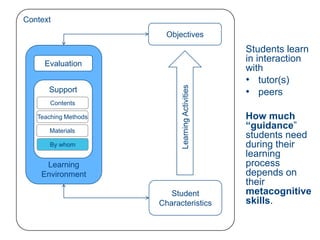
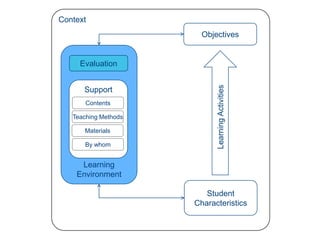
Instructional design is the process of improving instruction through analyzing learning needs and systematically designing and developing learning environments and materials. It involves analyzing the learning context and objectives, designing appropriate learning activities, content, teaching methods and materials based on student characteristics, and evaluating whether the objectives are achieved. Technology and multimedia are often used as tools to enhance instruction. Common instructional design models include ADDIE, which involves the phases of analysis, design, development, implementation and evaluation.