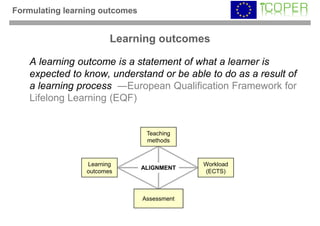
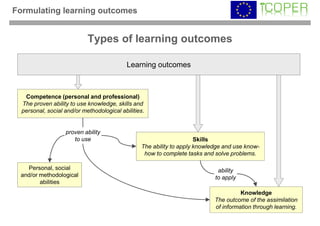
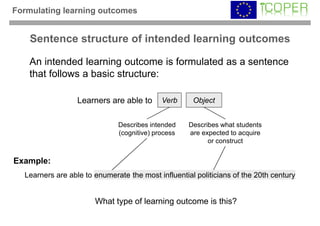
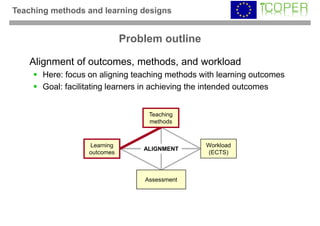
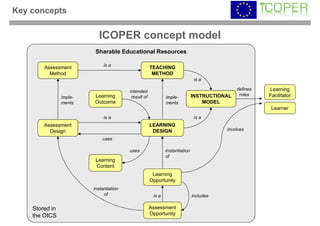
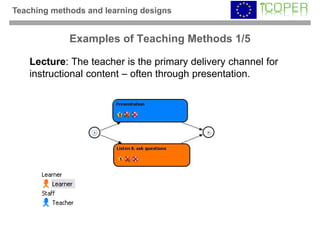
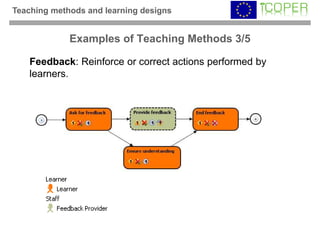
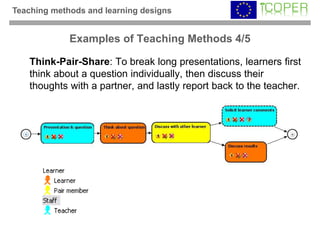
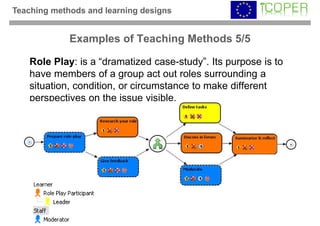
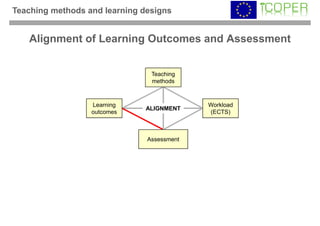
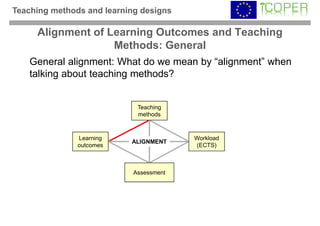
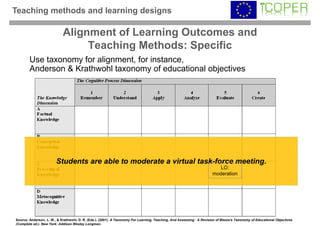
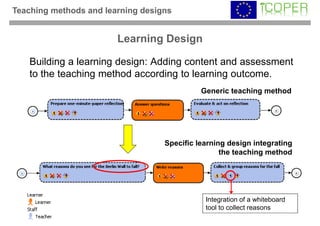
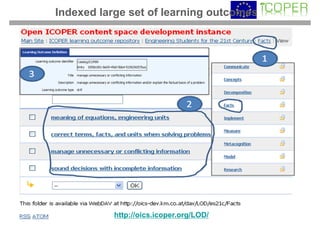
This webinar provided an overview of outcome-based learning opportunities. It discussed the background and motivation for outcome-based education, how to formulate learning outcomes, aligning teaching methods and assessments with learning outcomes, and standards for describing learning outcomes and opportunities. The webinar covered topics such as defining intended vs achieved learning outcomes, examples of learning outcome types, guidelines for writing learning outcomes, and aligning outcomes with instructional models and assessments. Upcoming webinars will discuss e-content for designing outcome-based learning, outcome-based assessment, and applications.