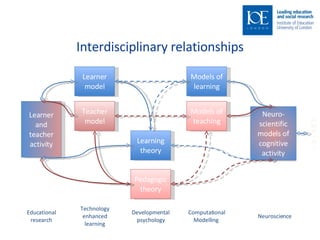
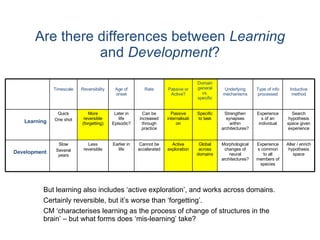
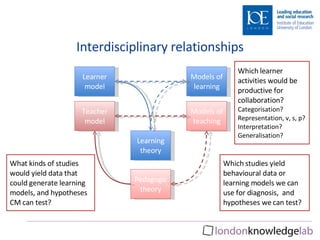
This document discusses computational modeling approaches to learning from an educational perspective. It touches on relationships between learning theory, pedagogical theory, developmental psychology, and models of learning and teaching. It also discusses differences between learning and development, and challenges in modeling mislearning. Notes from a special education classroom provide an example of using learner and teacher modeling to understand a student's challenges with counting and tailor instruction.