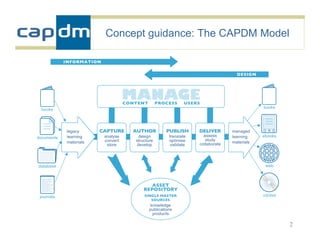
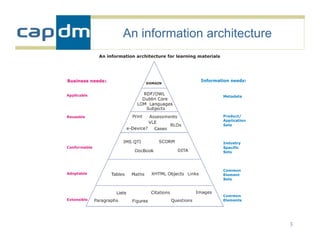
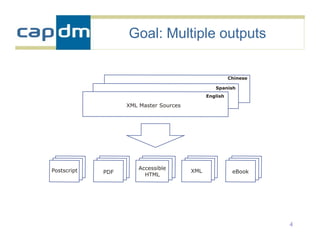
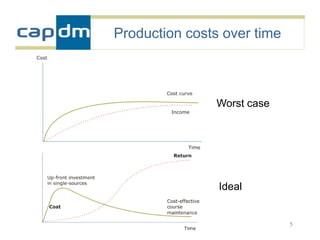
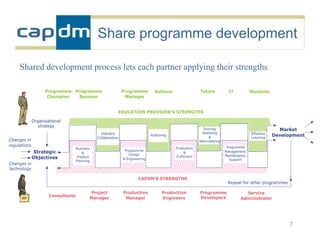
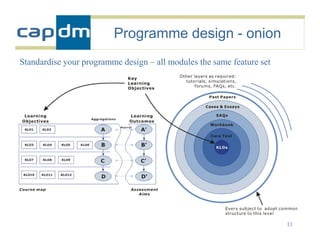
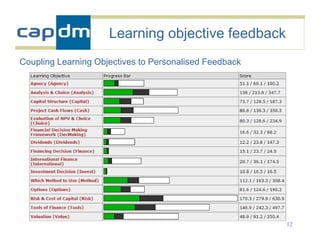
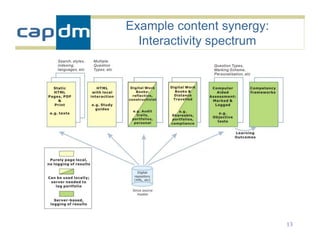
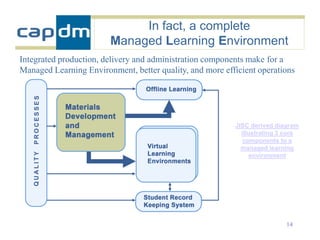
The document discusses the CAPDM model for developing learning materials. It recommends investing in standards to ensure long-term usability and reusability. Developing materials through a single source publisher can reduce costs by 40-60%. Working with an experienced partner can help share best practices. The document also discusses flexible learning approaches, components of online courses, integrating learning objectives with feedback, and how a managed learning environment can improve quality and efficiency.