Subsidiary books are books of original entry where transactions are first recorded. They include purchase books, sales books, cash books, and return books. Subsidiary books allow for division of labor and increased efficiency. However, they require some accounting knowledge and can be expensive for small businesses.
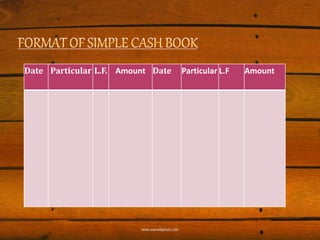
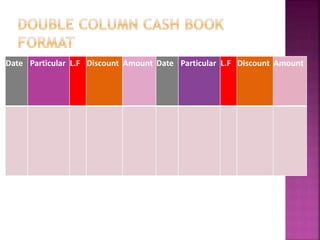
The main types of subsidiary books are discussed, including cash books, purchase books, and sales books. Cash books record all cash transactions and come in simple, double-column, and triple-column formats. Double-column cash books include a discount column while triple-column cash books also include a bank column. Petty cash books are used to record small expenses.