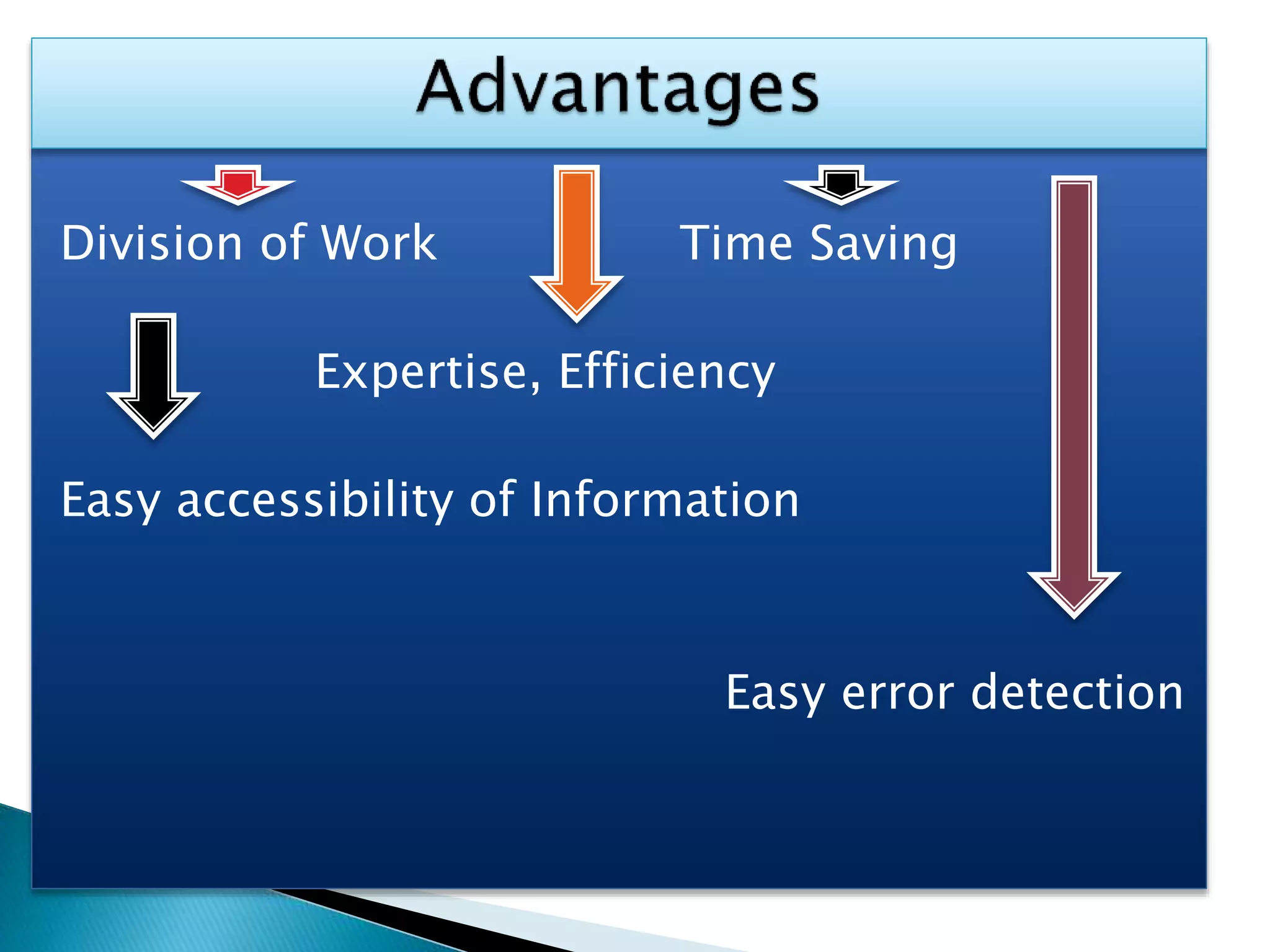
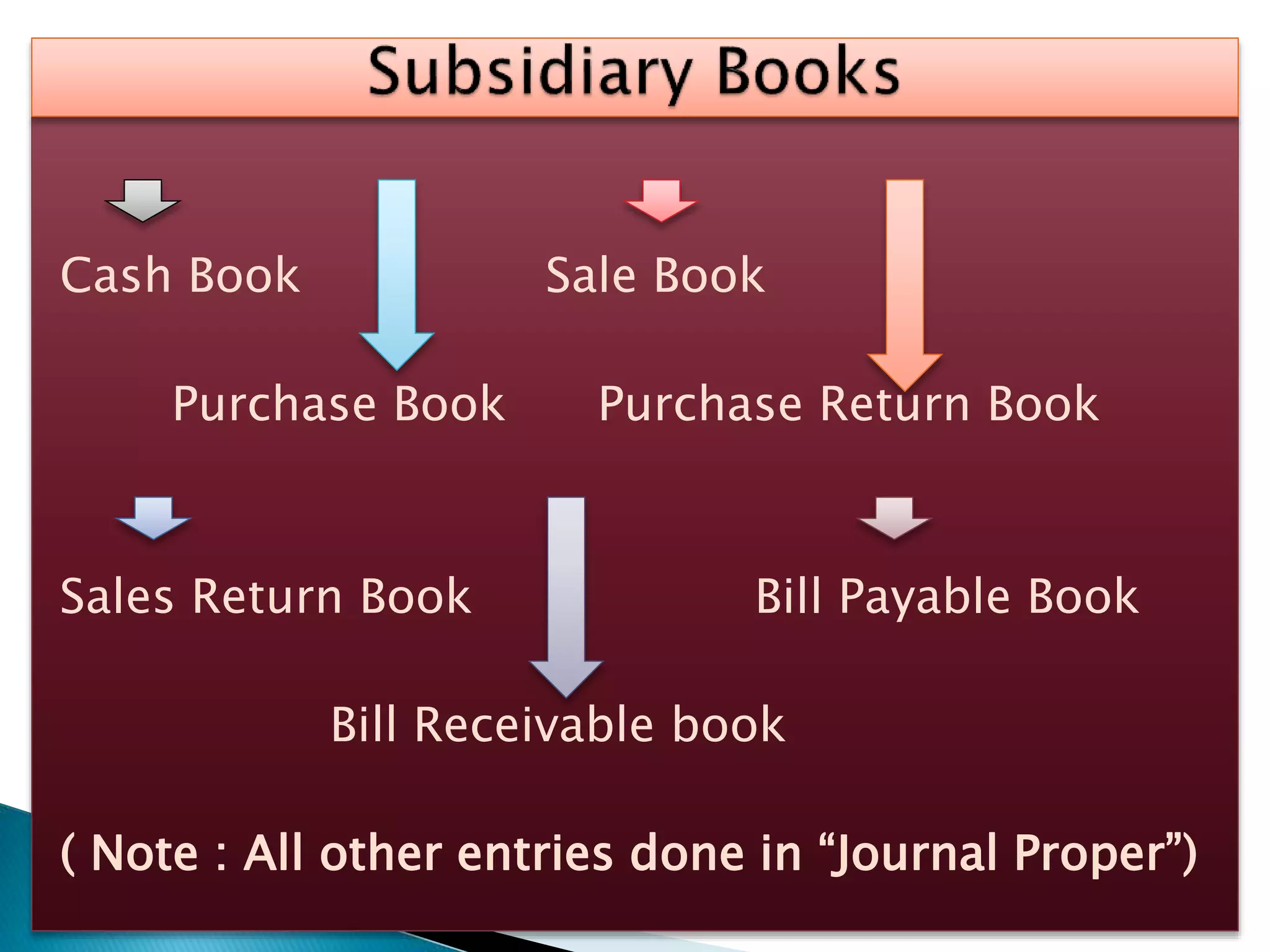
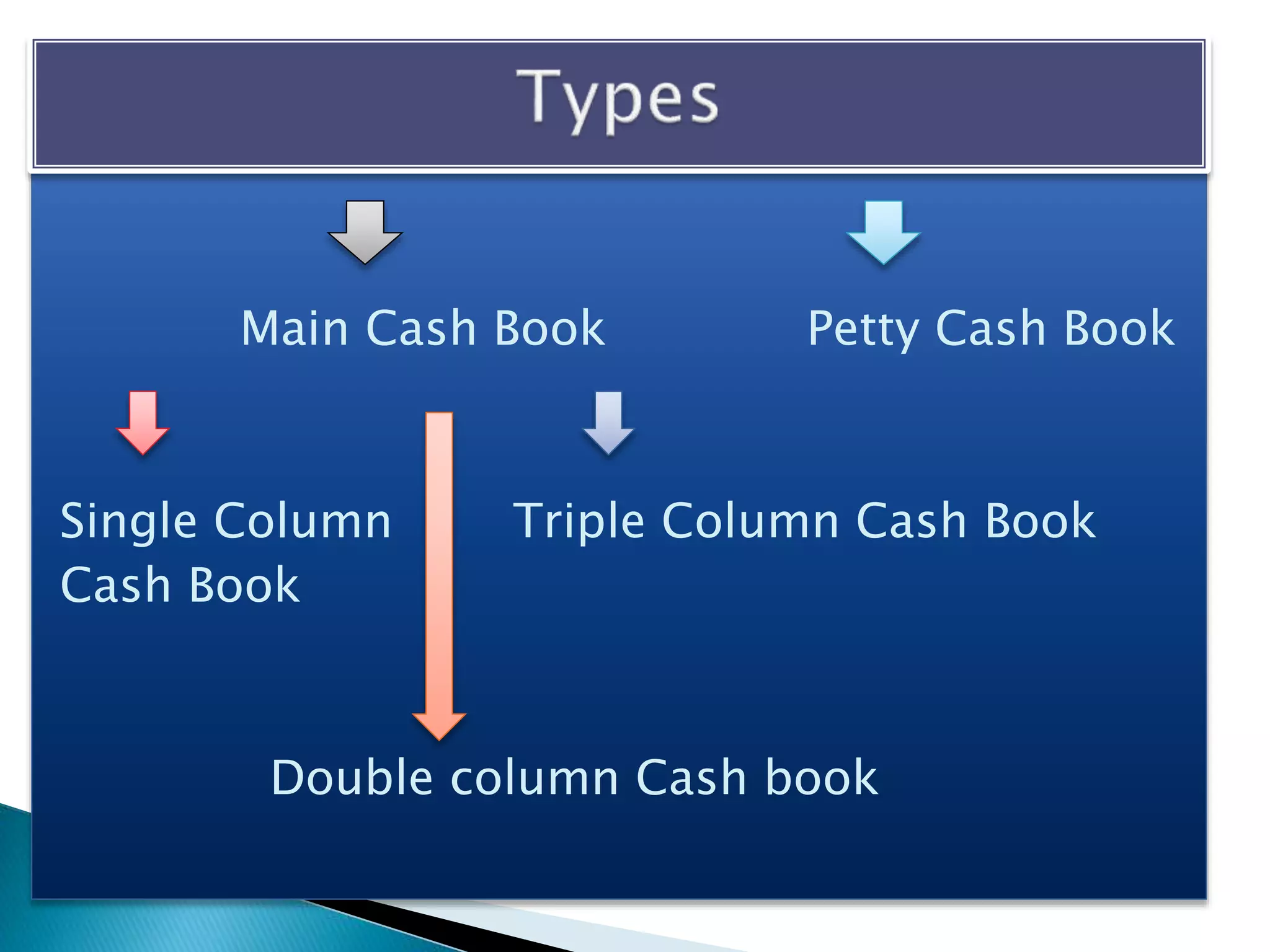
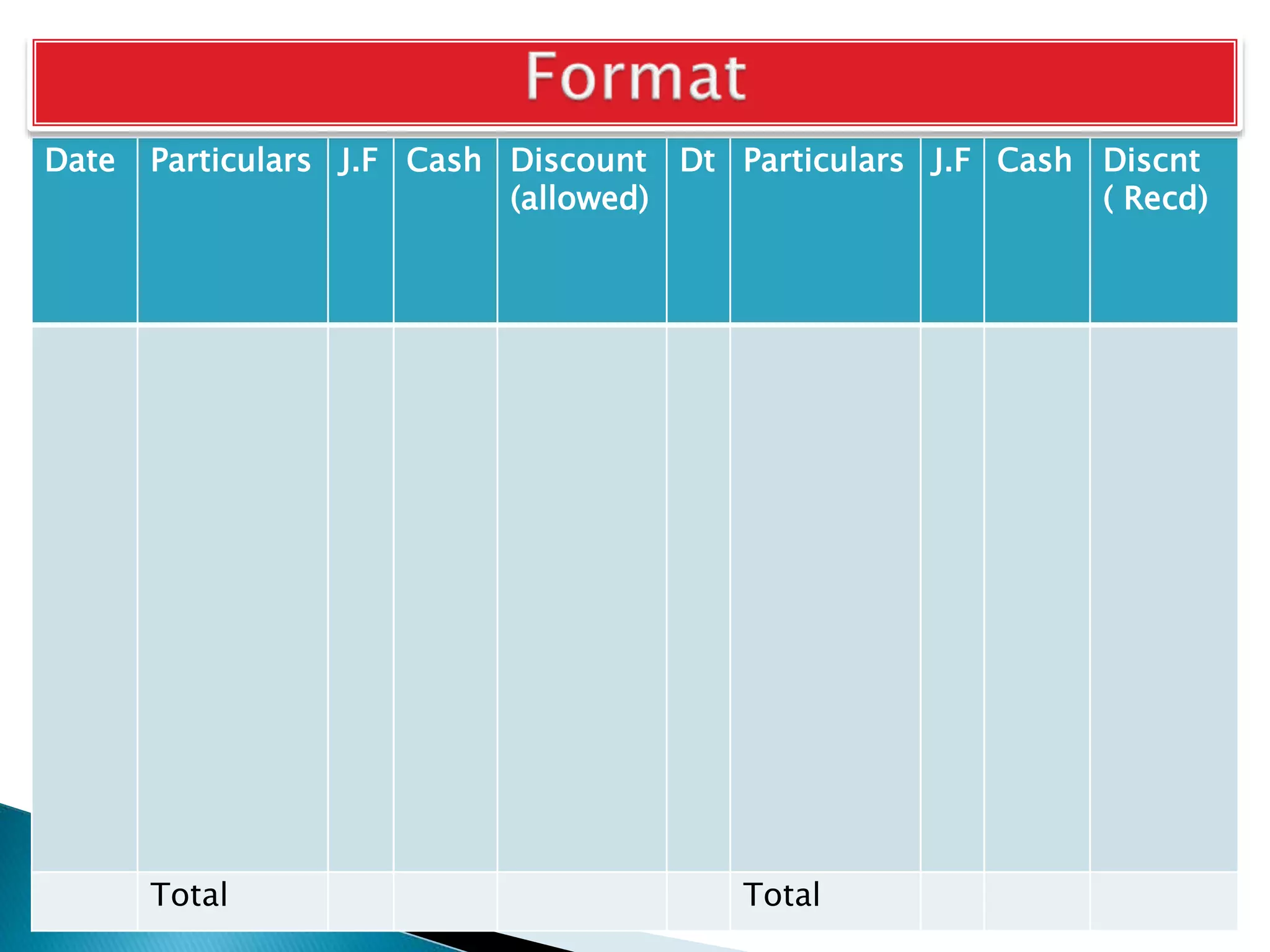
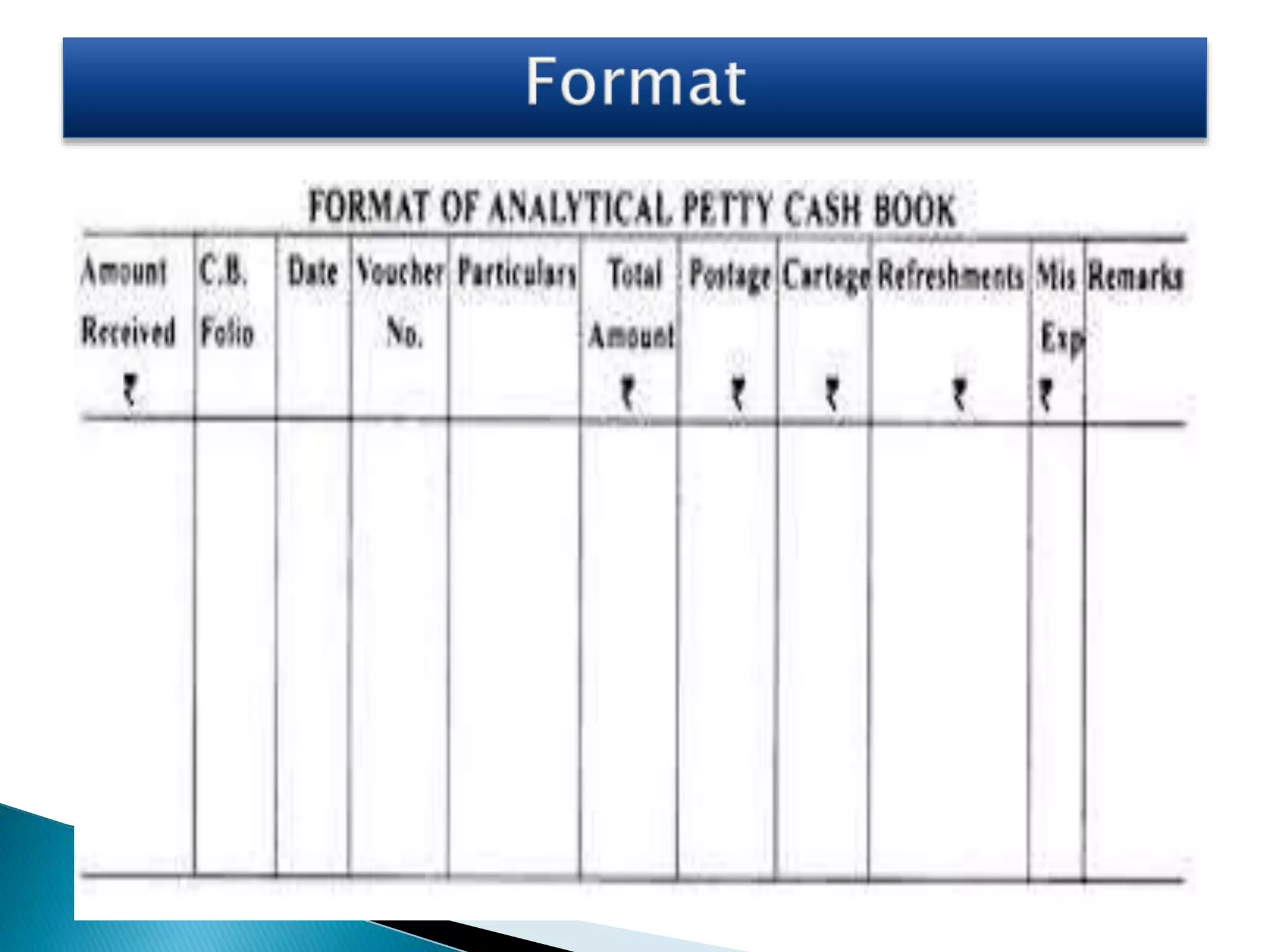
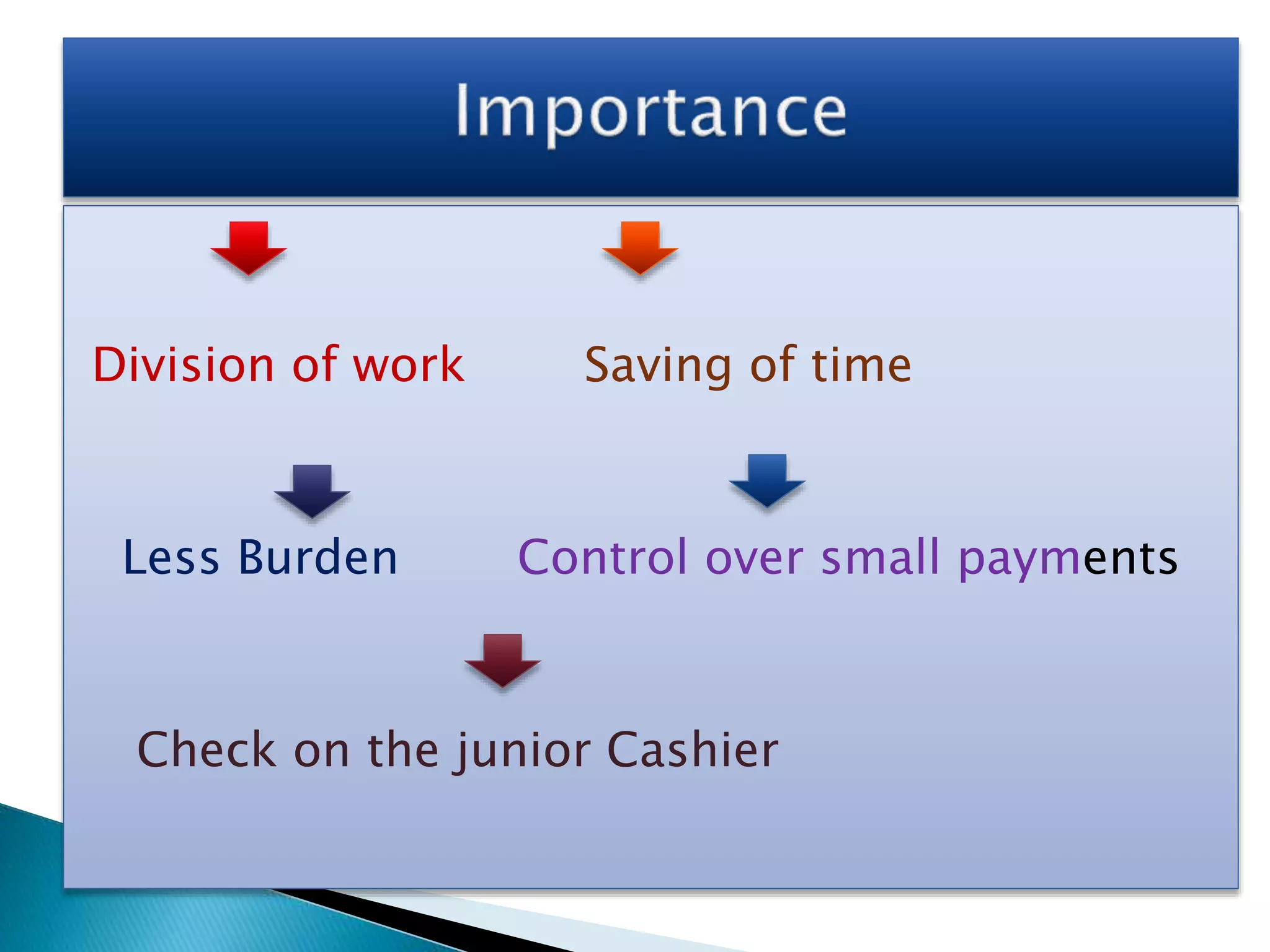
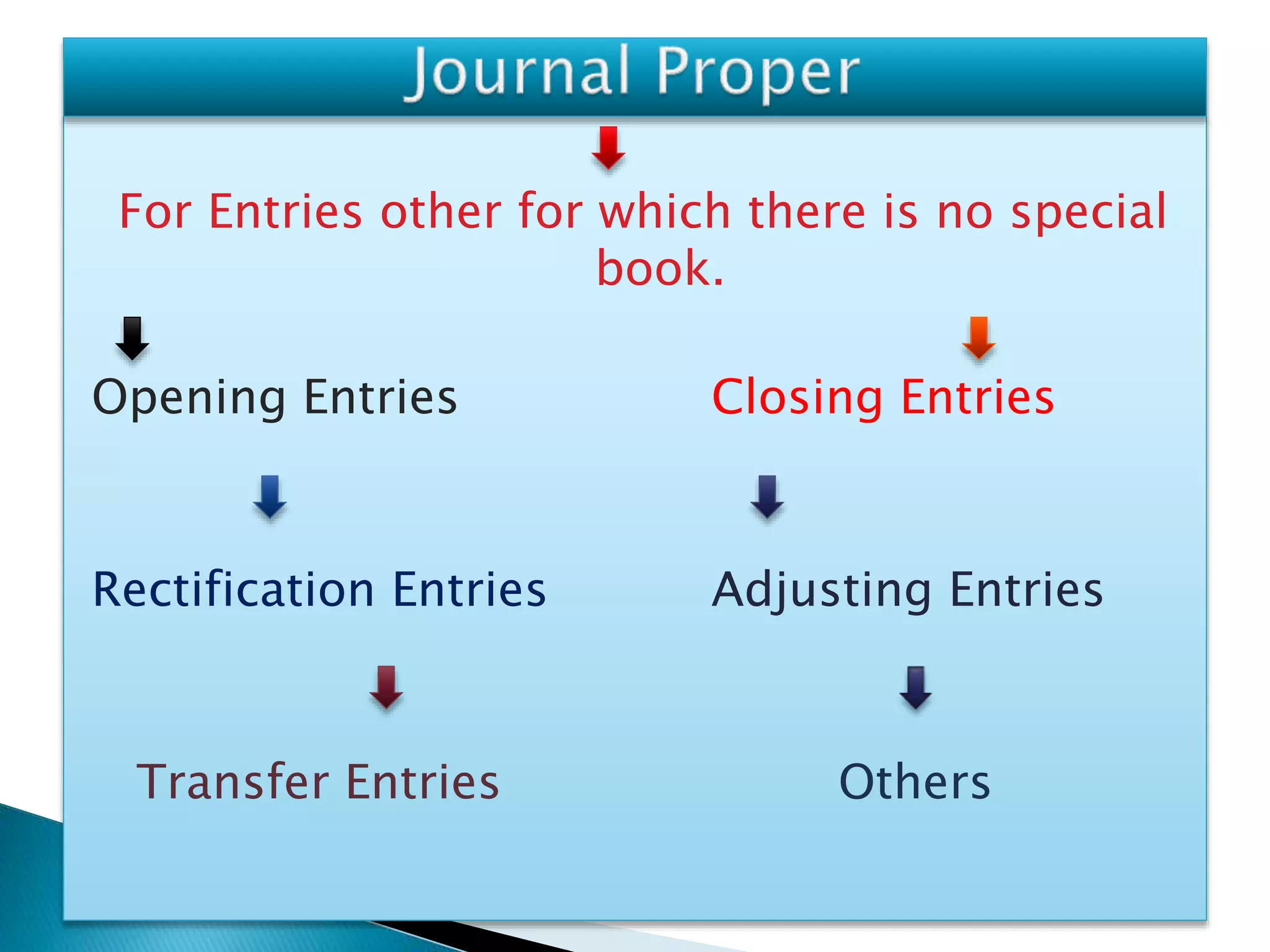
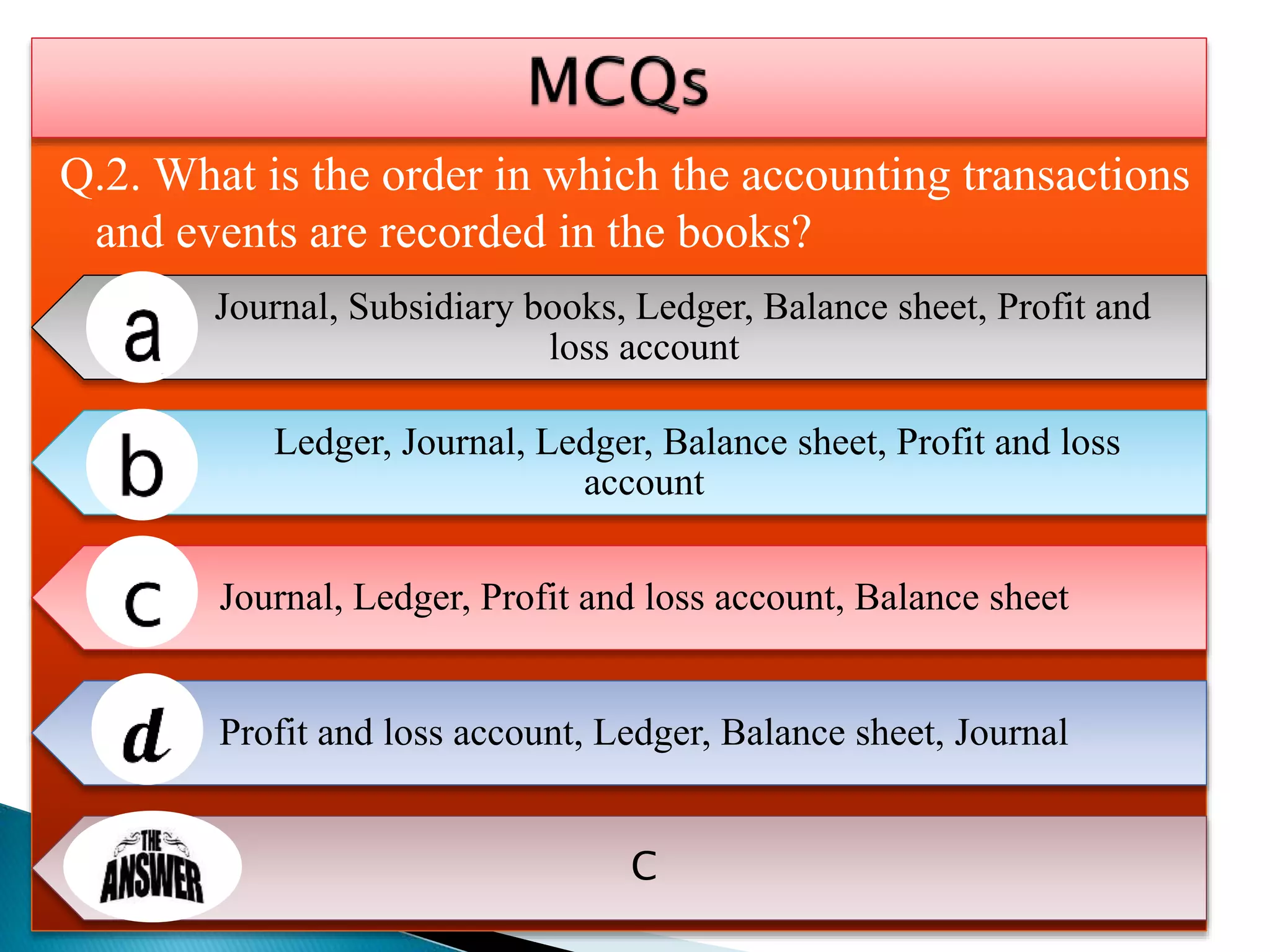
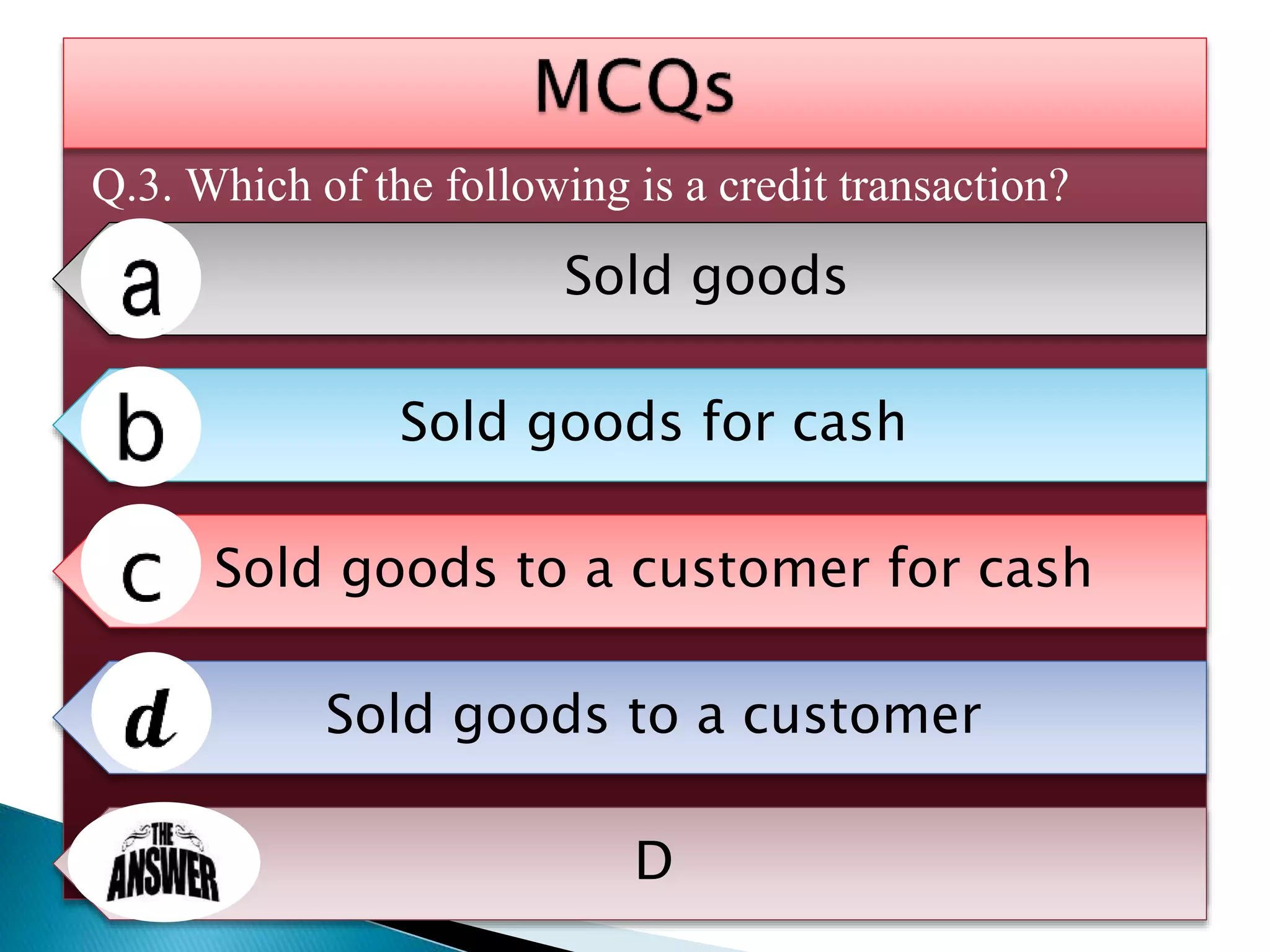
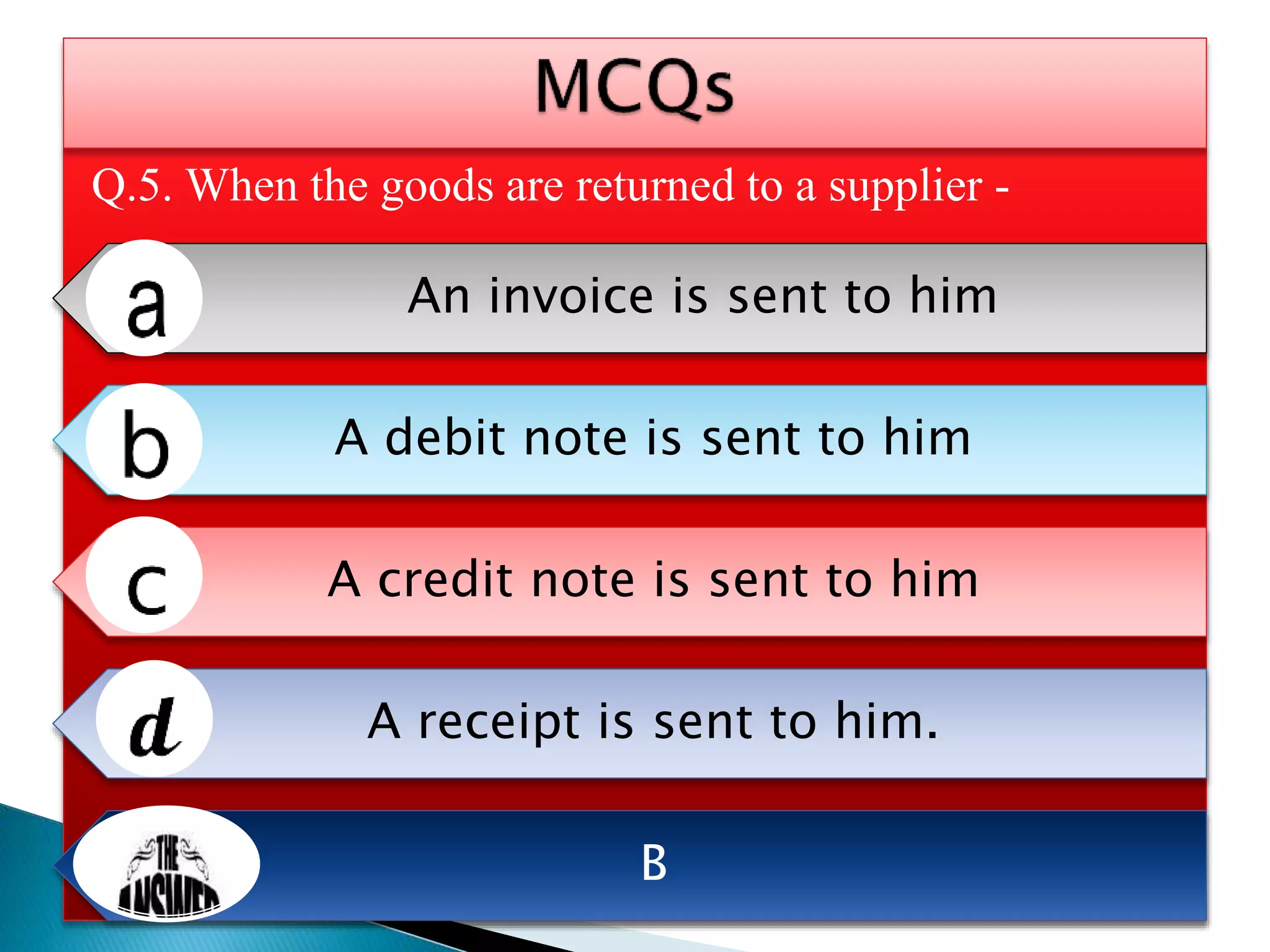
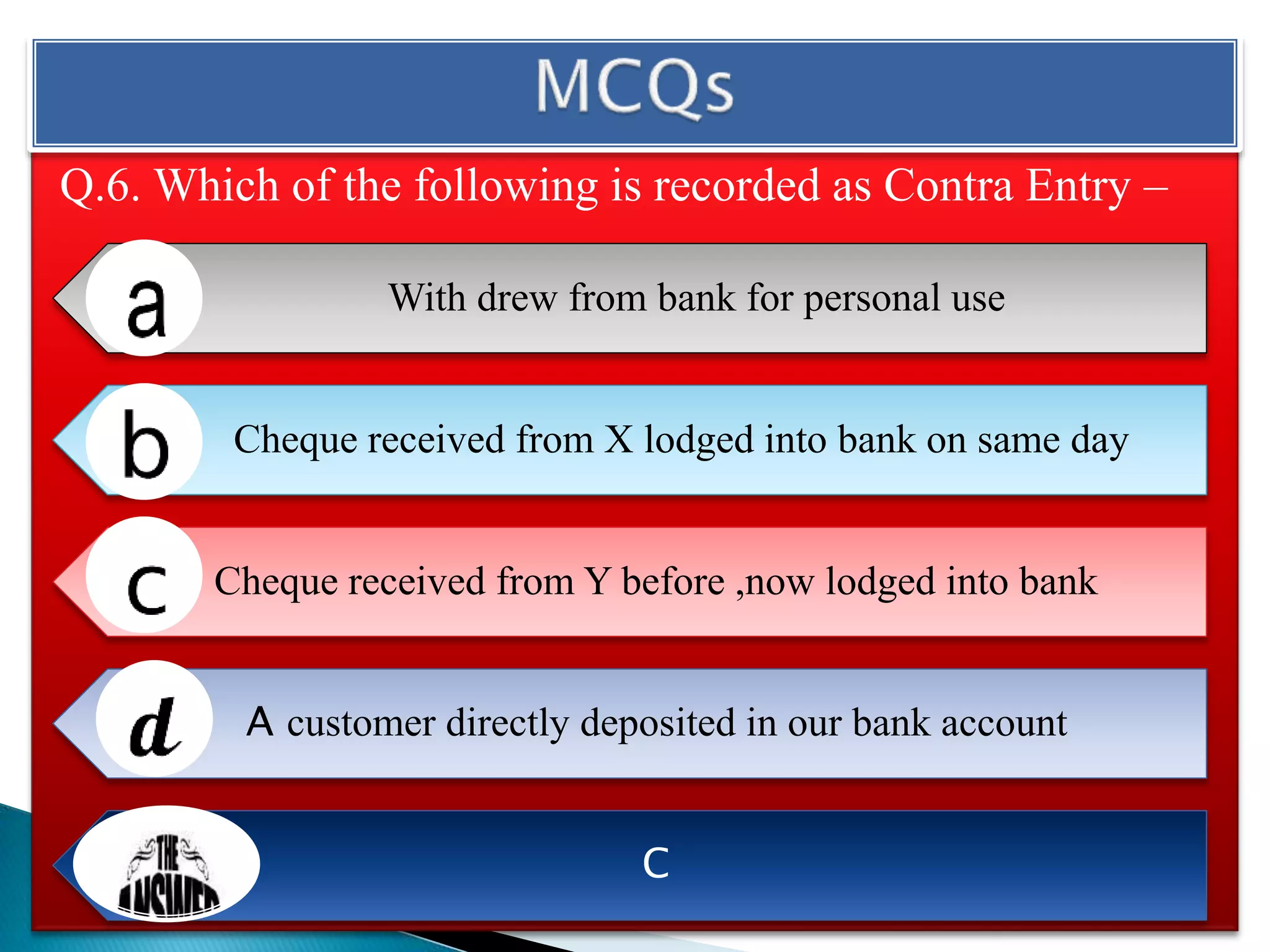
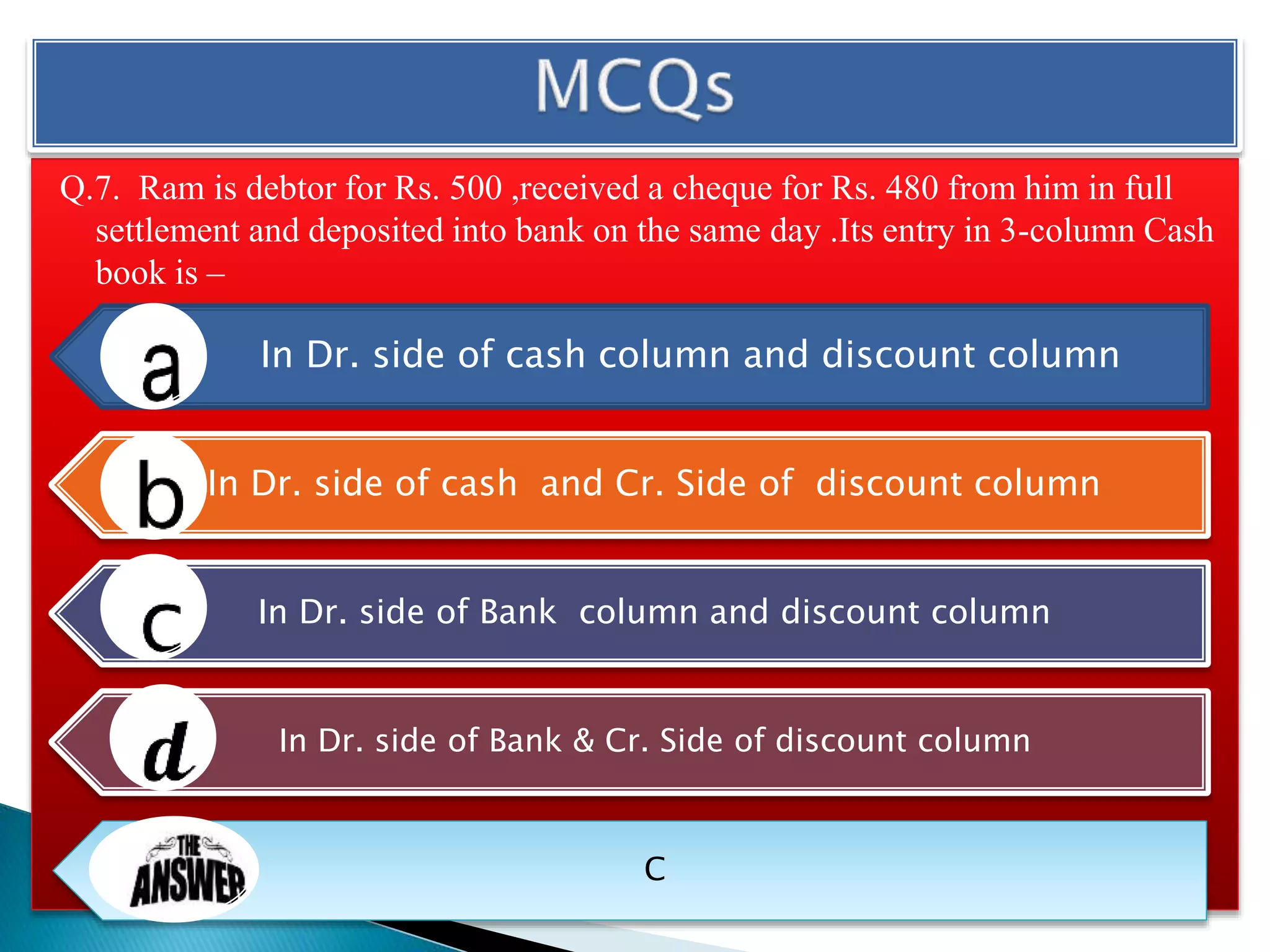
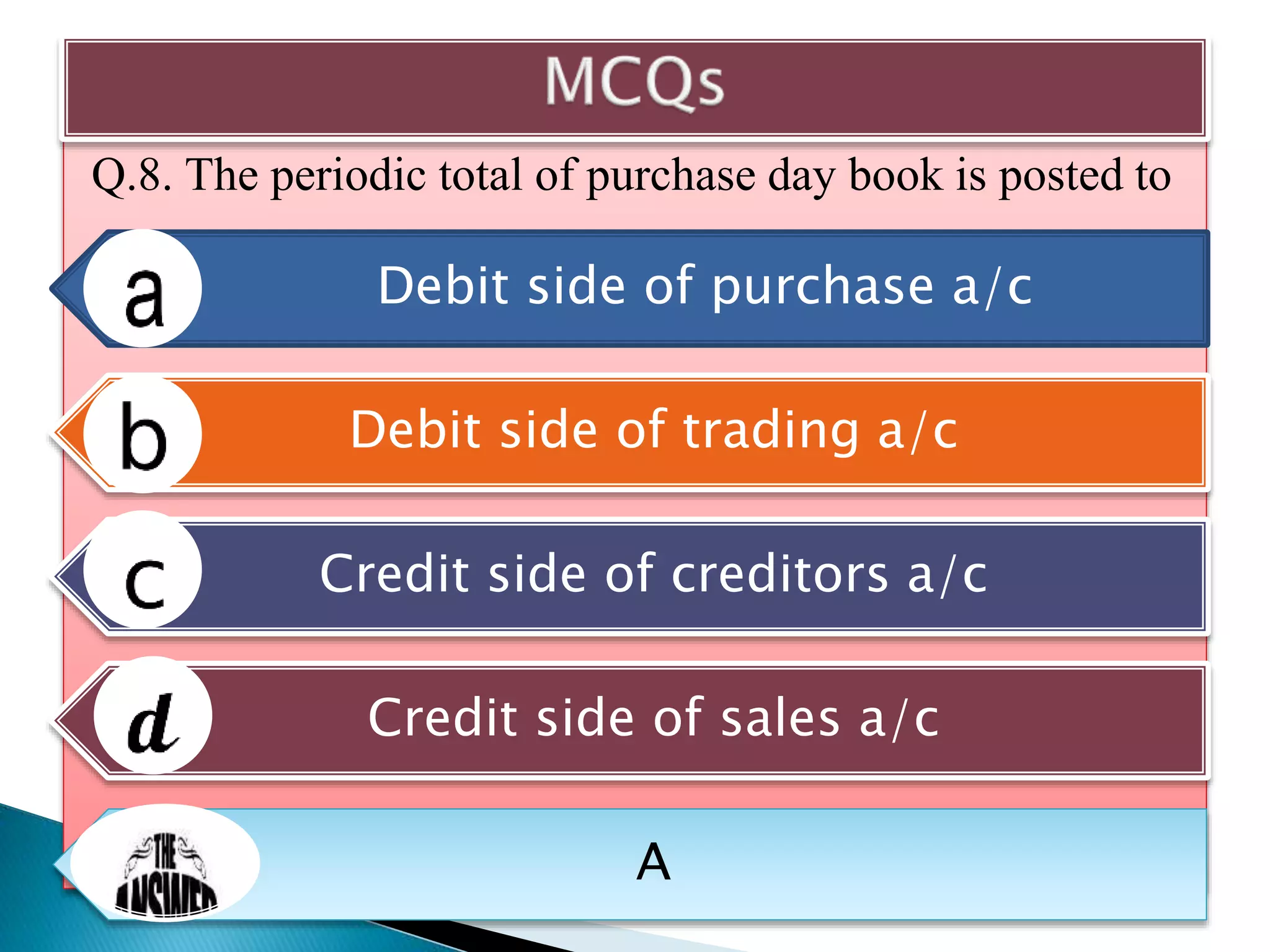
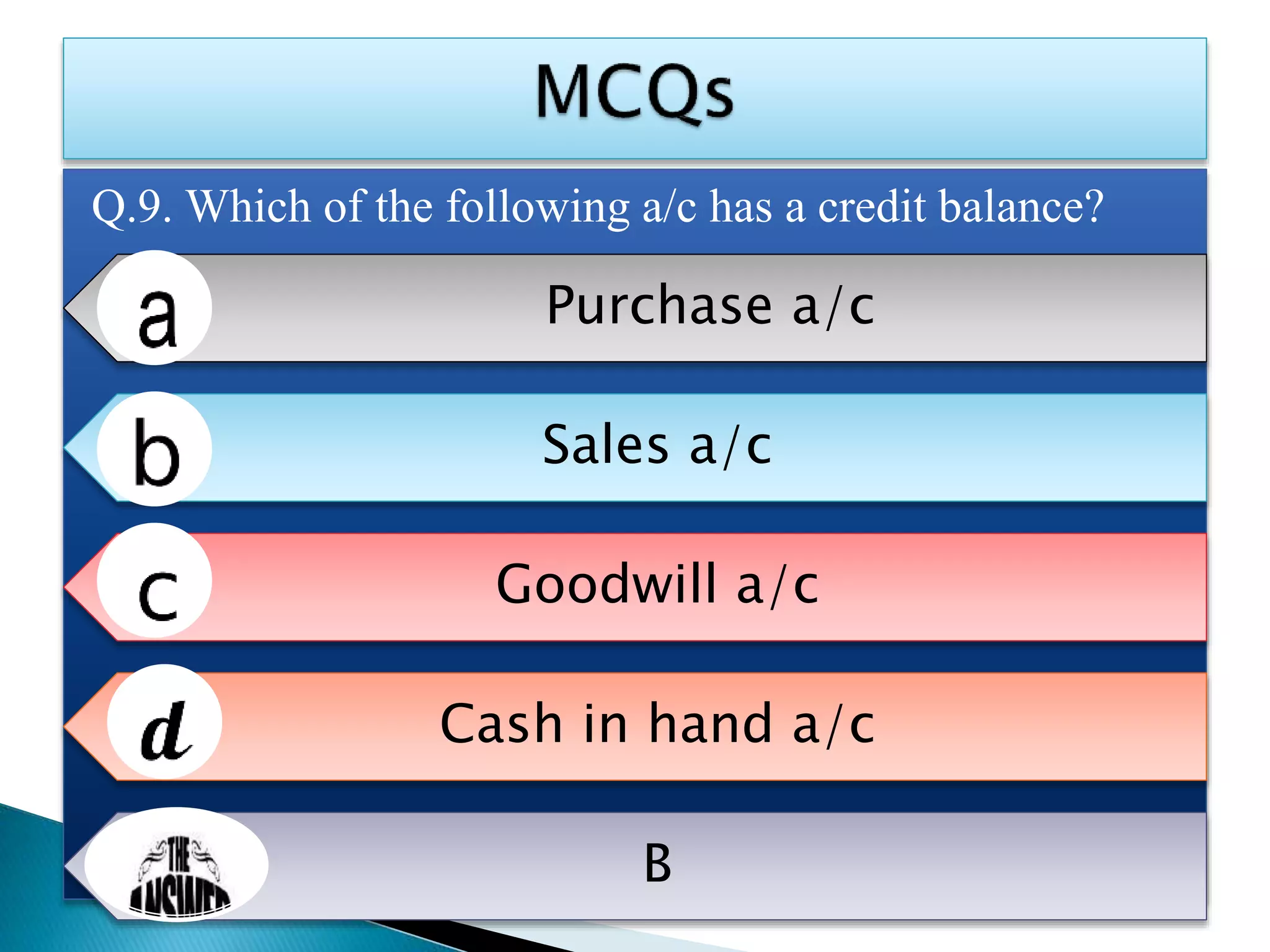
The document explains the importance of subsidiary books in accounting, detailing various types such as cash books, sales books, and purchases books, which support the main journal by recording specific transactions efficiently. It elaborates on the structure and functioning of these books, including the cash book's role as both a subsidiary and principal book, and emphasizes the recording of credit transactions and the corresponding adjustments for discounts and taxes. Additionally, it highlights the significance of structured documentation like debit and credit notes for returned goods and the posting of totals to respective ledger accounts.