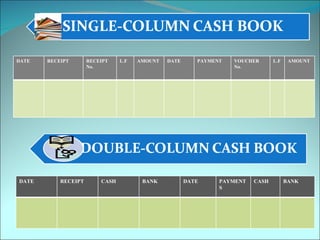
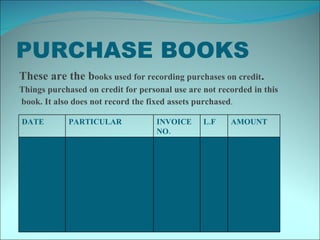
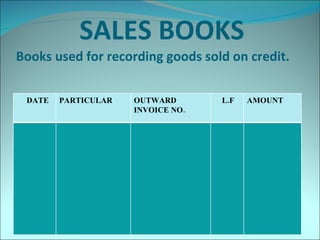
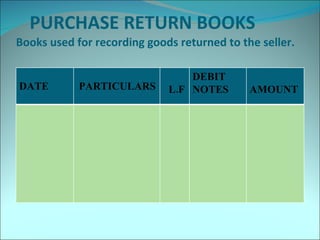
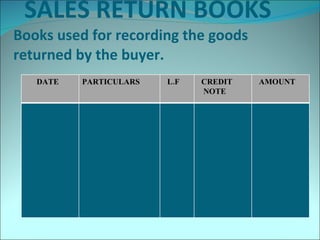
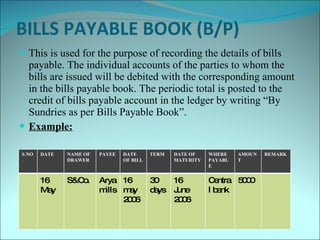
This document discusses subsidiary books, which are specialized journals used to record specific transaction types. It provides examples of common subsidiary books like cash books, purchase books, sales books, bills receivable books, bills payable books, and petty cash books. Subsidiary books are needed to avoid repetition, provide prompt information, facilitate internal checks, and classify transactions.