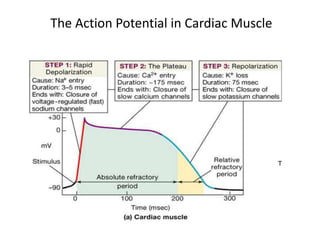
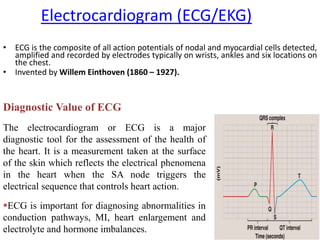
The document discusses the cardiac action potential phases, including depolarization, plateau, and repolarization, detailing the roles of ion channels in these processes. It explains the conduction system of the heart, focusing on the SA node and AV node functions, and the significance of Purkinje fibers in coordinating ventricular contraction. Additionally, it outlines the diagnostic importance of electrocardiograms (ECG), including the representation of heart activity through different waves and intervals.