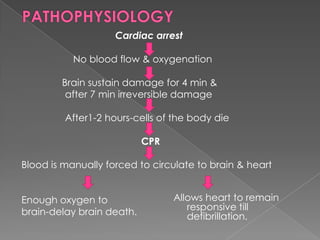
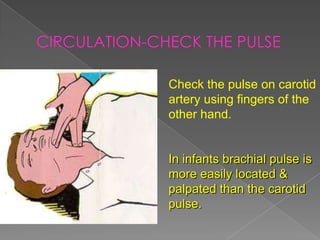
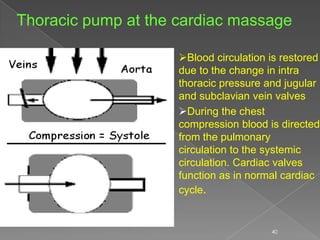
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating effectively due to failure of electrical signaling or pumping function, preventing blood from circulating to vital organs, and CPR involves chest compressions and rescue breaths to manually circulate blood to the brain and heart until spontaneous circulation can be restored through defibrillation or other medical treatment. The document provides details on causes, diagnosis, treatment including the steps of CPR, and outcomes of cardiac arrest.