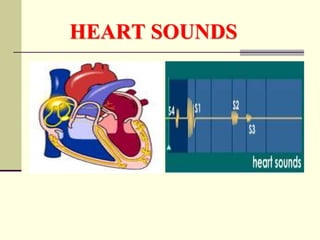
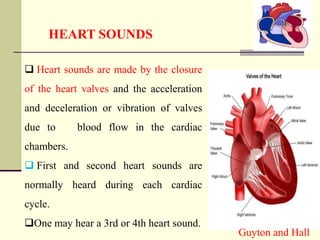
The document discusses heart sounds, including the four main types: S1, S2, S3, and S4. S1 and S2 are normally heard with each heartbeat while S3 and S4 may sometimes be heard. S1 occurs with the closure of the atrioventricular valves at the beginning of systole. S2 occurs with the closure of the semilunar valves at the end of systole. S3 occurs during early ventricular filling and S4 occurs during atrial contraction just before S1 of the next cycle. The sounds are associated with different parts of the cardiac cycle and changes in sounds can provide information about cardiac function and health issues.


![FIRST HEART SOUND (S1)
First heart sound is produced due to the closure of Atrio-
ventricular valves (Tricuspid and Mitral).
It occurs at the beginning of the systole
Sounds like LUB
Frequency: 25-45 CPS (cycles per second) or Hz.
Soft when the heart rate is slow because ventricles are well
filled with blood and the leaflets of the A-V valves float
together before systole begins.
Time: 0.14 sec [Guyton]; 0.15 Sec [Ganongs] Guyton and Hall
Ganongs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lzjes28hrksoclzdlgut-signature-59098a277156ec972f508d54d748a71581a711c784cd5778306fffd246e41dfc-poli-200409031303/85/Heart-sounds-5-320.jpg)
![SECOND HEART SOUND (S2)
This sound is produced by the vibration associated with the
closure of the semilunar valves (aortic and pulmonary) at the
end of ventricular systole.
ECG relationship: The second heart sound occur soon
after the T-wave of ECG.
Duration: 0. 11 sec [Guyton]; 0.12 [Ganong].
Frequency: 50 Hz or CPS.
This sound is sharp and loud and described as “DUB.”
Two sub components
Pulmonary component heard at the level of 2nd left
intercostal space.
Aortic component is heard at the level of the 2nd right
interscostal space near the right border of the sternum.
Guyton and Hall; Ganong](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lzjes28hrksoclzdlgut-signature-59098a277156ec972f508d54d748a71581a711c784cd5778306fffd246e41dfc-poli-200409031303/85/Heart-sounds-6-320.jpg)


![FOURTH HEART SOUND (S4)
OR ATRIAL SOUND
Occurs at the last one third of Diastole [Just before S1]
Produced due to Atrial contraction which causes rapid flow of
blood from Atria to Ventricle and vibration in the blood.
Frequency: 20 cycles / sec or less [Htz]
Third and Fourth heart sound are low pitched sounds therefore
not easily audible normally with stethoscope
S3 may be heard in children and young adults](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lzjes28hrksoclzdlgut-signature-59098a277156ec972f508d54d748a71581a711c784cd5778306fffd246e41dfc-poli-200409031303/85/Heart-sounds-9-320.jpg)




