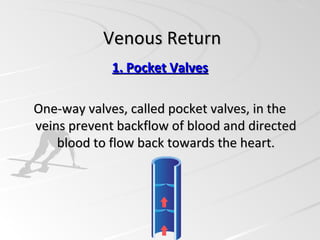
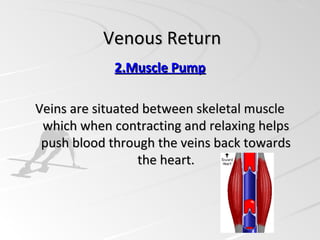
Venous return is the volume of blood flowing back to the heart through the veins. Blood from the systemic veins flows into the right atrium, where the pressure is called central venous pressure. Venous return is regulated by the balance between the heart's ability to pump blood out of the right atrium and ventricle into the lungs, and the tendency of blood to flow from the peripheral veins into the right atrium. There are five main factors that enable blood to flow back to the heart: one-way valves in the veins, muscle pumps that push blood during contraction, the respiratory pump during exercise, sympathetic activation of veins, and gravity draining blood from the upper body.