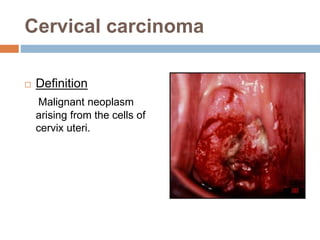
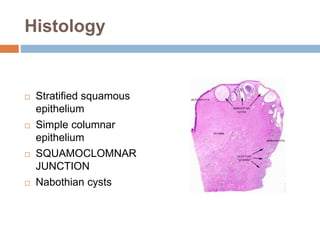
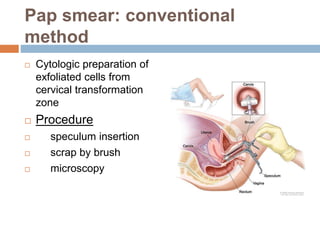
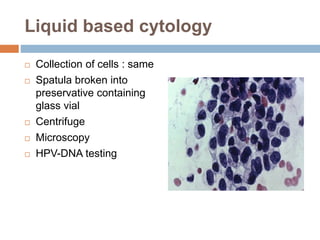
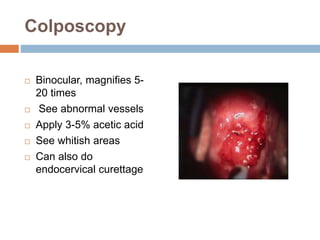
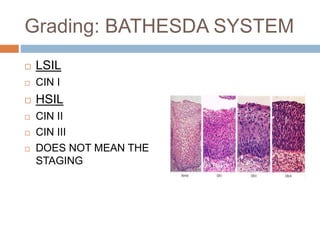
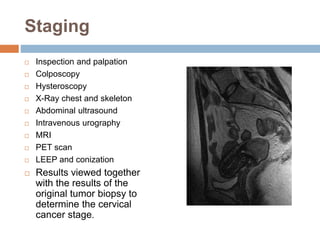
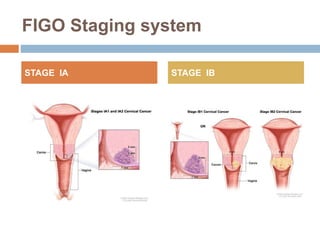
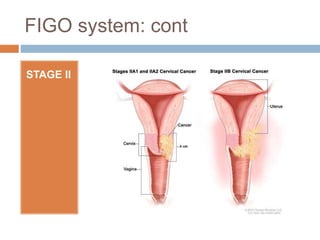
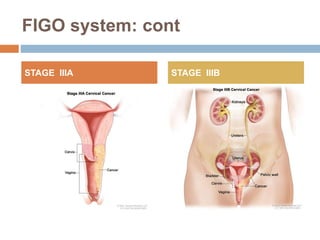
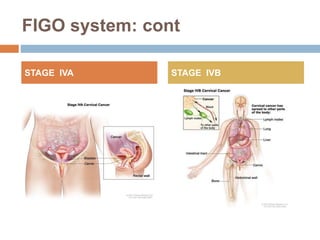
Cervical carcinoma is the second most common cancer in women globally, with over 16 cases reported per 100,000 women each year. It arises from the cells of the cervix uteri. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the primary risk factor. Symptoms may include abnormal bleeding or discharge. Diagnosis involves history, physical exam, Pap smear, colposcopy, and biopsy. Staging uses the FIGO system and treatment options depend on stage, including LEEP, hysterectomy, chemotherapy, and radiation. Regular screening through Pap smears and HPV testing can help prevent cervical cancer by detecting pre-cancerous lesions.