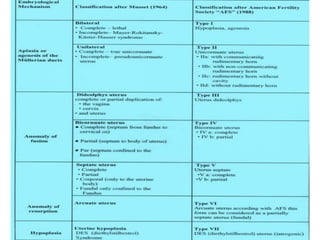
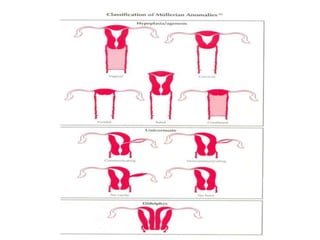
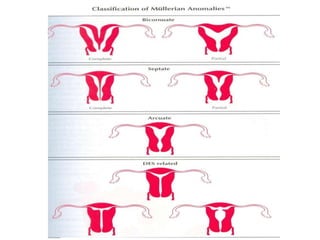
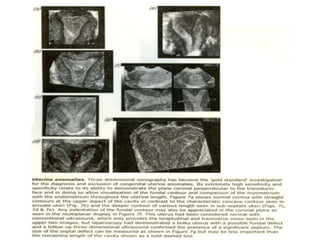
This document discusses congenital malformations of the female genital tract. It begins by outlining the normal development of the Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts. It then describes various types of malformations that can occur due to abnormalities in this development, including aplasia, hypoplasia, atresia, nonfusion, hermaphroditism and others. Specific conditions like vaginal atresia, imperforate hymen, and uterine fusion defects are explained. The clinical features, diagnosis and treatment of some of these congenital anomalies are provided.