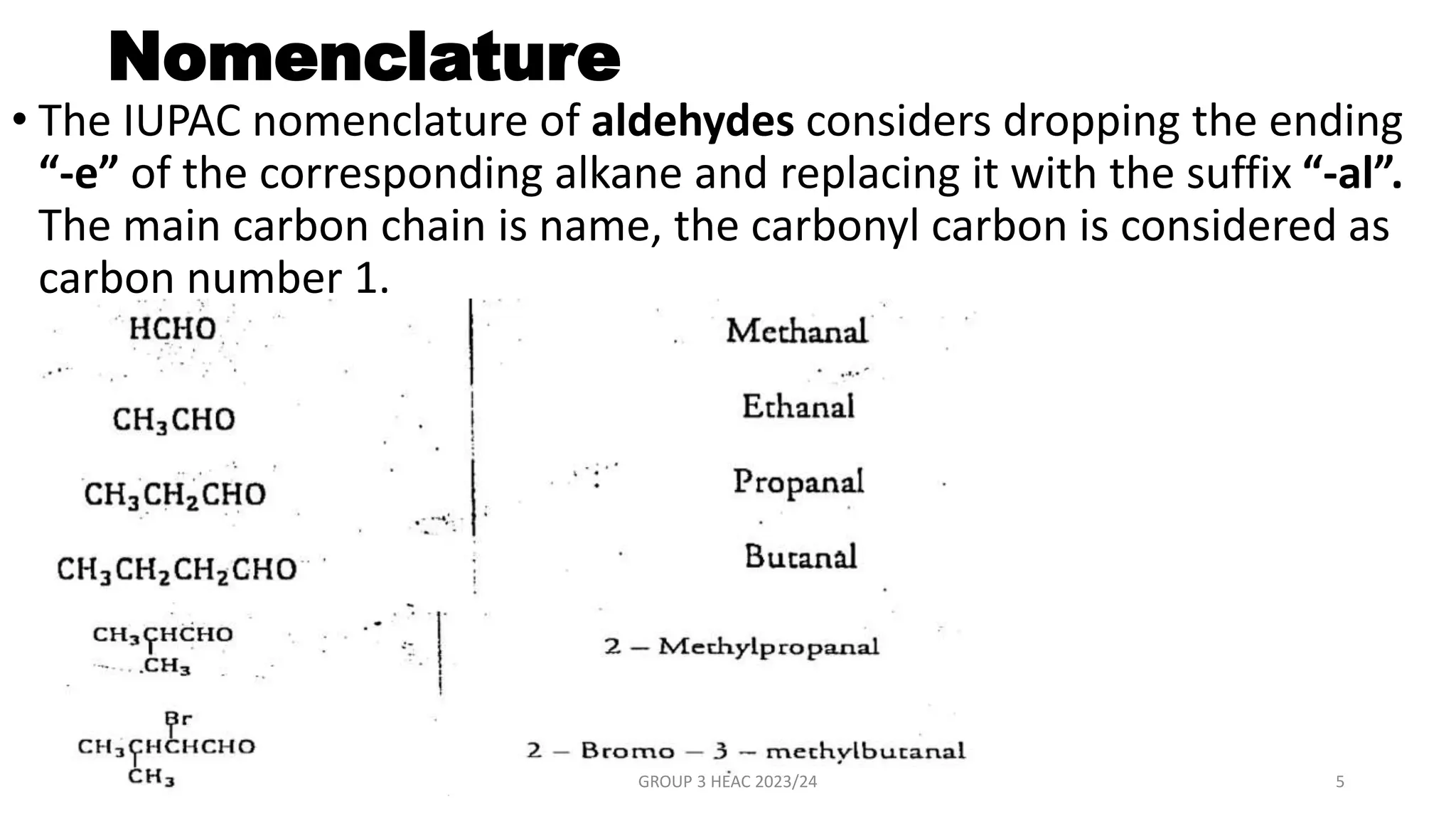
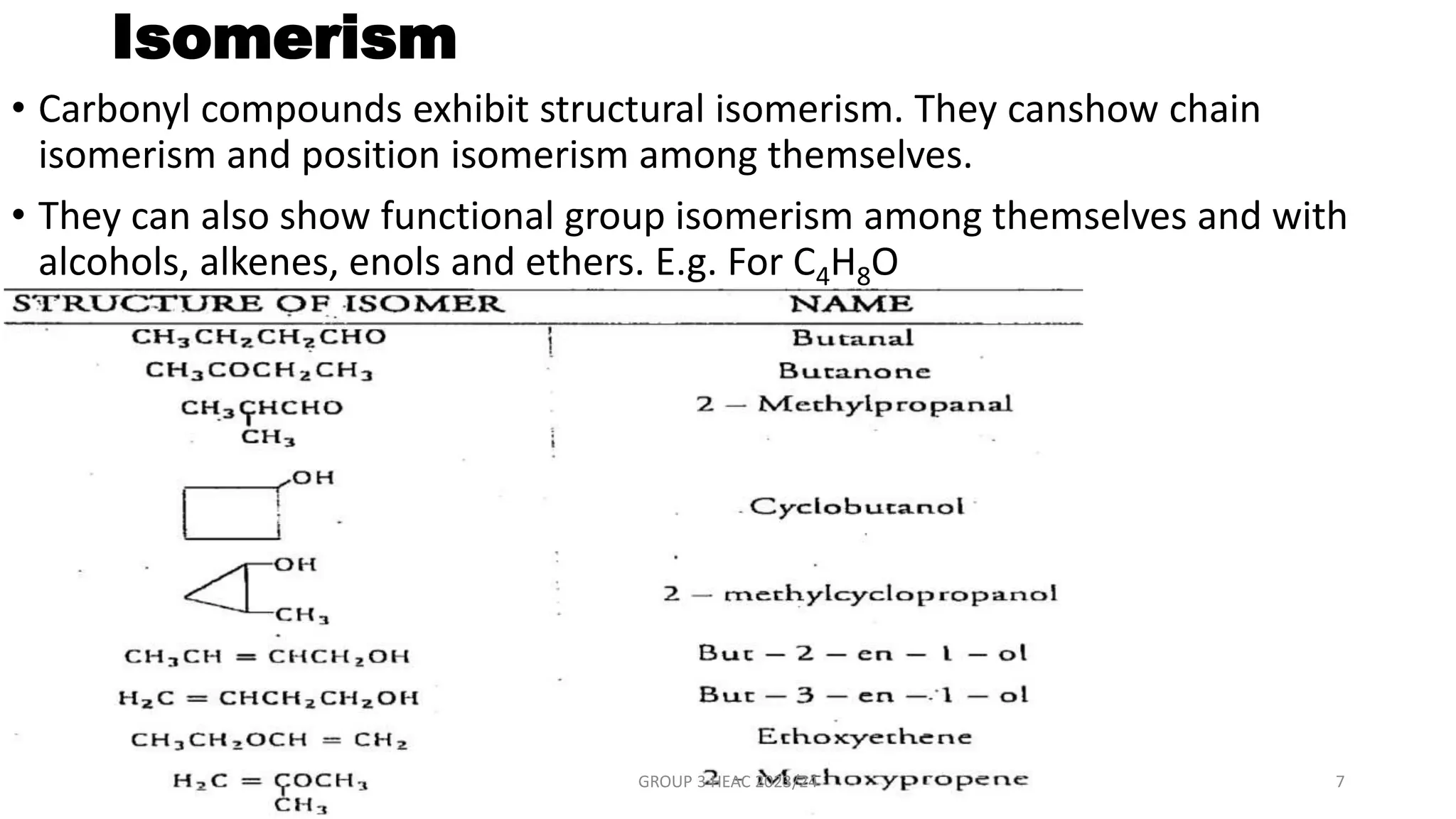
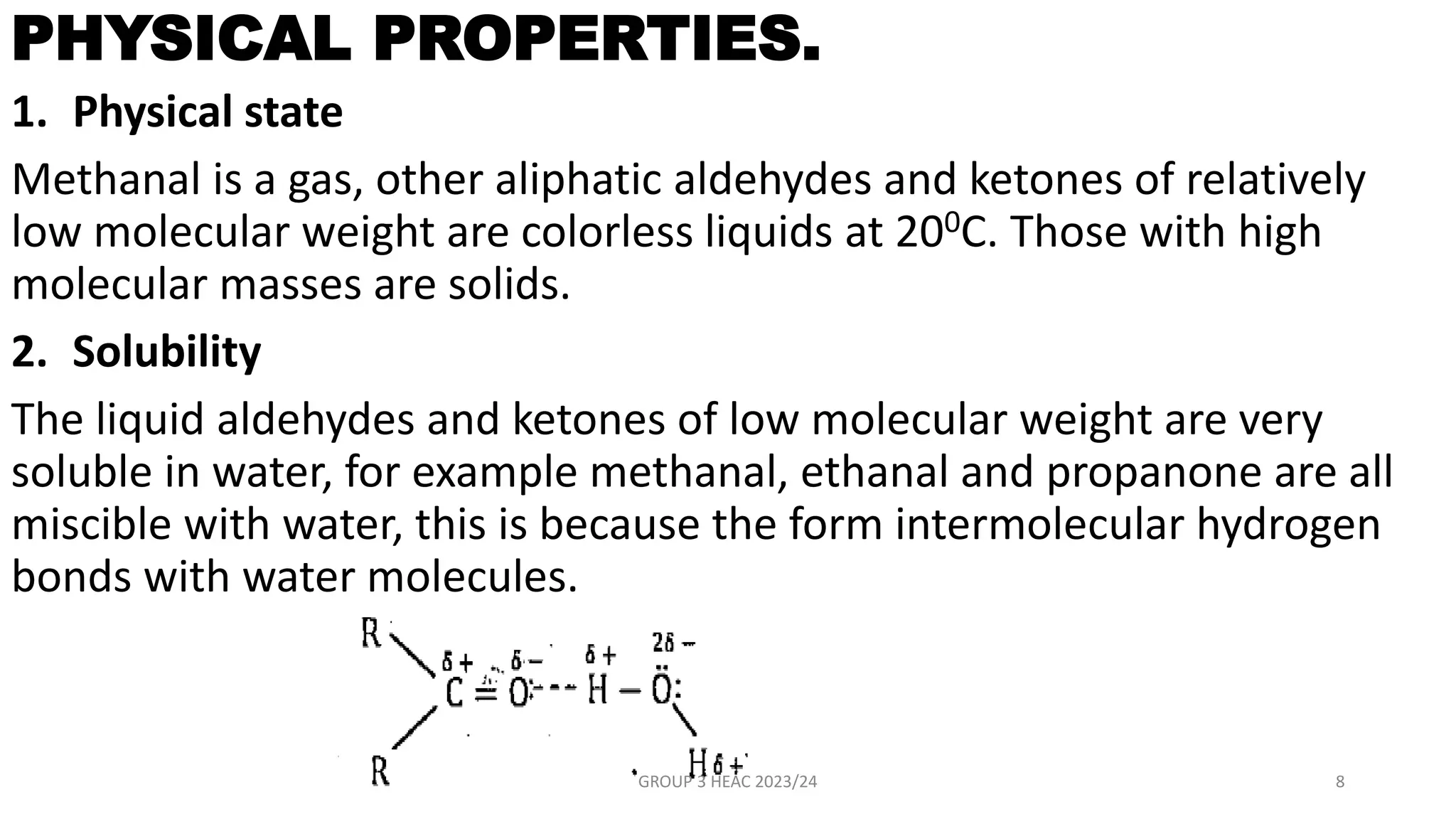
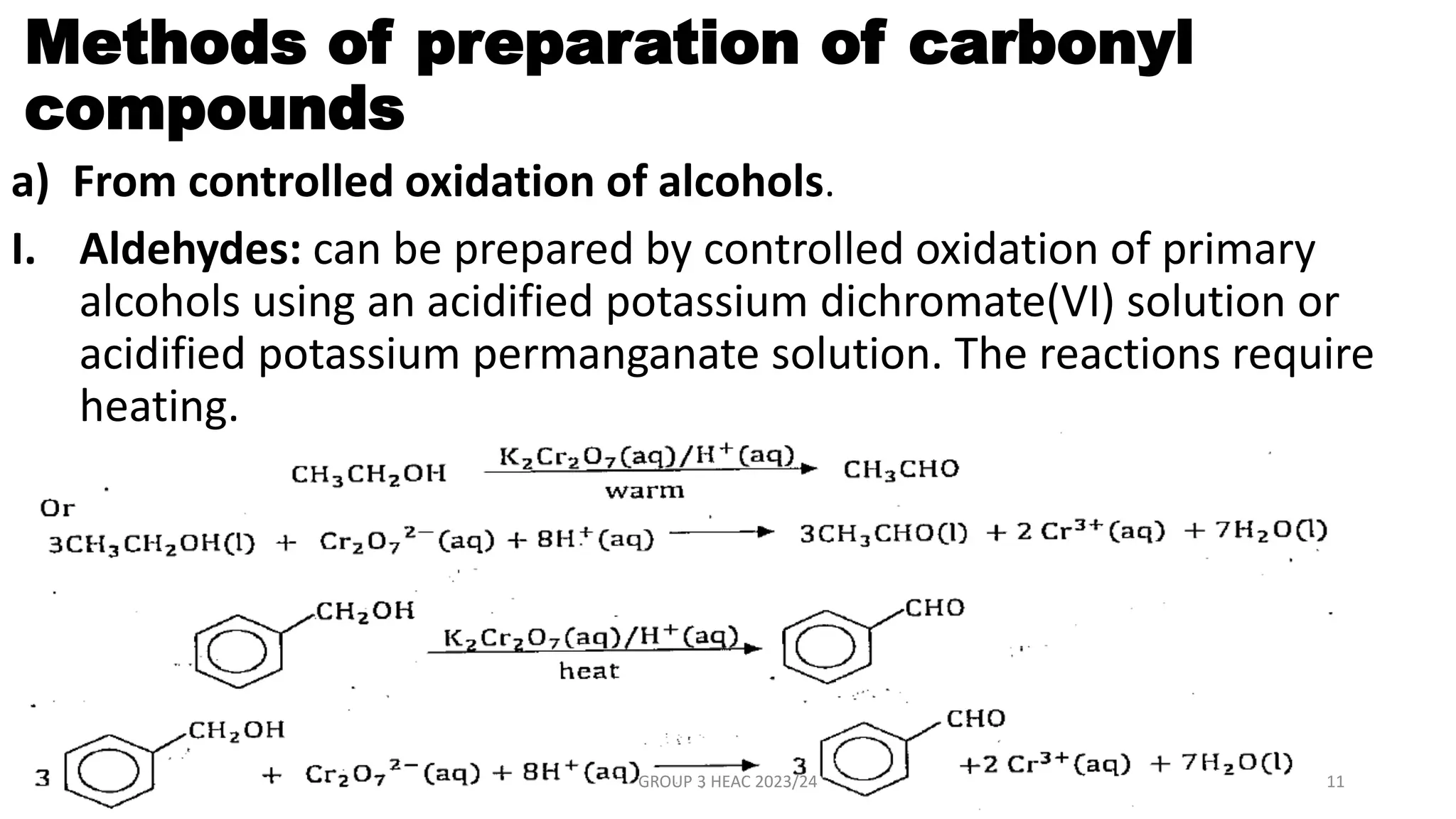
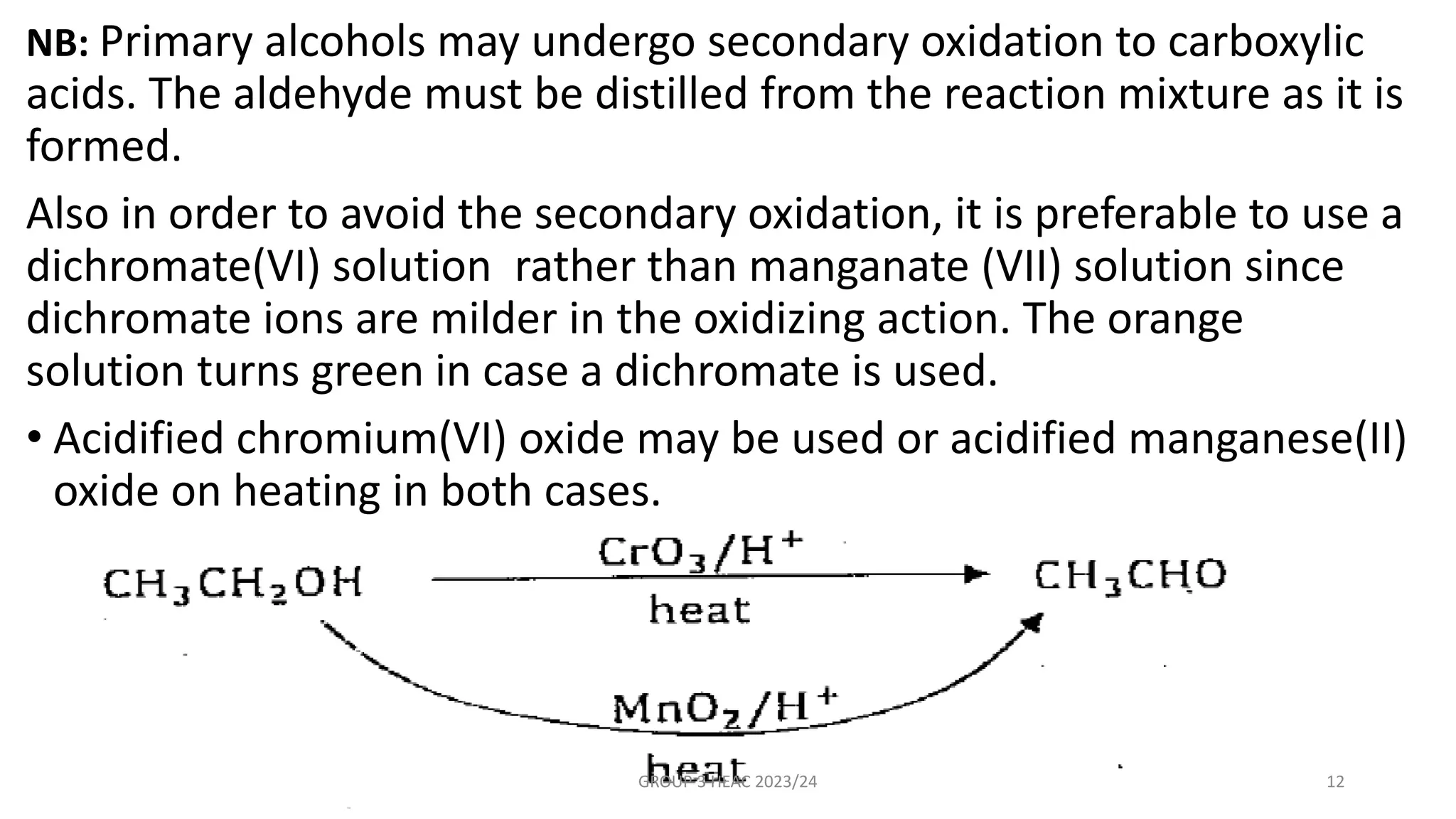
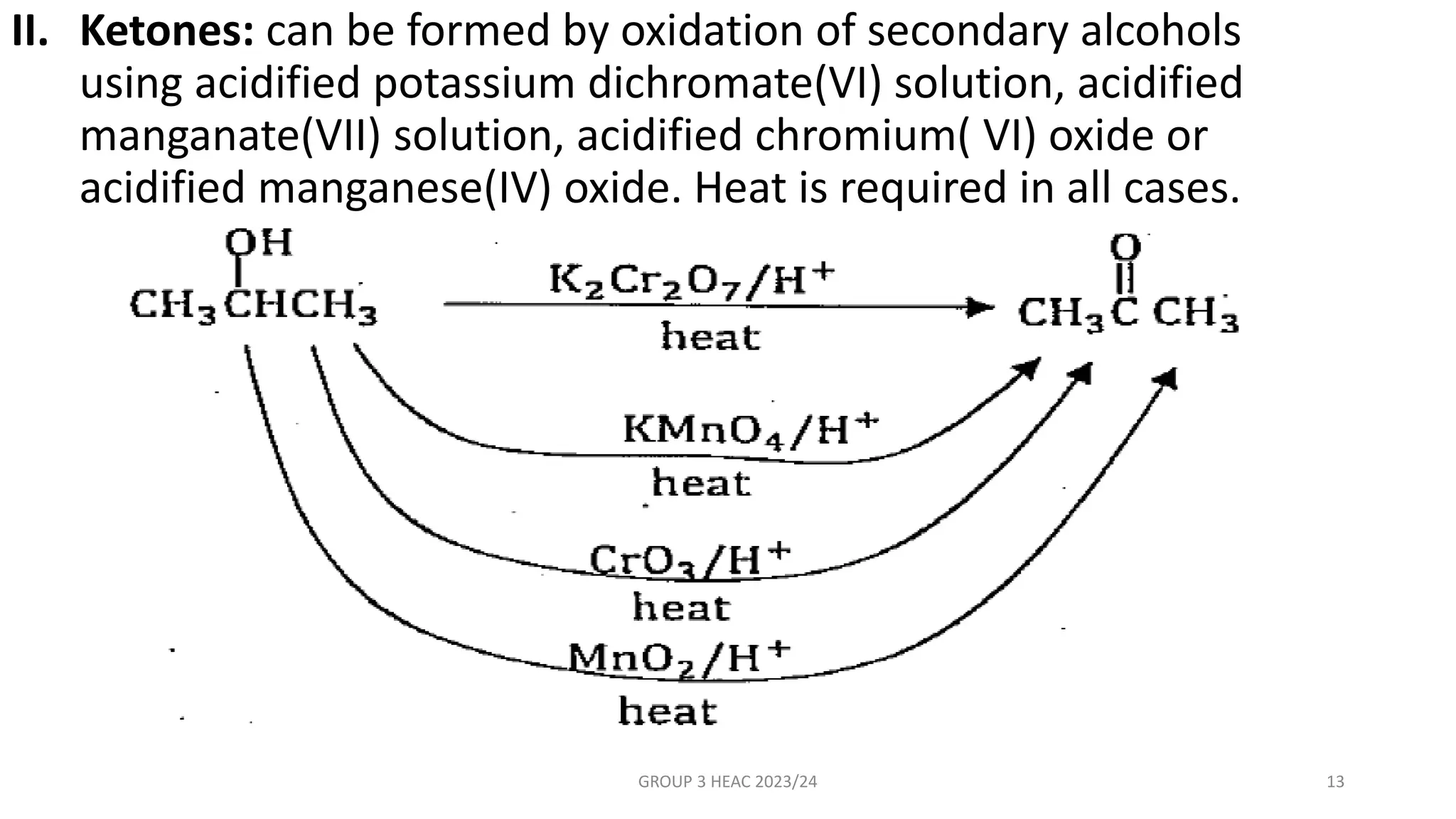
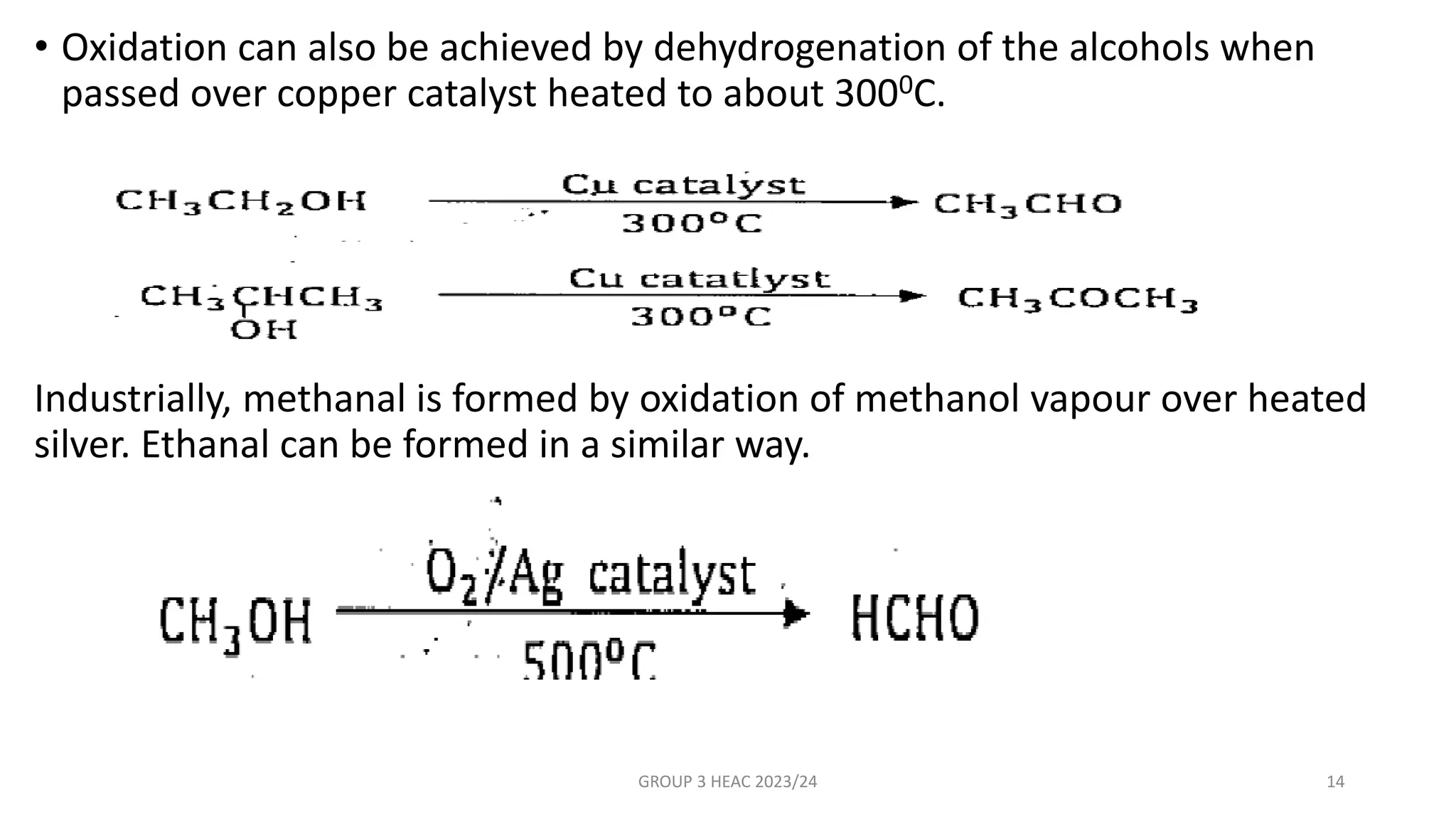
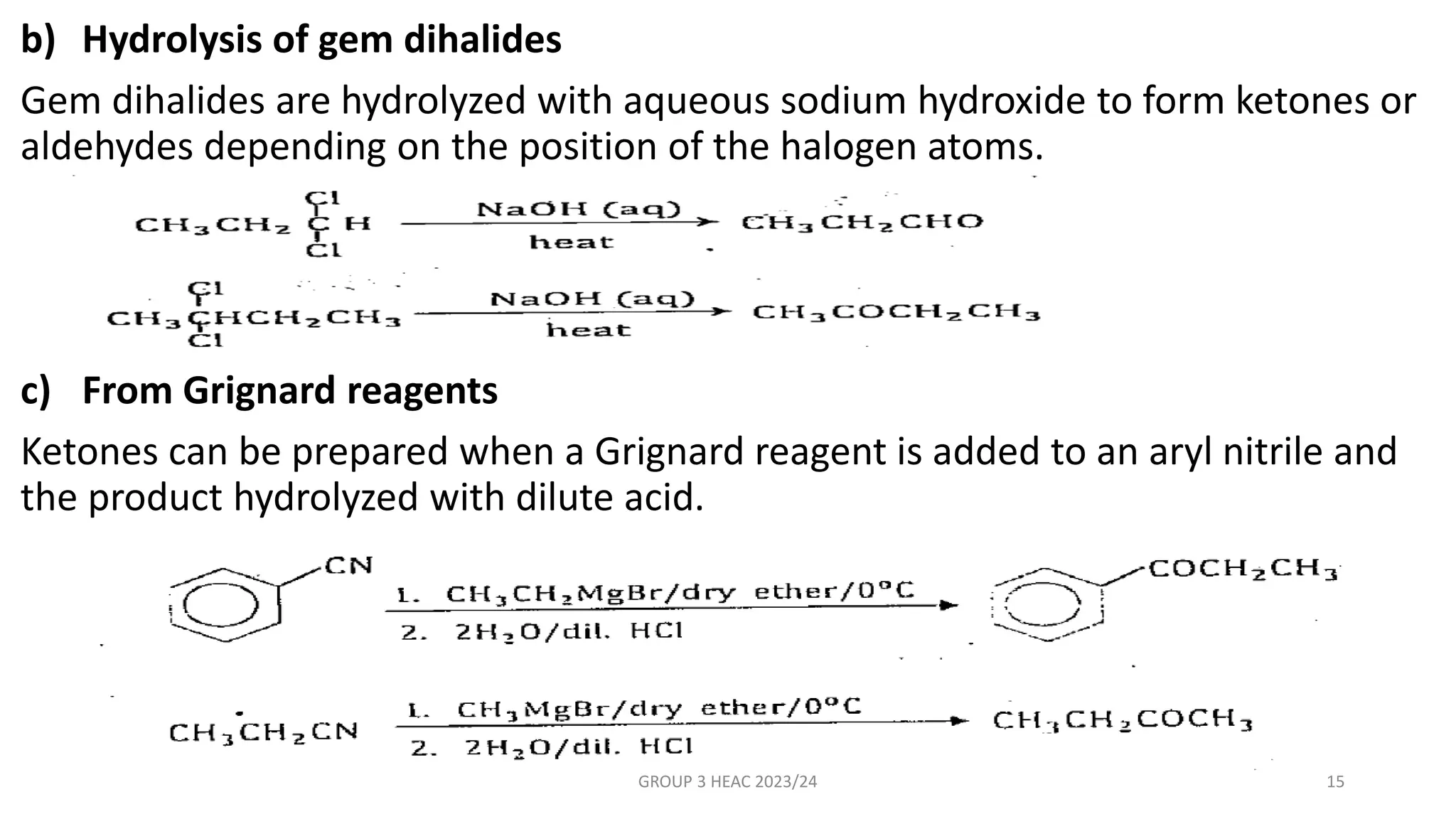
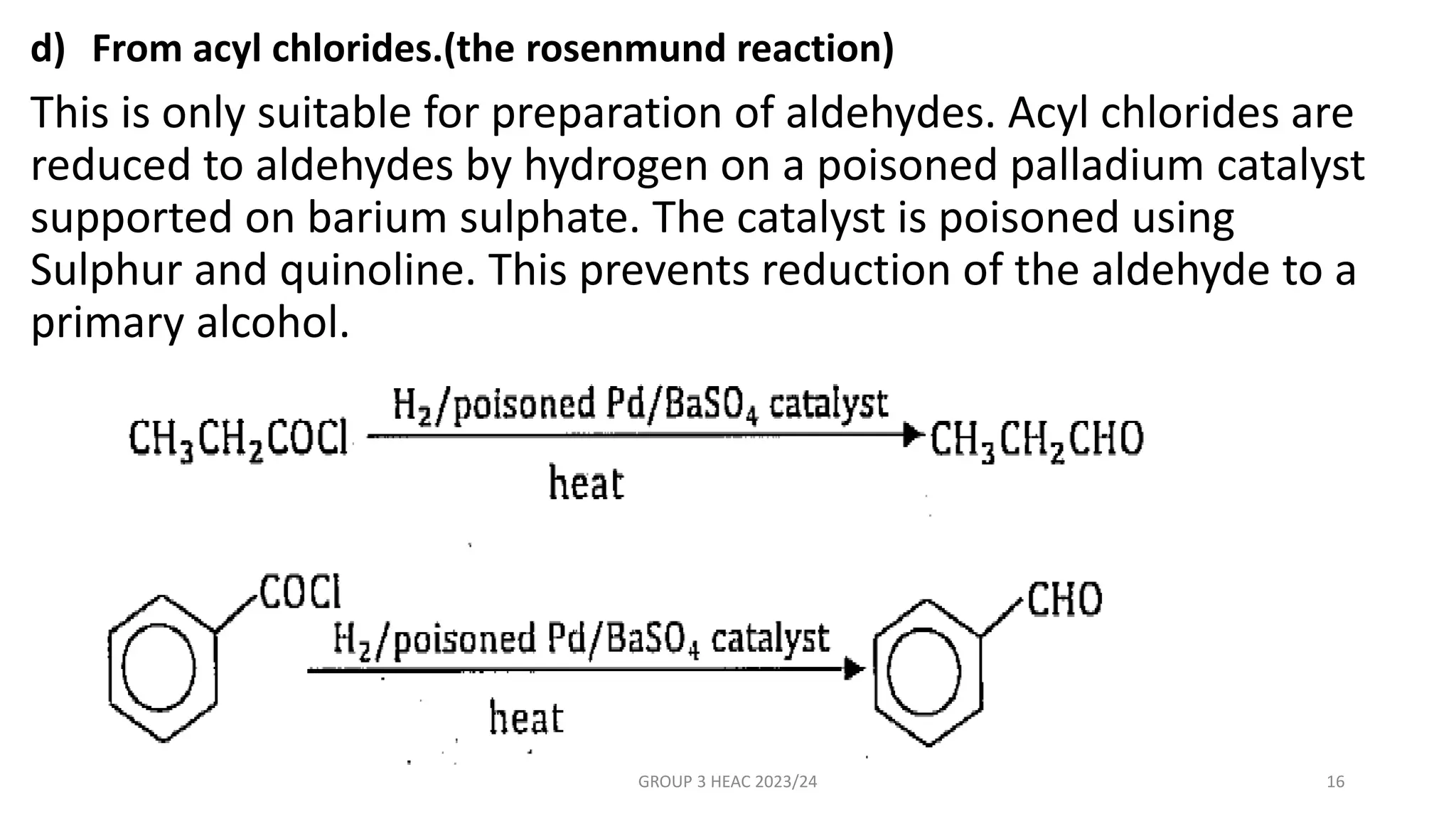
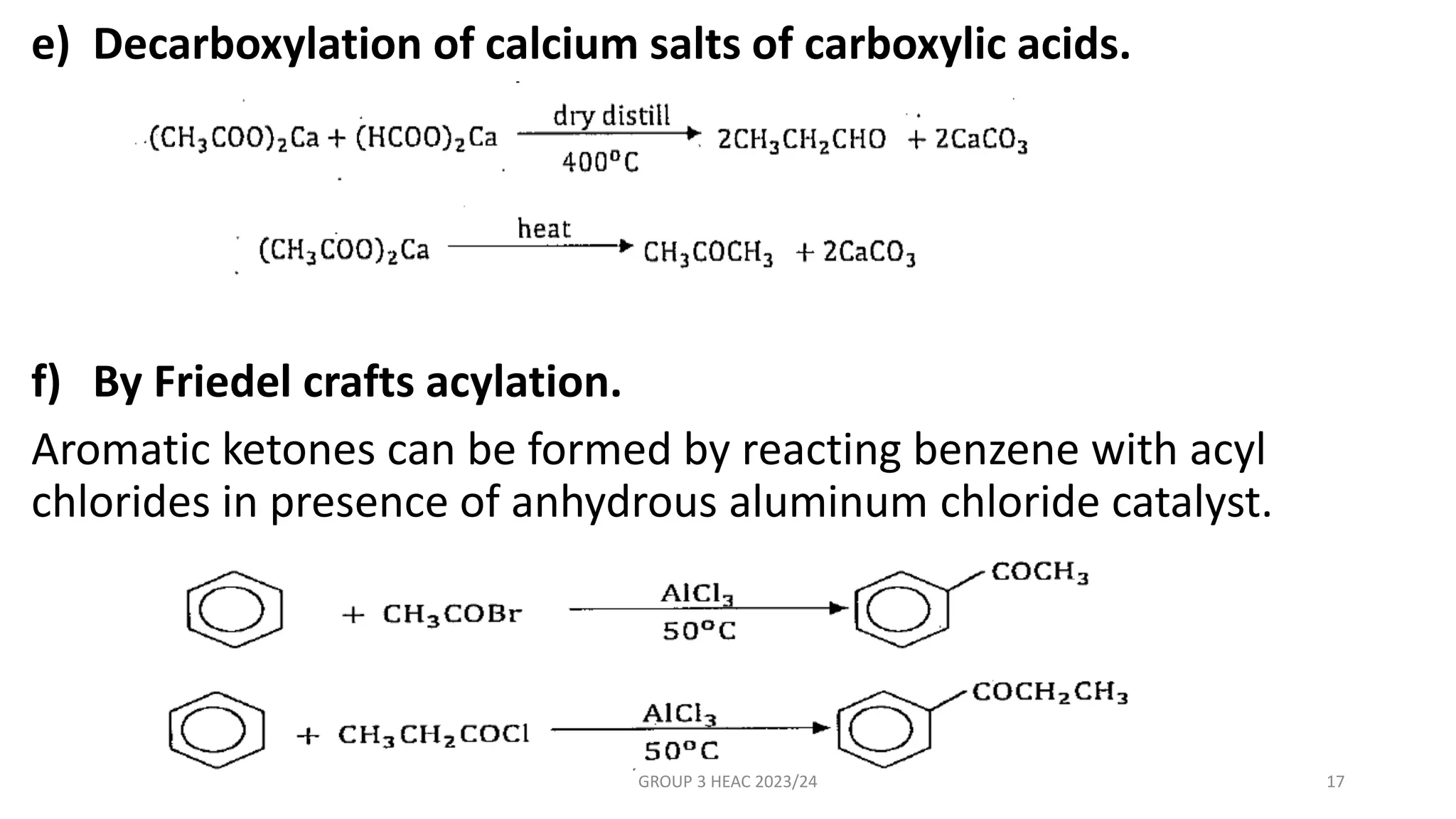
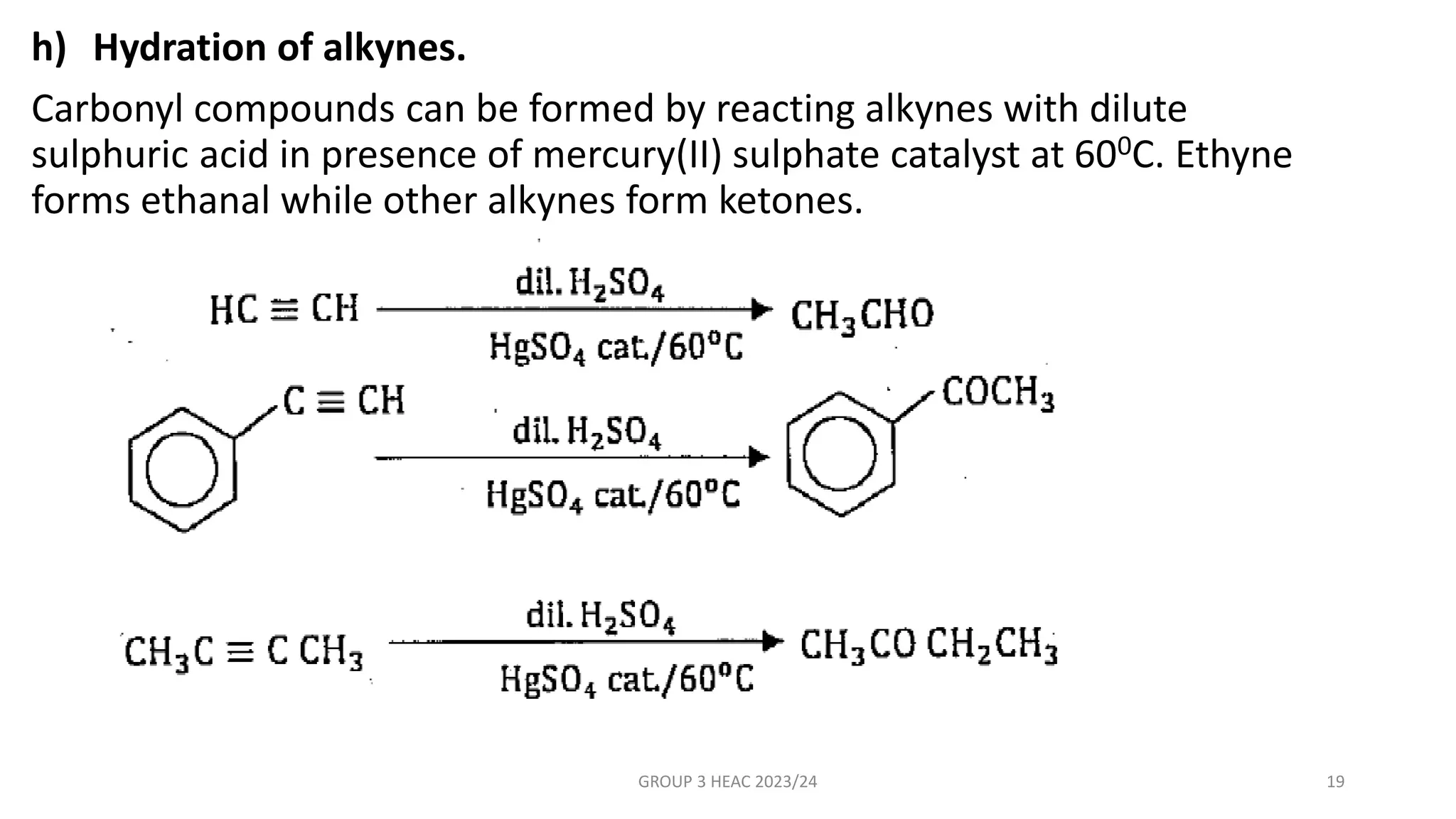
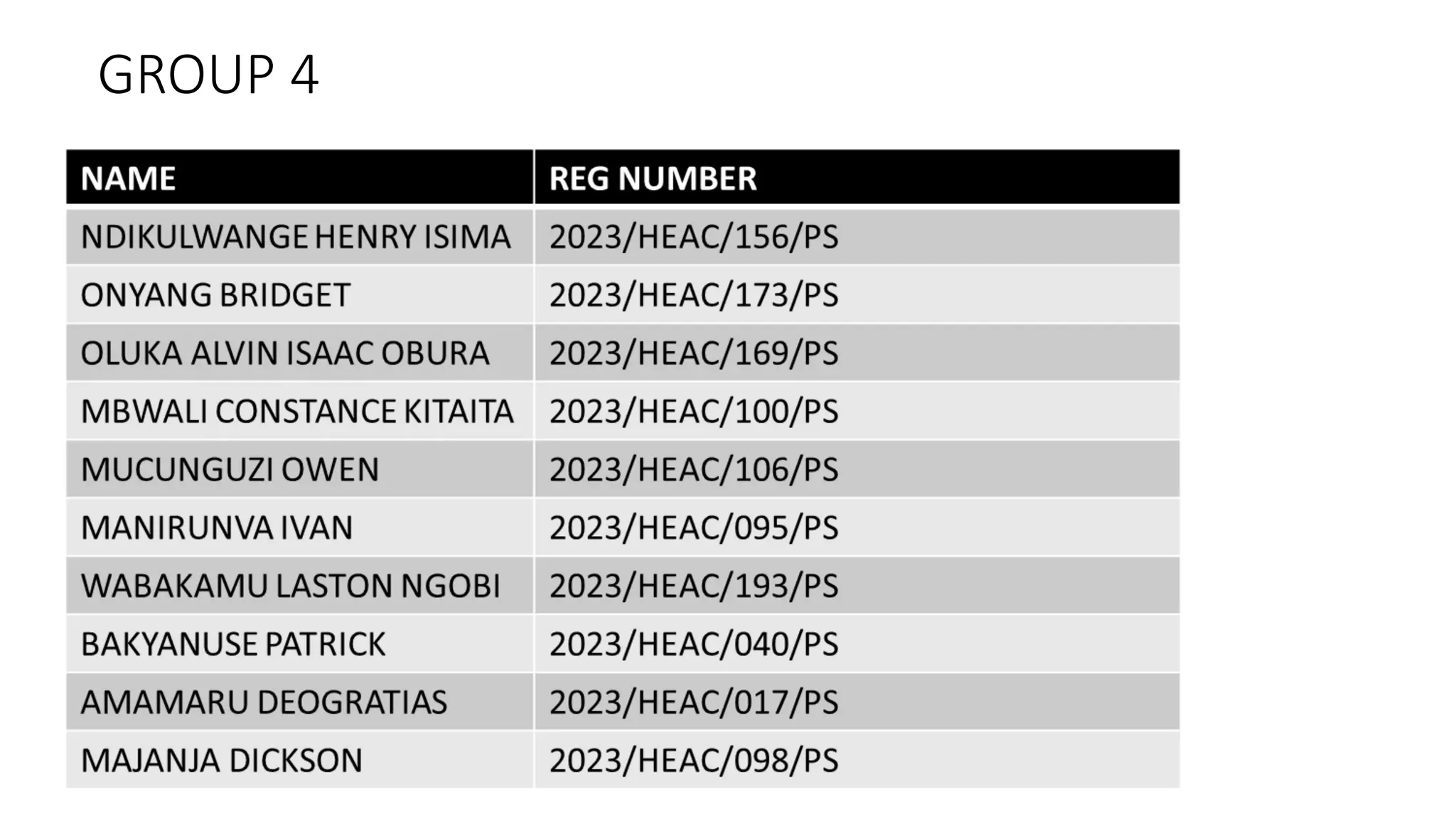
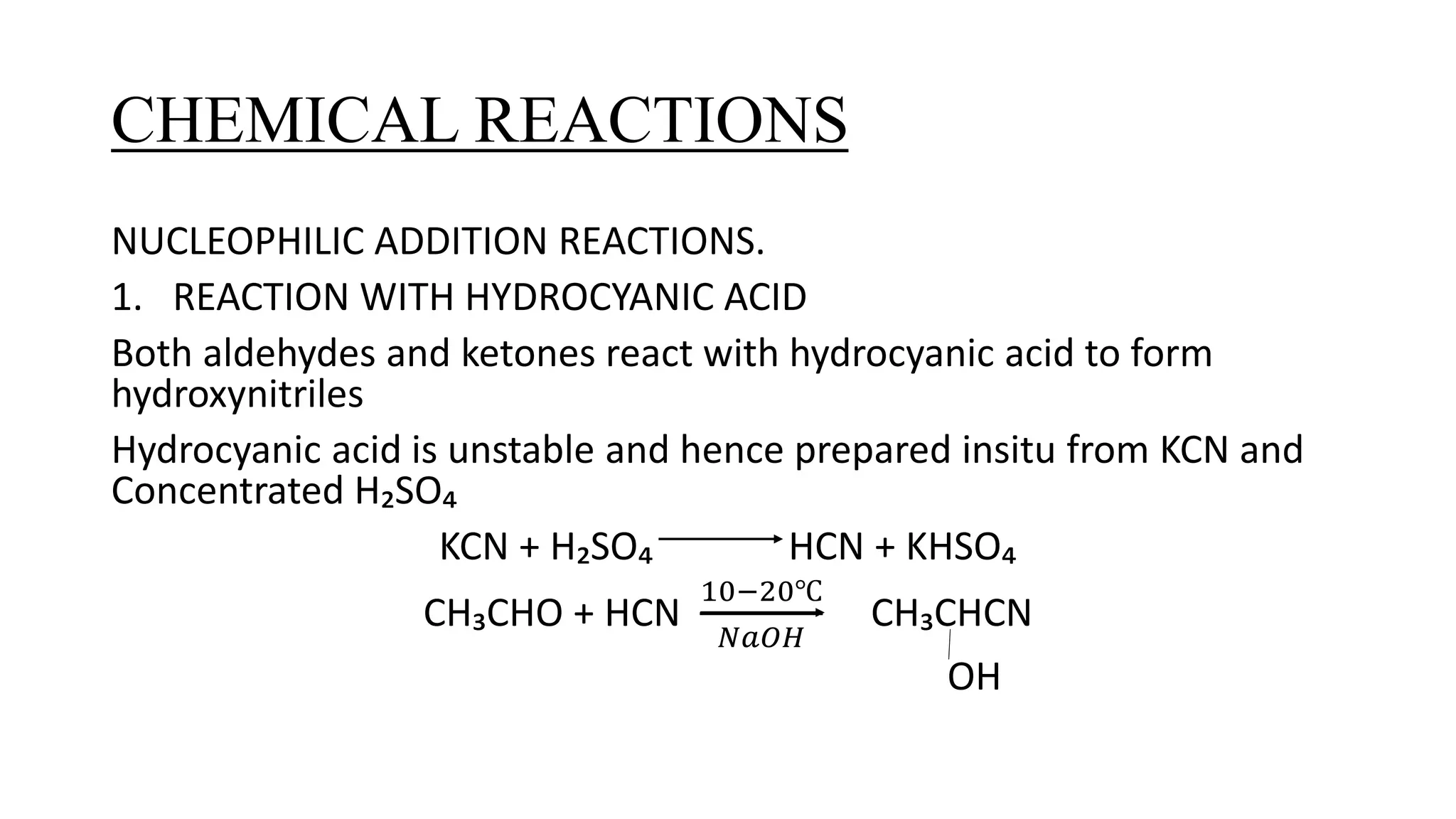
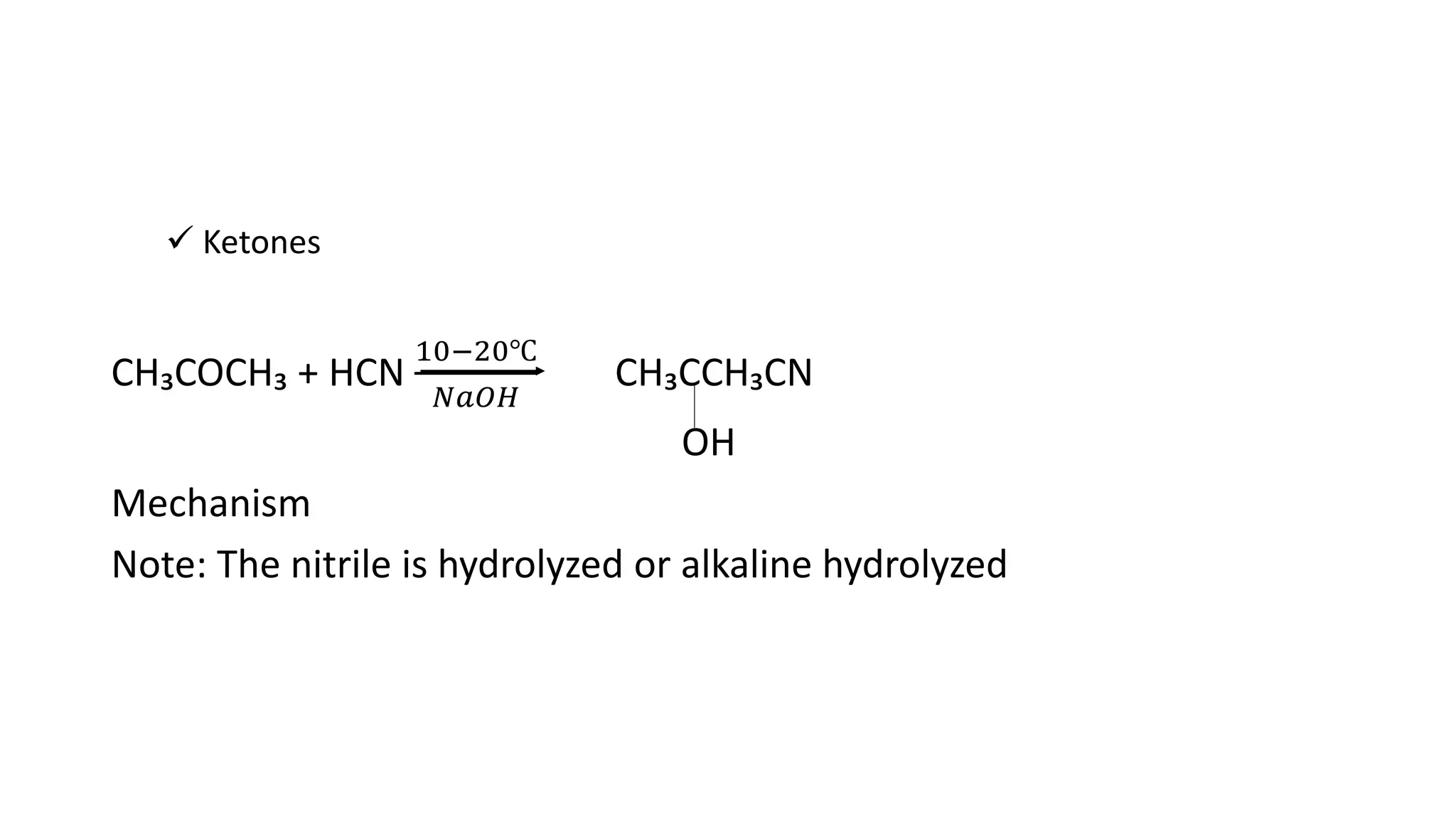
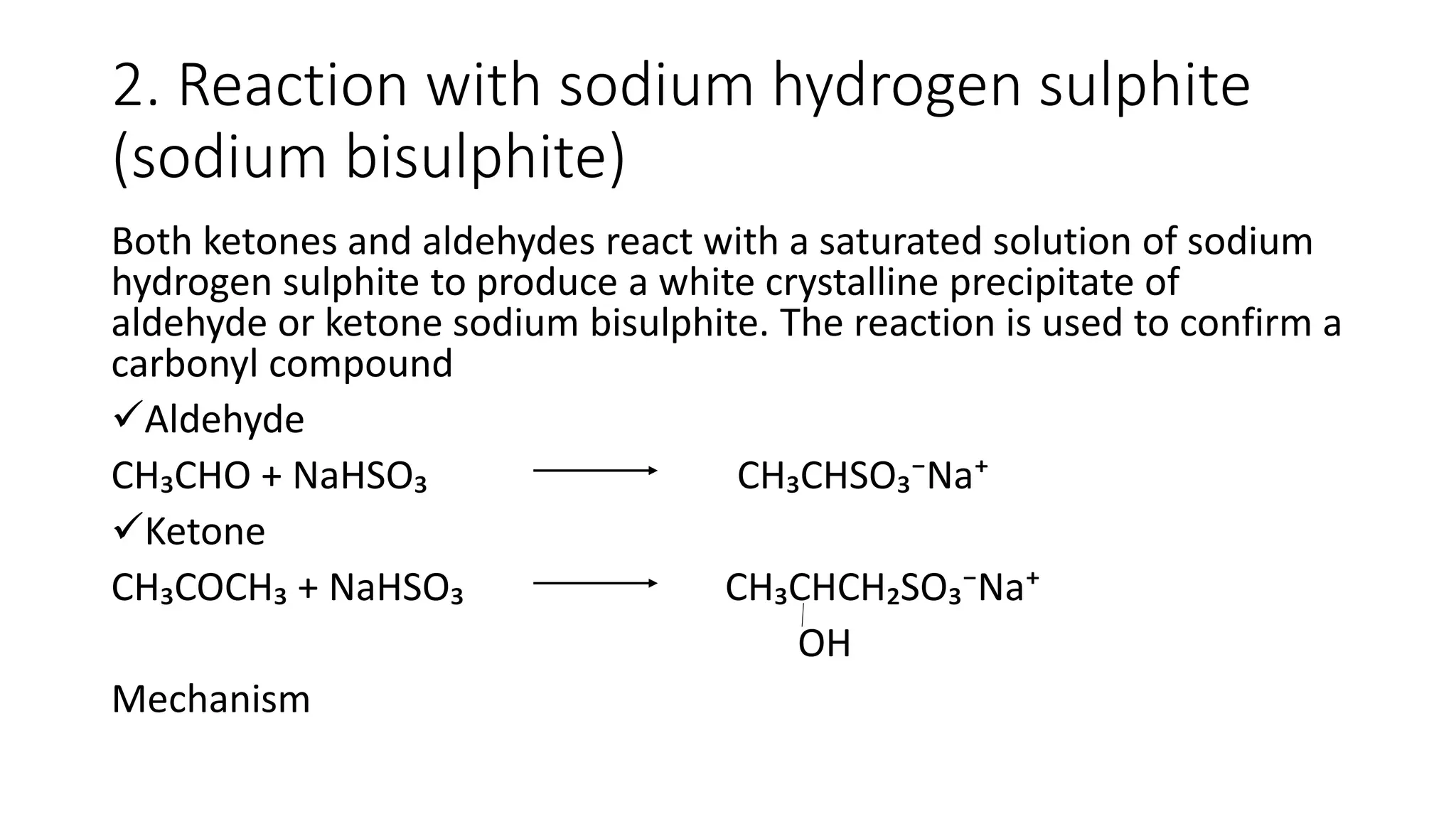
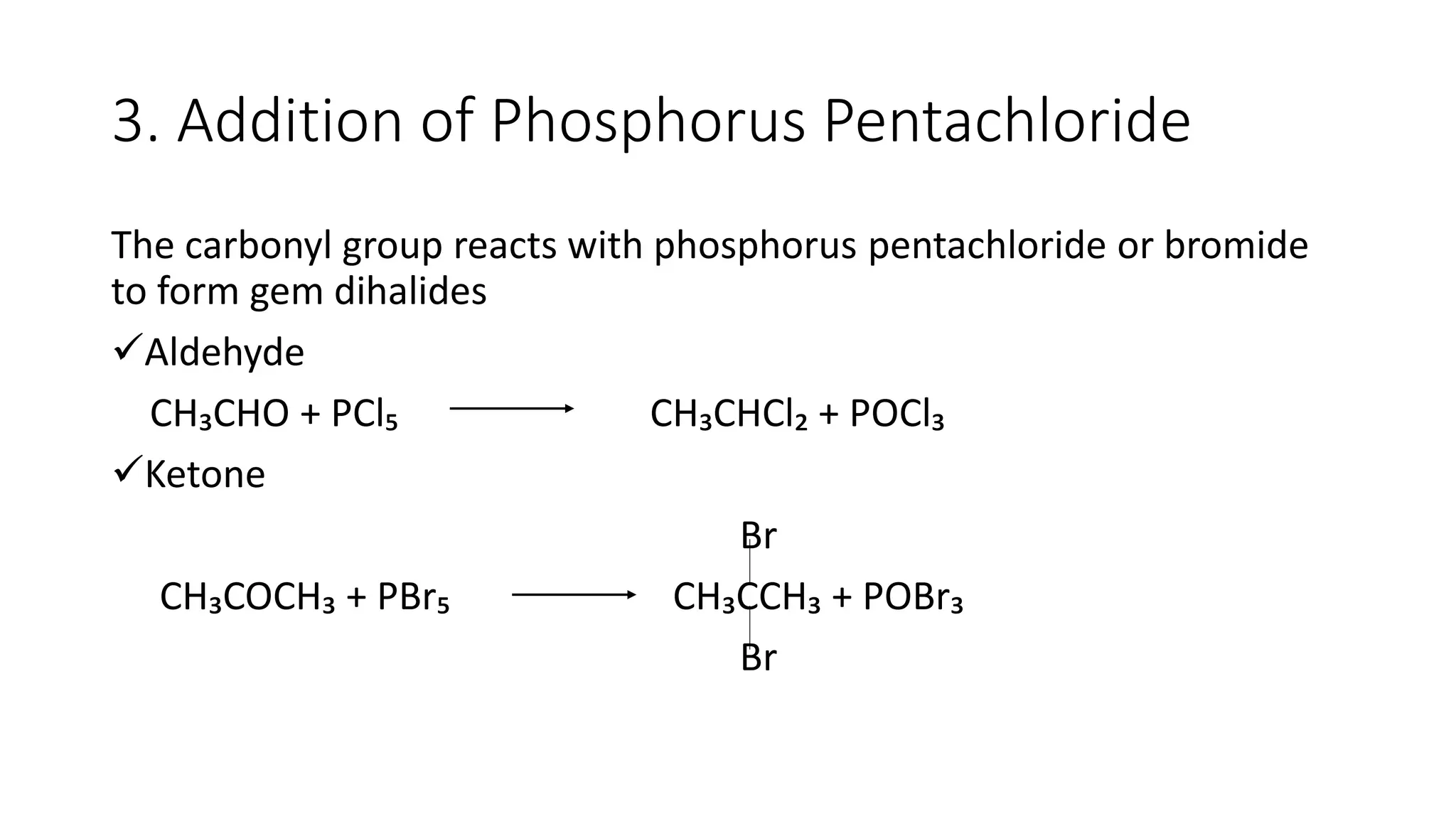
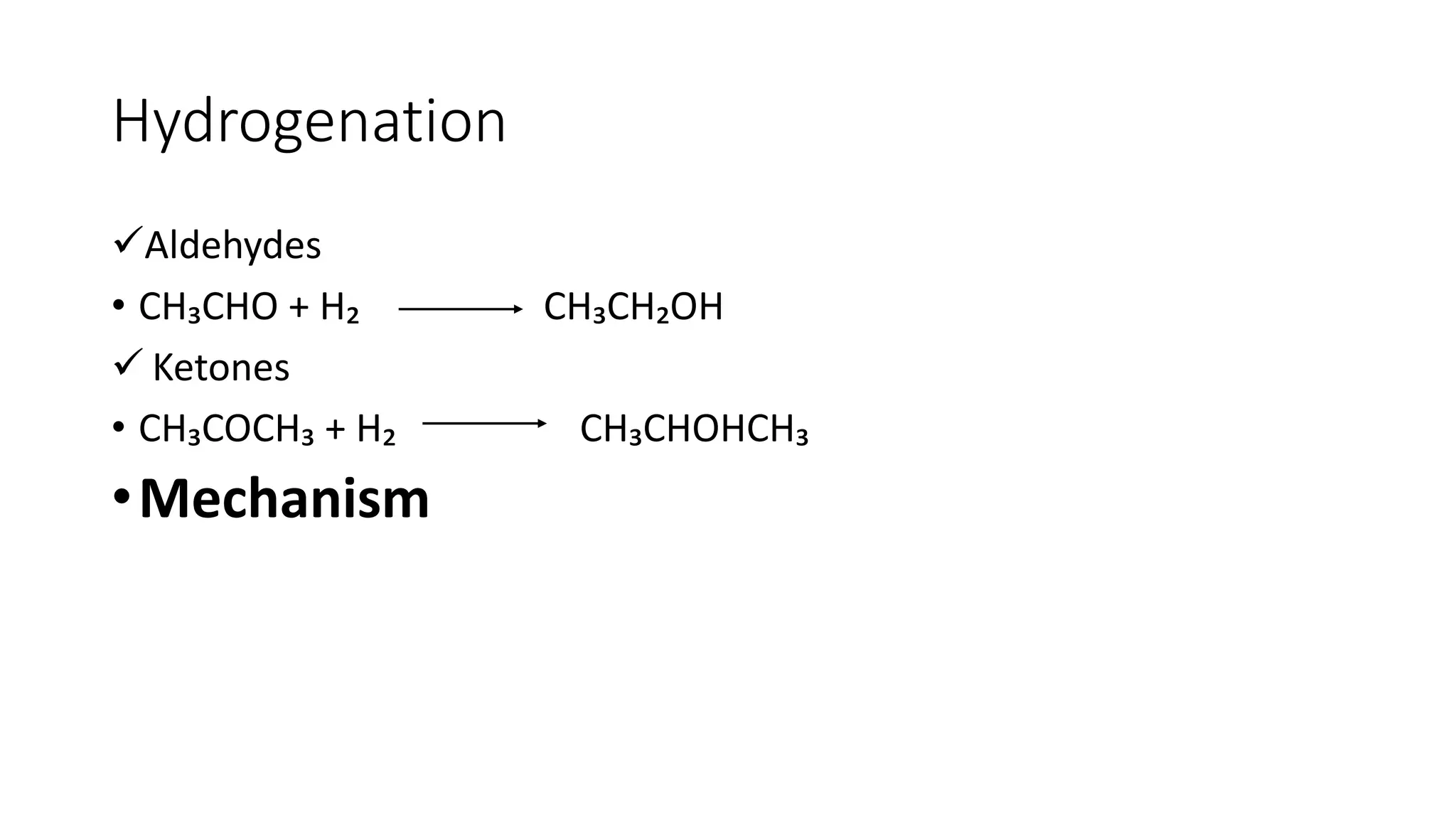
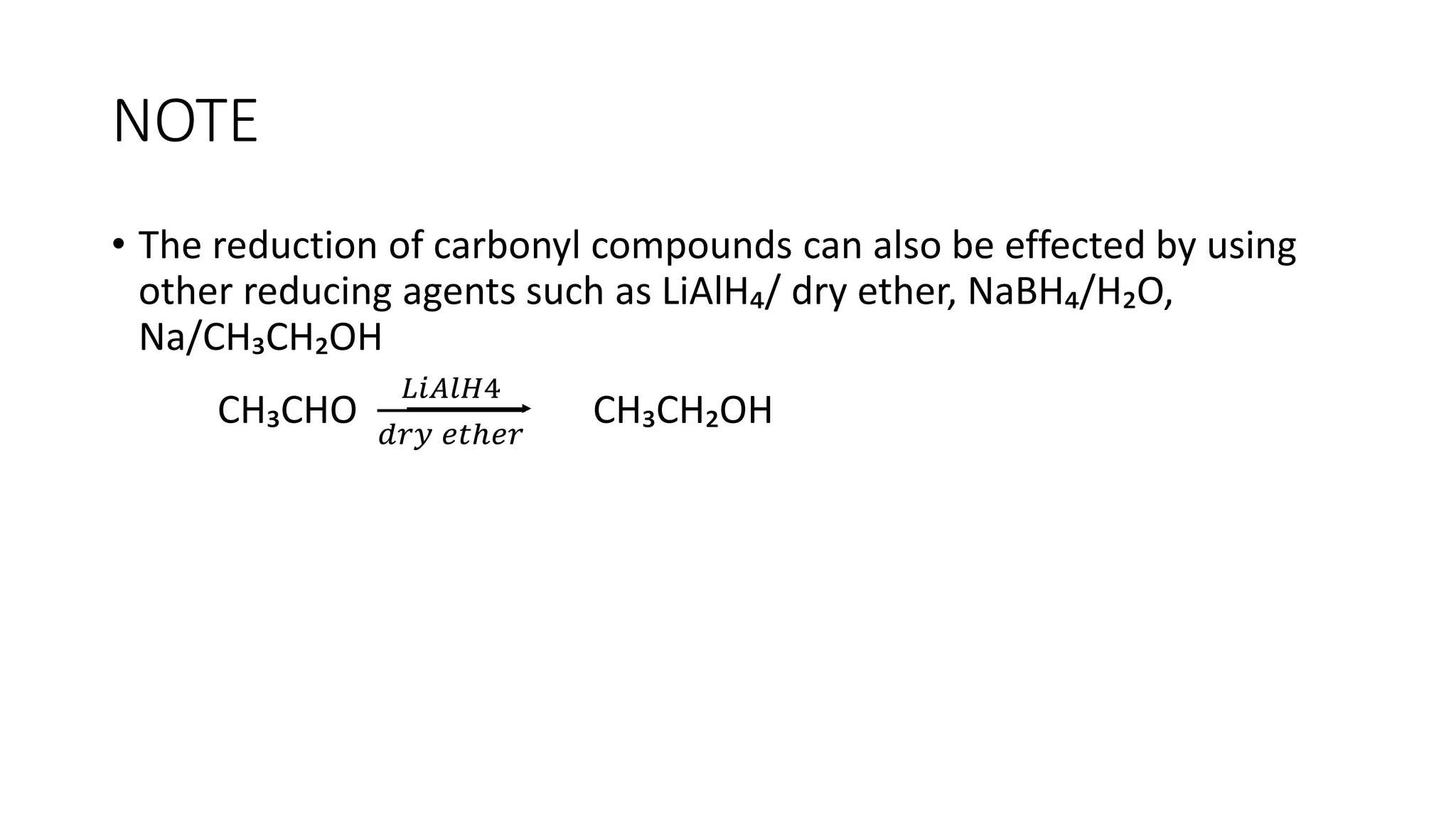
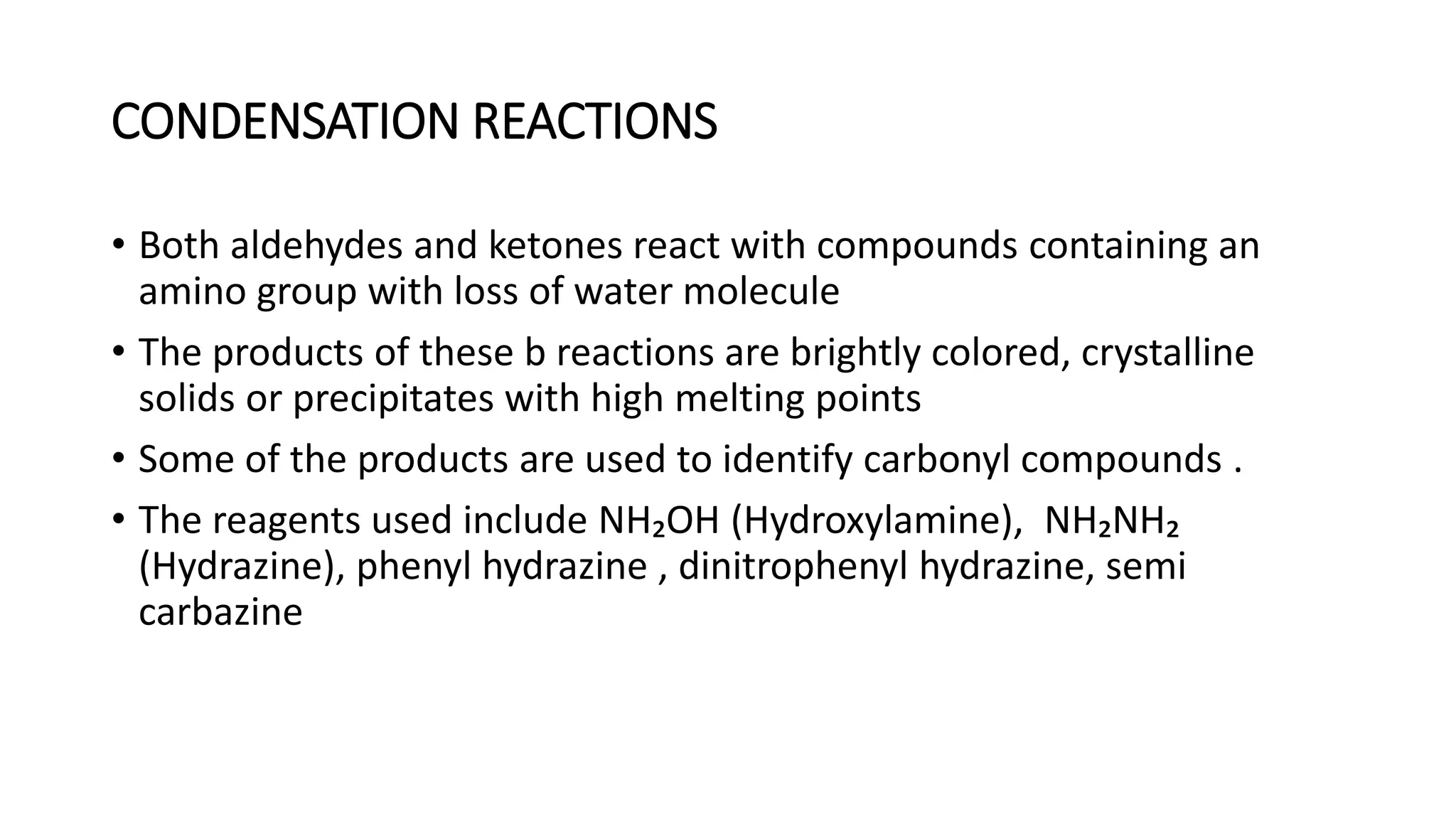
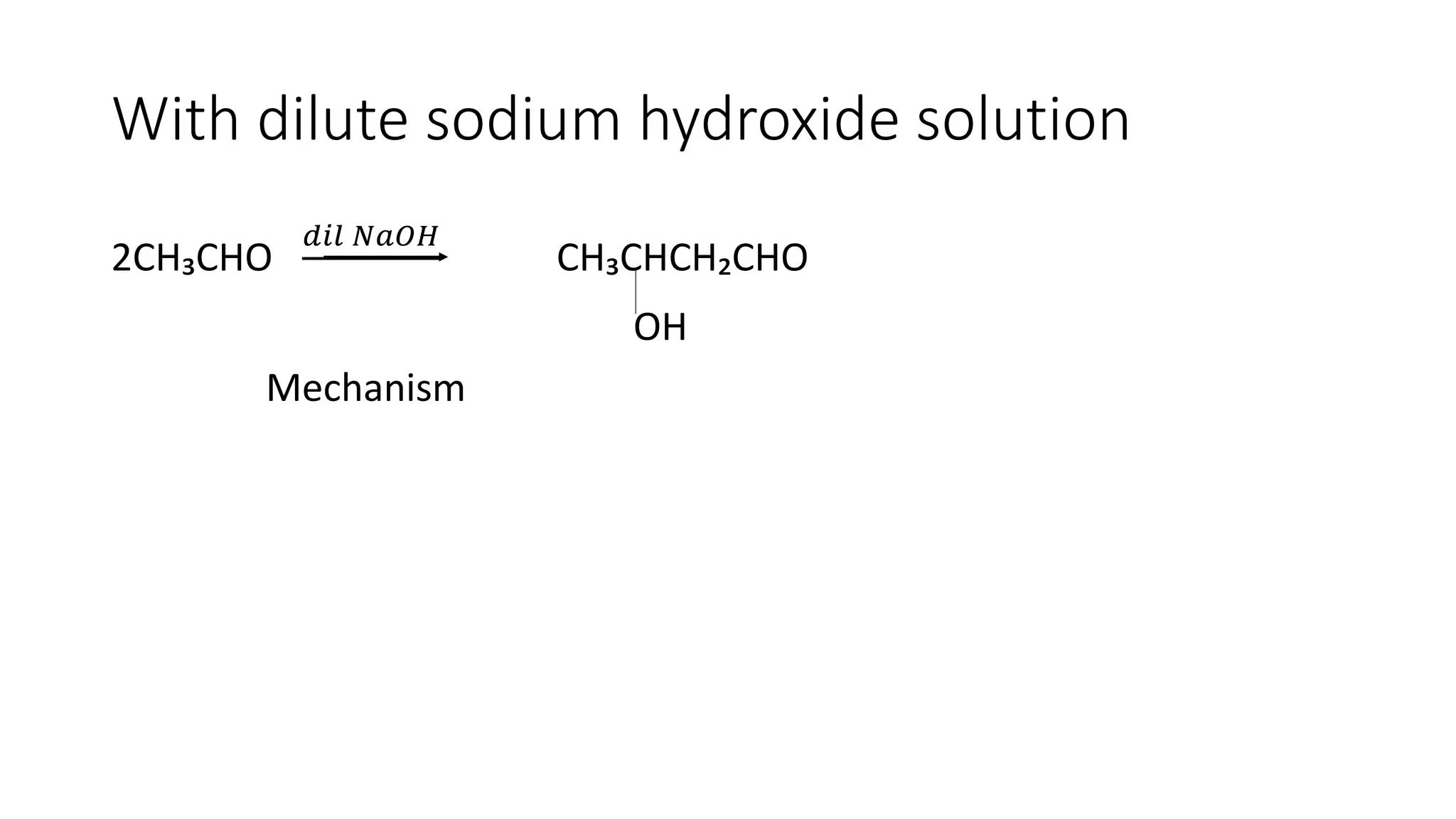
The document describes carbonyl compounds and was presented by Group 3 and 4. It defines carbonyl compounds as organic compounds containing a carbonyl functional group. The two main classes are aldehydes and ketones. The document discusses their structures, nomenclature, properties, methods of preparation, and characteristic reactions including nucleophilic addition, condensation, oxidation, and reduction reactions. Representative equations are provided to illustrate key reaction types.