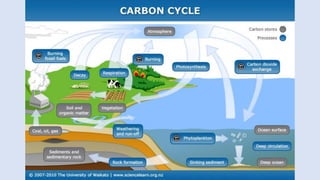
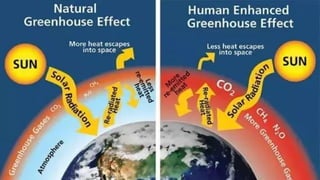
The carbon cycle describes the movement of carbon through Earth's biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Carbon is exchanged between the atmosphere, living organisms, oceans, soil, rocks through various processes like photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, combustion of fossil fuels and weathering of rocks. Human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation have increased atmospheric CO2 levels, impacting Earth's climate by enhancing the greenhouse effect.