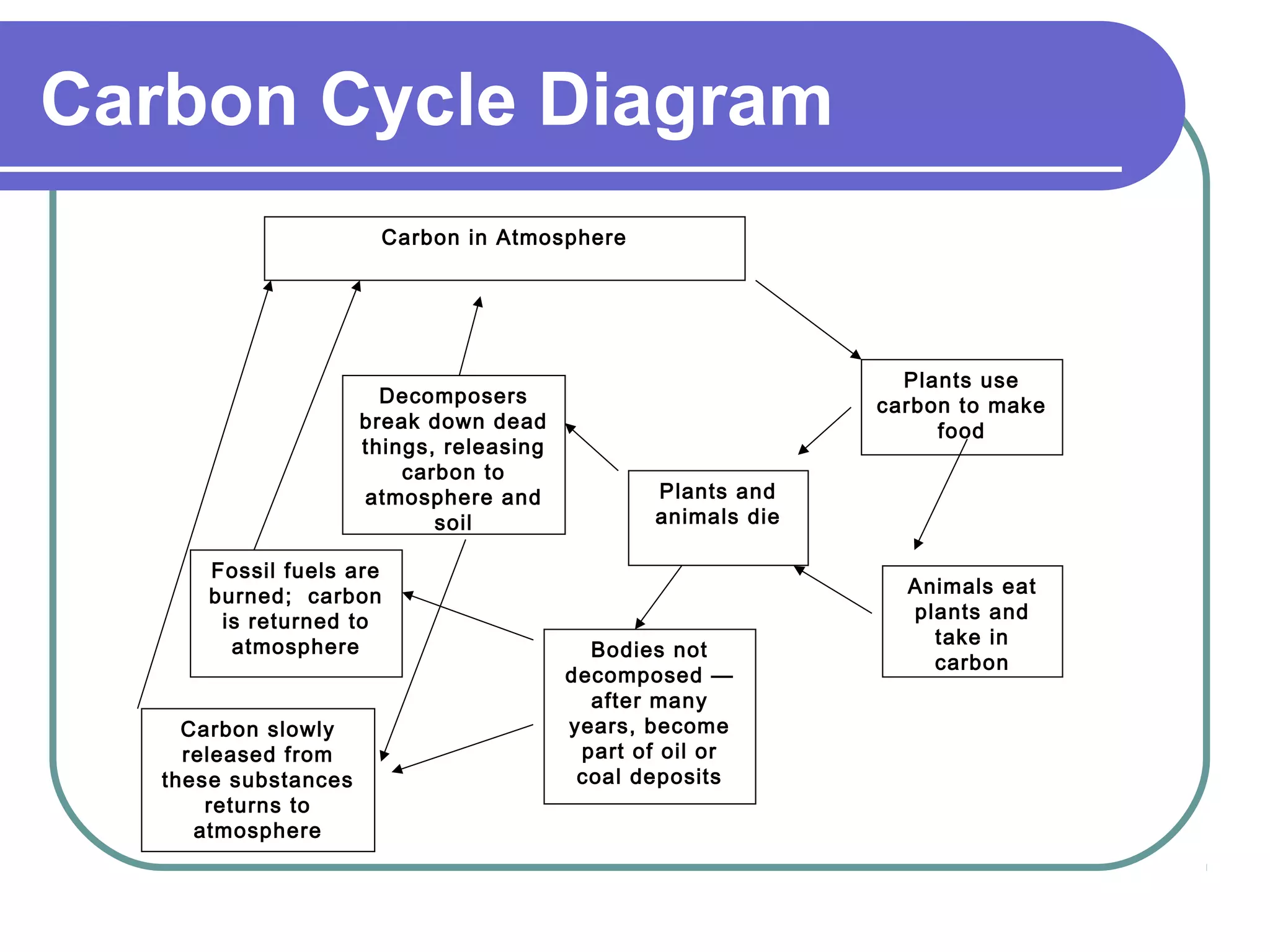
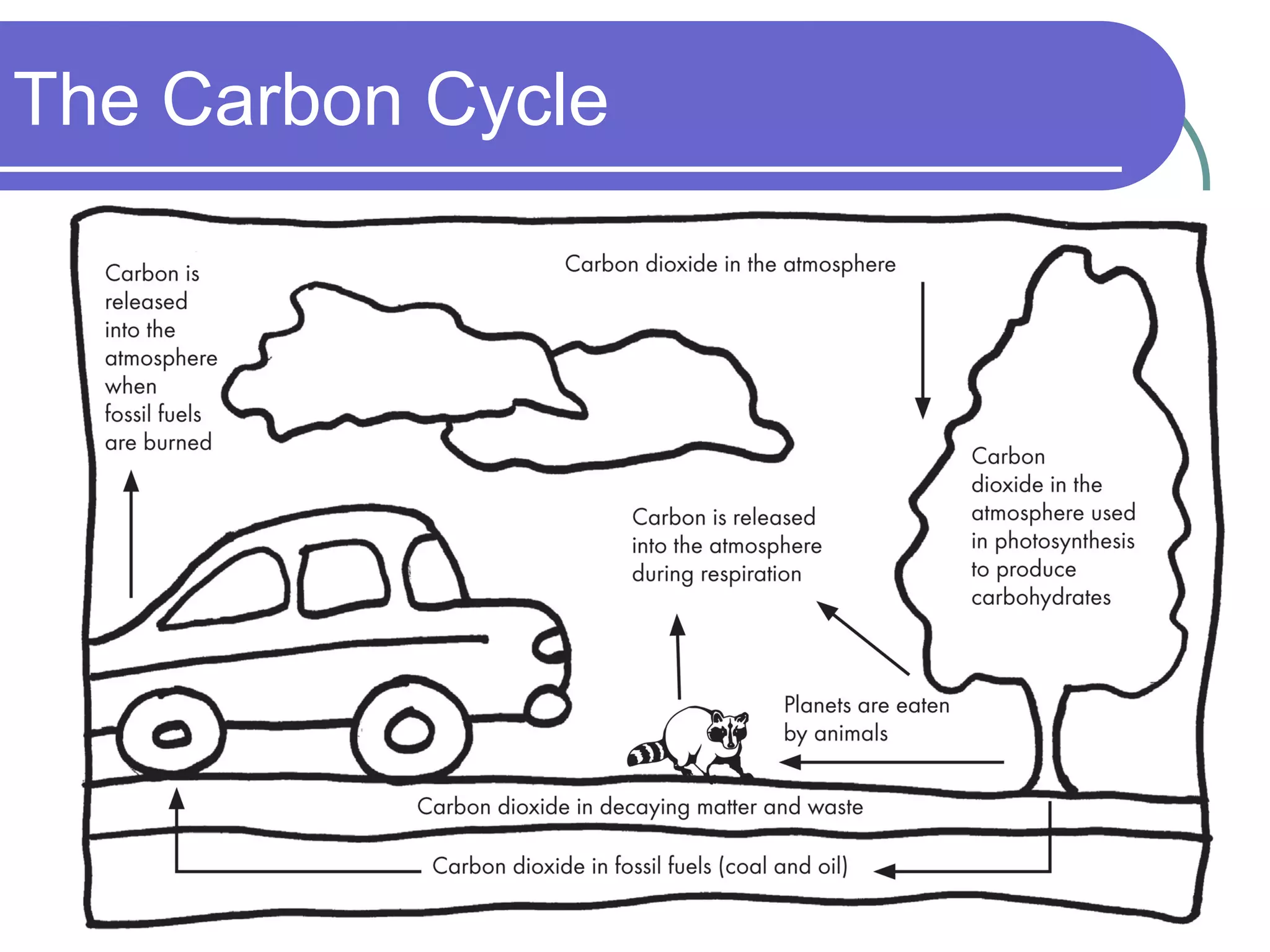
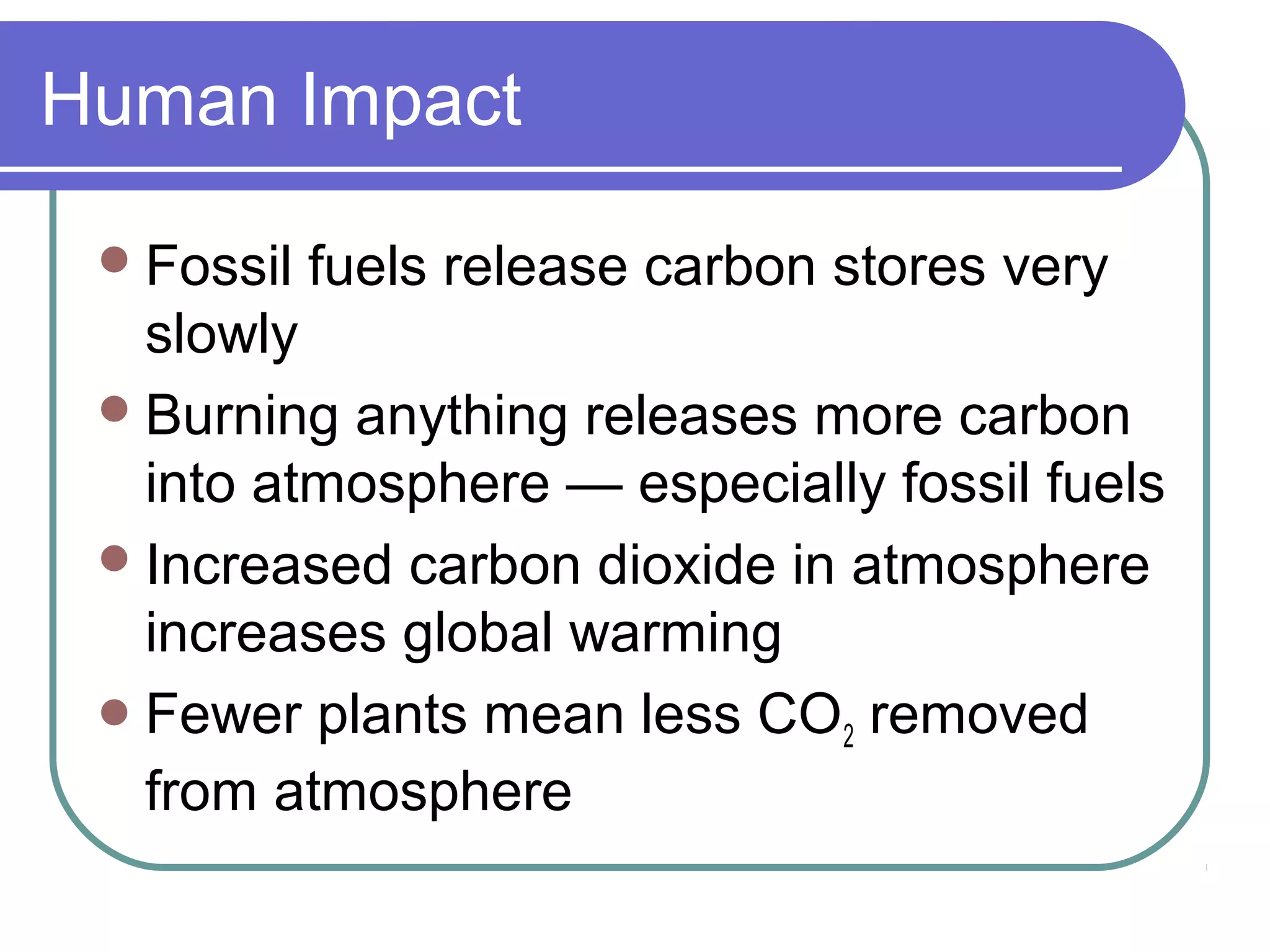
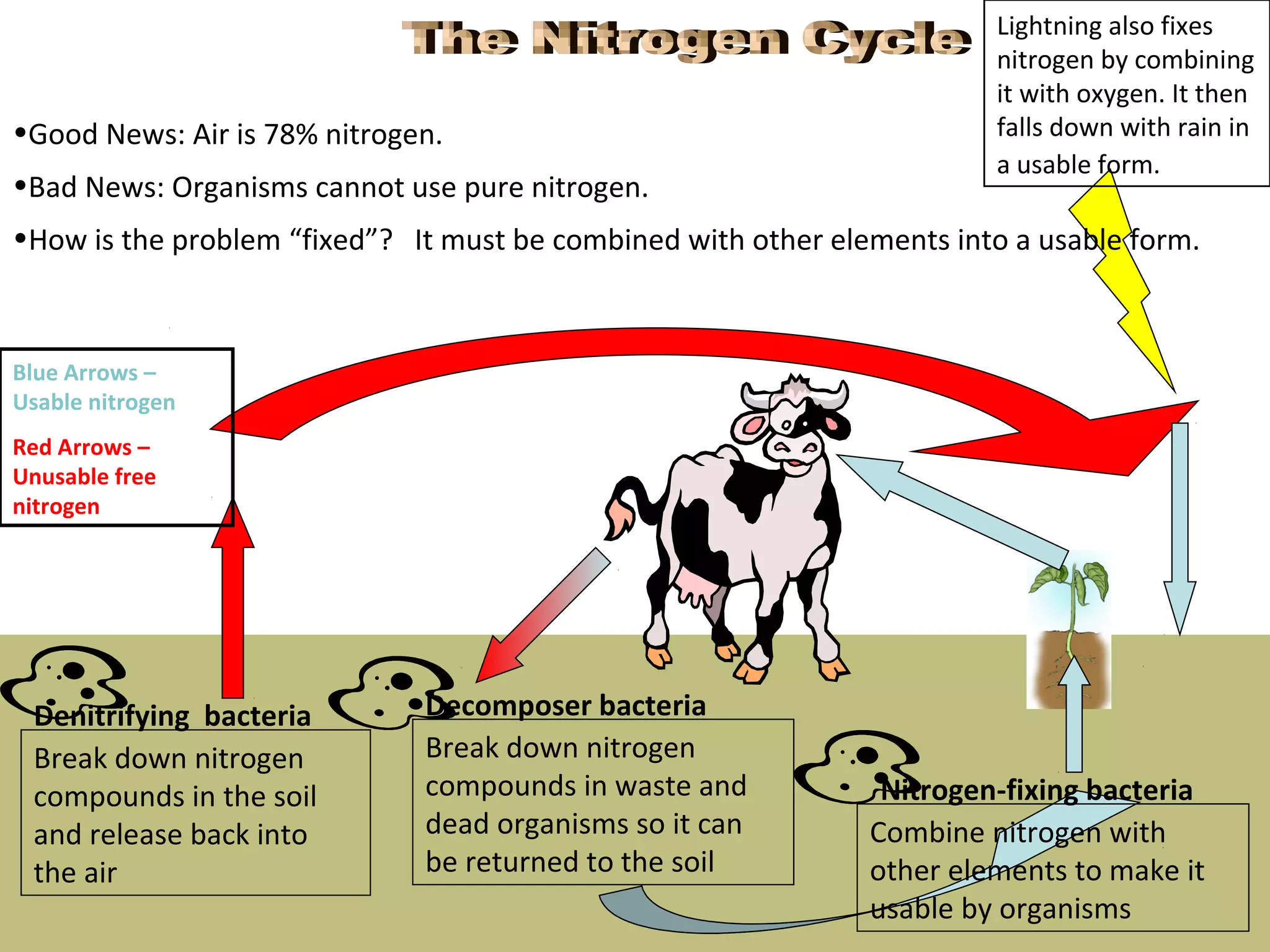
The carbon cycle describes the process by which carbon is exchanged between the biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon exists in different forms as it moves through the carbon cycle, including carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, carbon in living organisms, carbon dissolved in the ocean, and carbon stored in fossil fuels underground. The same carbon atoms are reused as they are exchanged between these reservoirs through various natural processes like photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion.