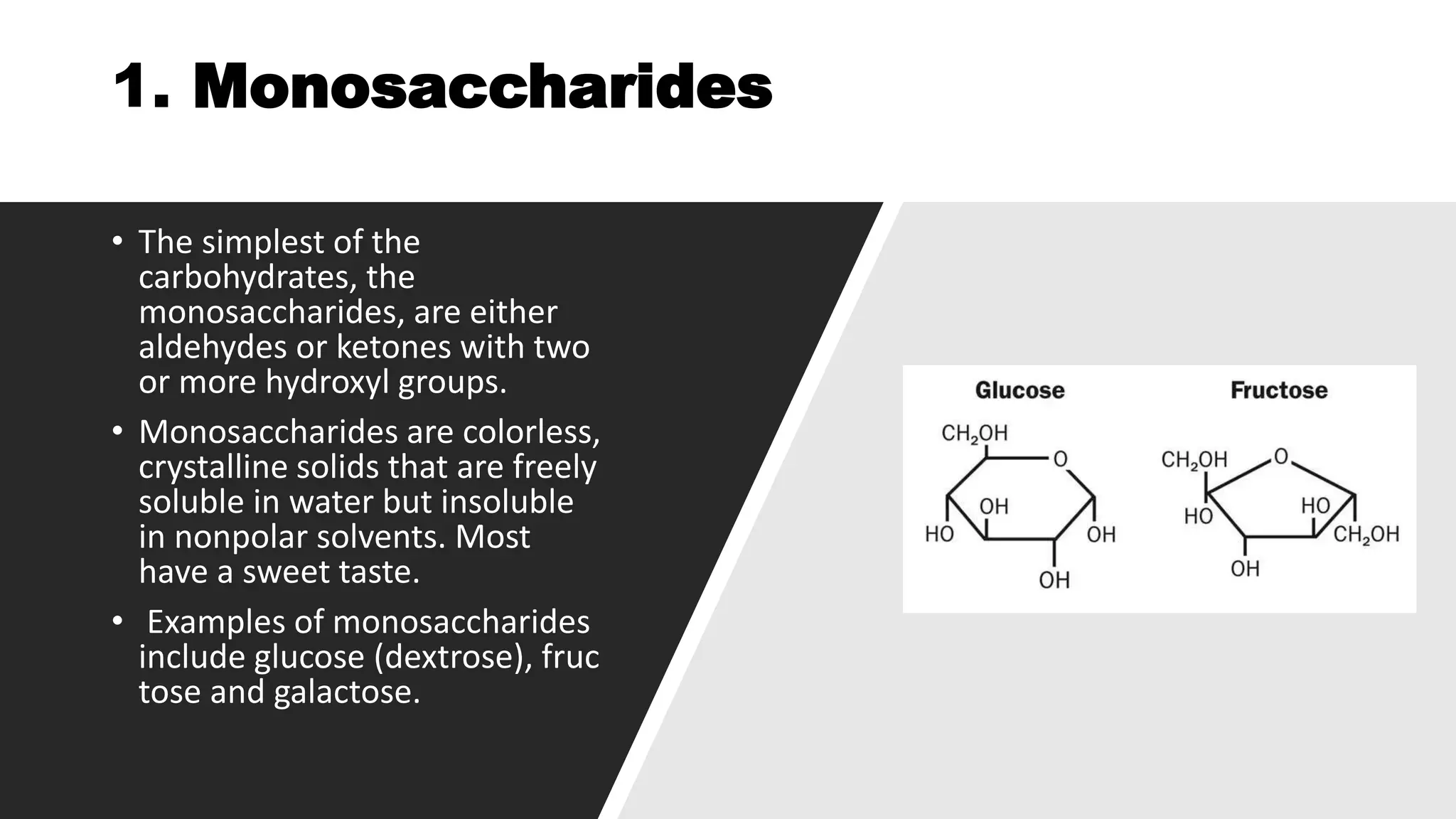
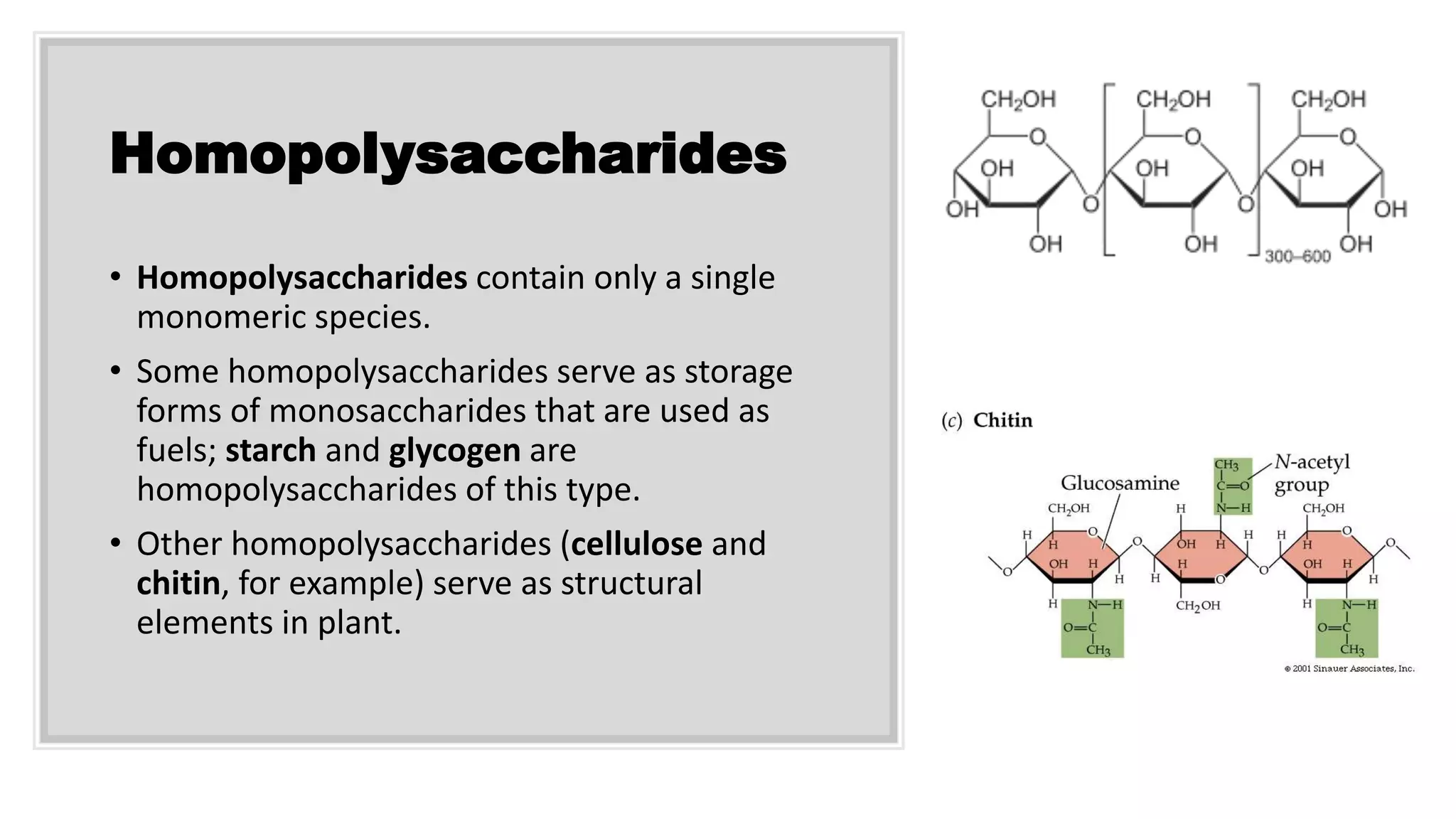
Carbohydrates are essential biomolecules made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, crucial for energy storage and structural functions in living organisms. They are classified into three main types: monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides, each serving different roles in biological processes. Sources of carbohydrates include cereals, fruits, and vegetables, while their diverse structures contribute to functions such as cell recognition and structural support.