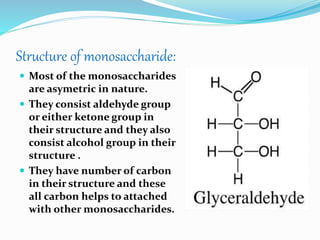
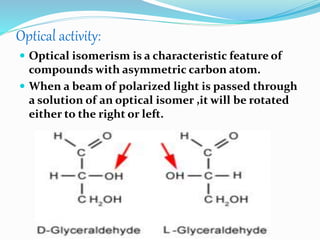
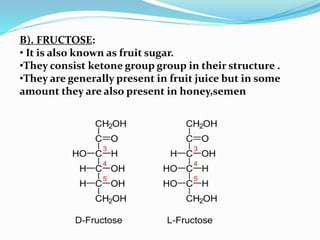
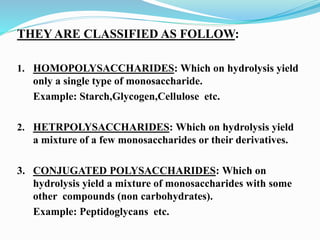
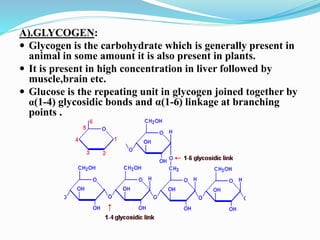
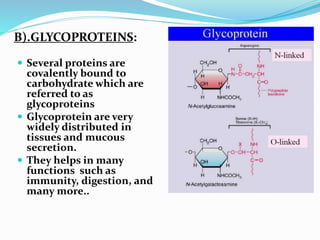
This document summarizes carbohydrates and their classification. Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and can be expressed by the formula (CH2O)n. They are classified as monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, or polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are the simplest form and include glucose and fructose. Oligosaccharides have 2-10 monosaccharide units and include sucrose and maltose. Polysaccharides are polymers of monosaccharides and include starch, cellulose, and glycogen. Carbohydrates serve important functions as energy sources and structural components.