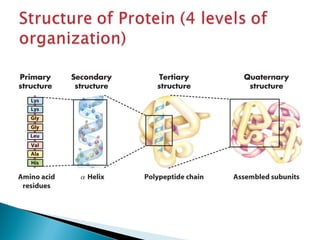
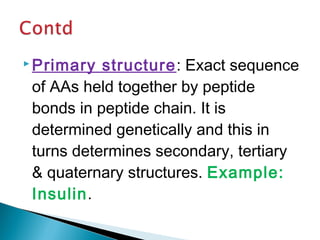
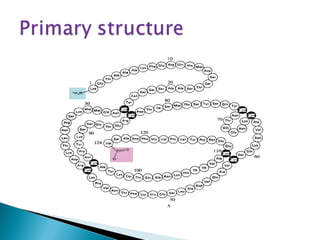
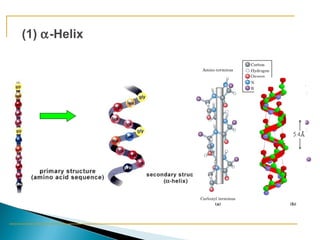
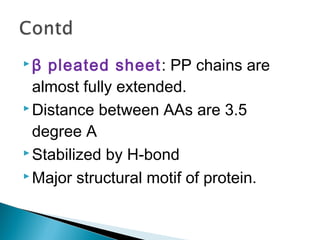
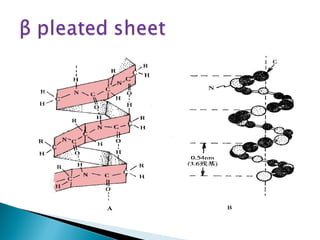
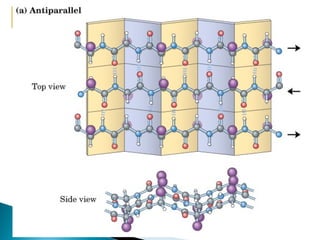
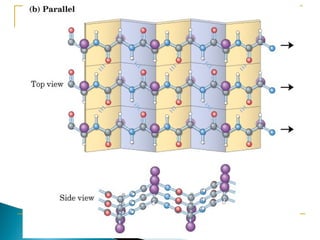
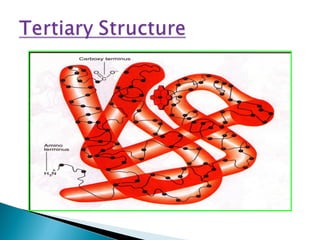
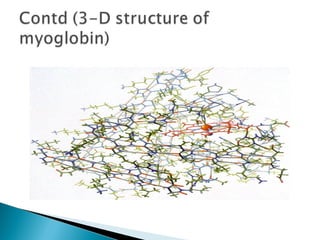
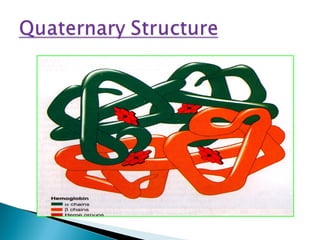
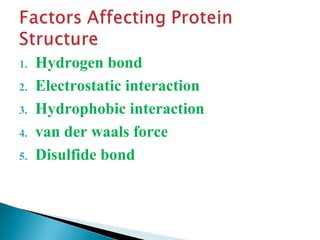
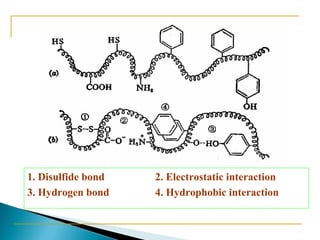
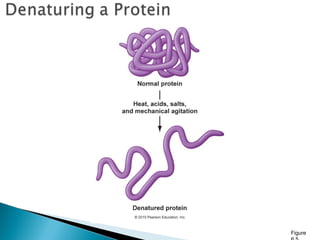
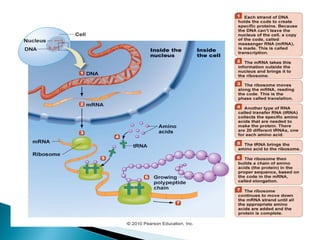
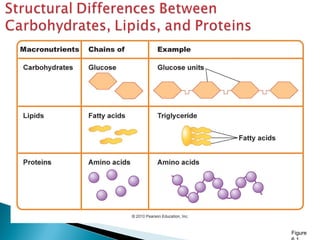
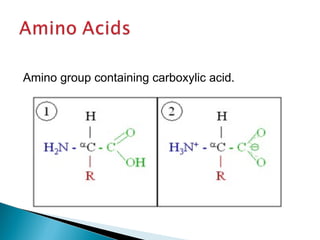
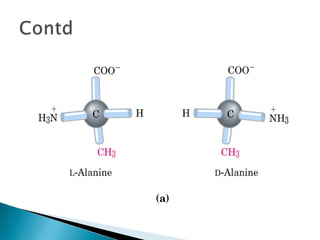
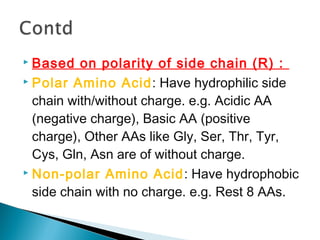
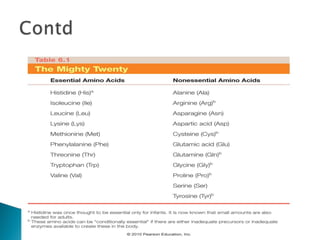
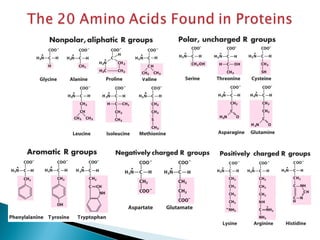
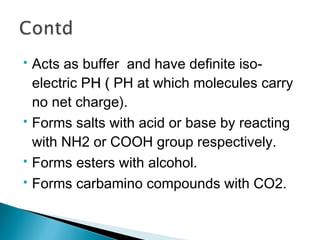
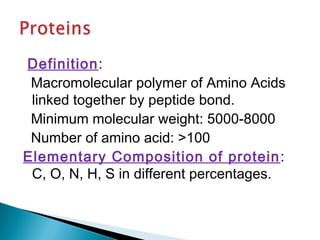
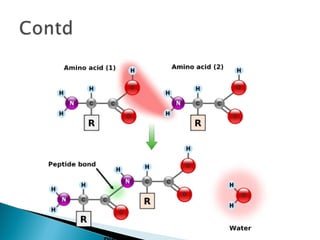
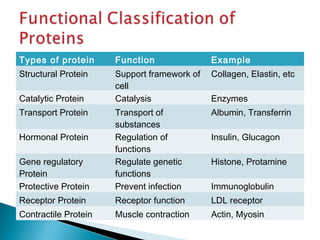
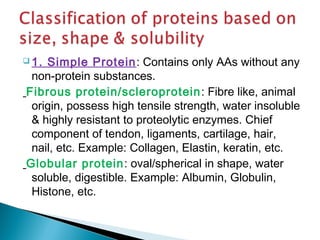
This document discusses proteins and amino acids. It defines proteins as large biomolecules composed of chains of amino acids that are essential to life processes. The 20 standard amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. They contain an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain that determines each amino acid's properties. Proteins have primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures that give them their final 3D shapes and functions in the body.














![ 1. Act as building block of peptides,
polypeptides & proteins.
[Arbitrarily peptide, polypeptide & protein
are made of 2-10 AAs, 10-100 AAs &
>100 AAs respectively.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/protein-141125215809-conversion-gate02/85/Amino-acid-Protein-23-320.jpg)



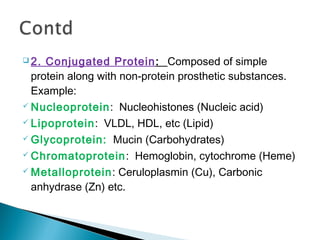
![3. Derived Protein: Denatured/degraded
products of simple/conjugated proteins.
Protein → Protean → Metaprotein → Proteose
→Peptone → Peptides → Amino Acids.
[Protean, Metaprotein → Primary derived
protein as no/little change in peptide bond,
Rest are secondary derived proteins
produced by progressive hydrolytic cleavage of
peptide bonds. ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/protein-141125215809-conversion-gate02/85/Amino-acid-Protein-32-320.jpg)