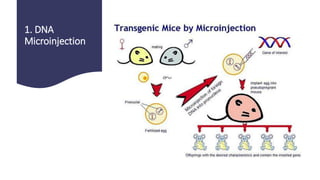
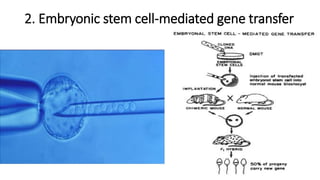
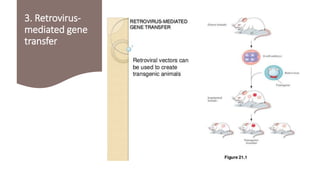
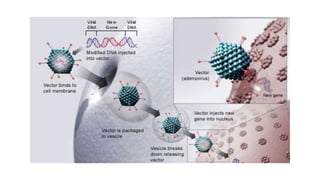
Transgenic animals are animals that have had a foreign gene deliberately inserted into their genome using recombinant DNA methodology. The first transgenic mice were created in 1980, and the first cloned mammal, Dolly the sheep, was born in 1996. There are three main methods for creating transgenic animals: DNA microinjection, embryonic stem cell-mediated gene transfer, and retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Transgenic animals produce useful products like monoclonal antibodies, blood clotting factors, and human milk proteins. They are used for medical research, toxicology studies, pharmaceutical production, and analyzing gene expression regulation. However, some ethical concerns exist regarding animal suffering during transgenic research experiments.