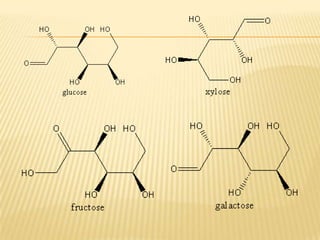
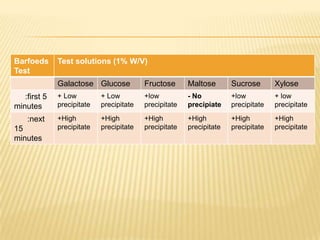
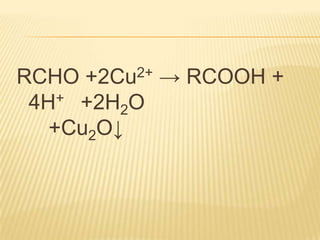
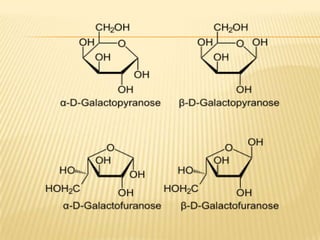
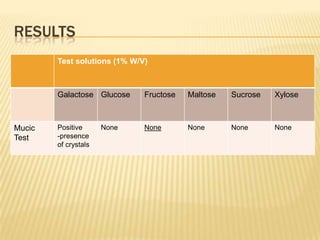
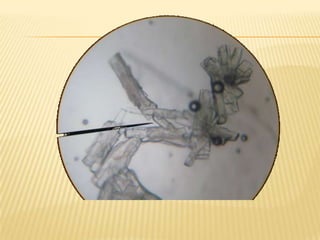
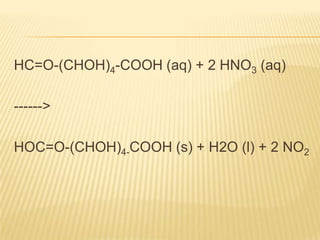
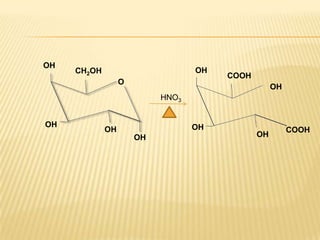
Barfoed's Test and the Mucic Test are chemical tests used to detect the presence of monosaccharides like galactose. Barfoed's Test detects monosaccharides by the reduction of copper(II) acetate to a brick-red copper(I) oxide precipitate. The Mucic Test identifies galactose specifically by oxidizing it with nitric acid to form insoluble saccharic acid crystals. These tests can help determine conditions involving monosaccharides like galactosemia, where the body cannot metabolize galactose properly.