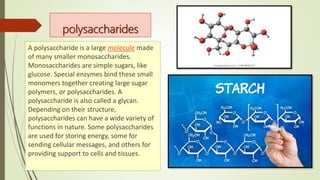
The document discusses carbohydrates, detailing their types (monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides) and functions in energy storage and cellular structures. Key monosaccharides mentioned are glucose, fructose, and galactose, along with important disaccharides like sucrose, lactose, and maltose. It also covers polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen, and cellulose, and addresses carbohydrate deficiency effects on health.