Embed presentation
Downloaded 339 times
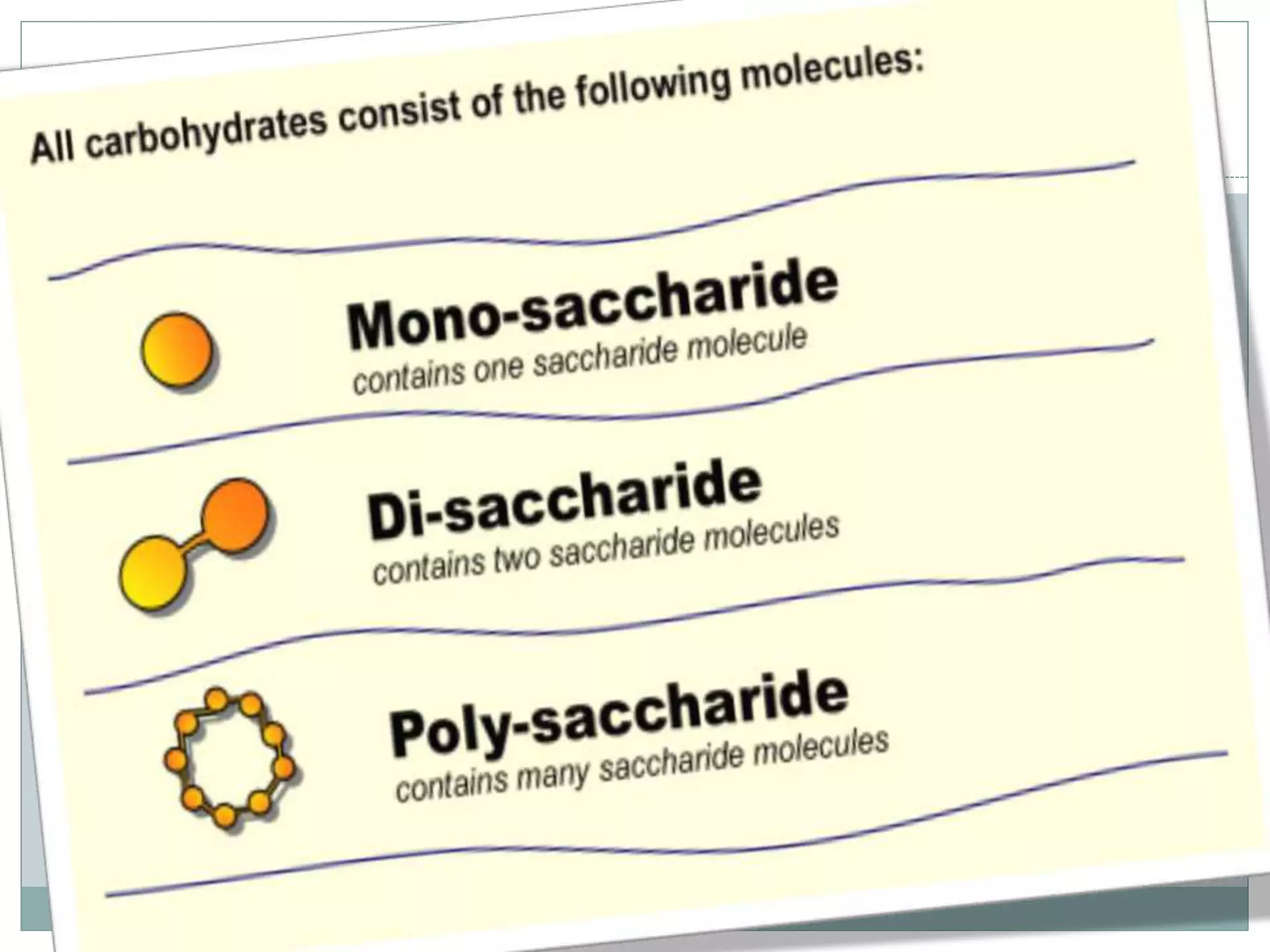
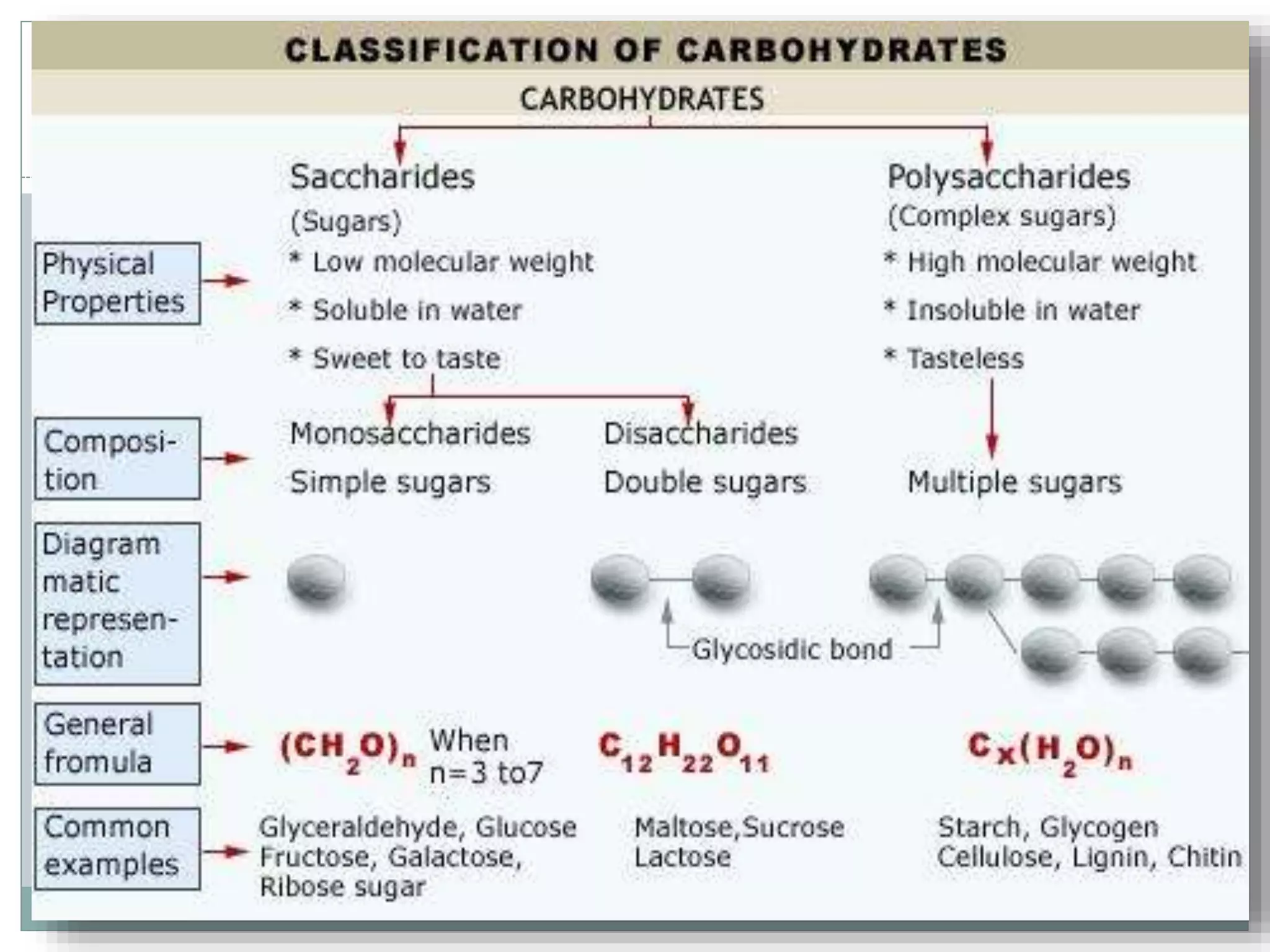


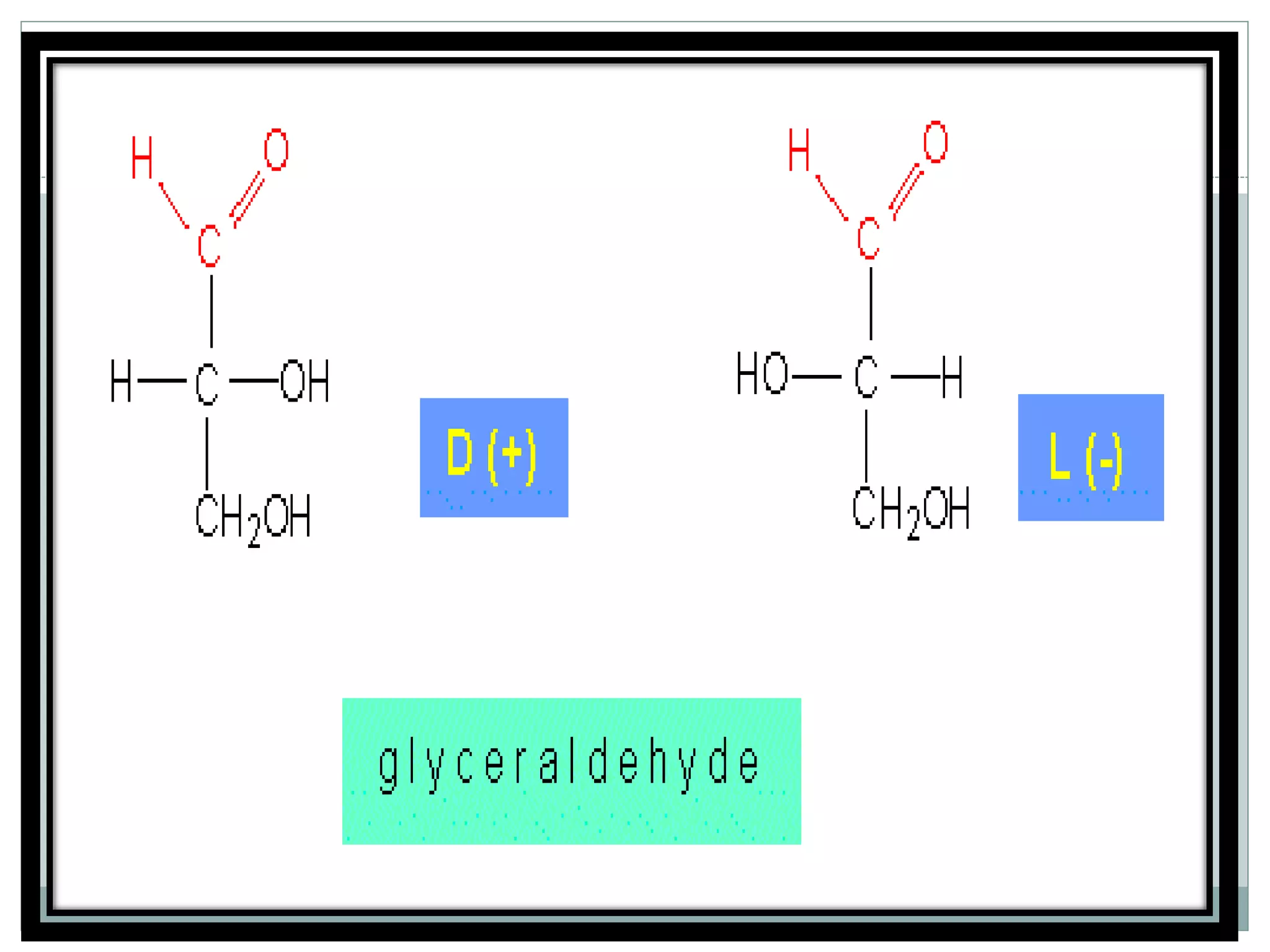
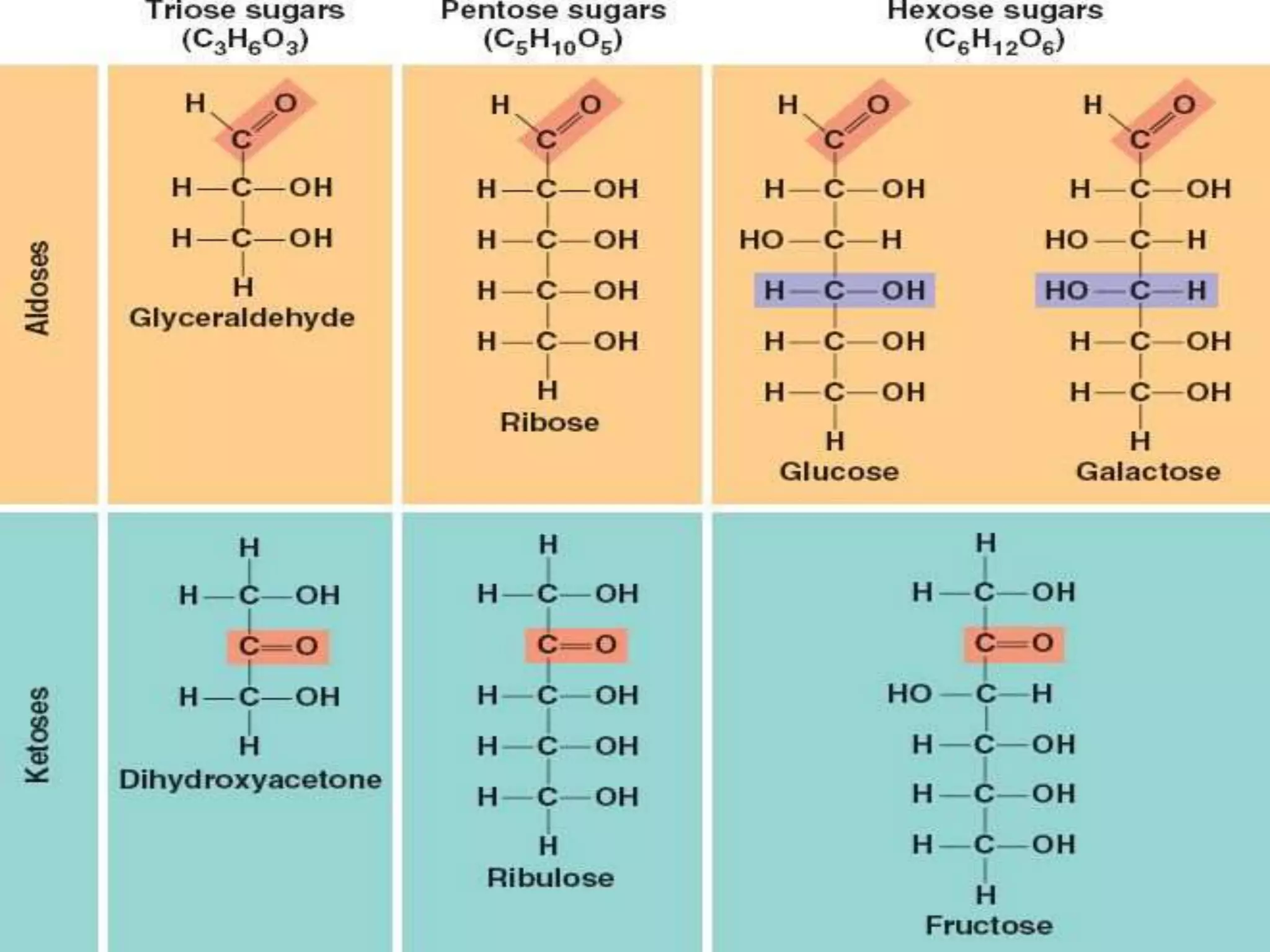




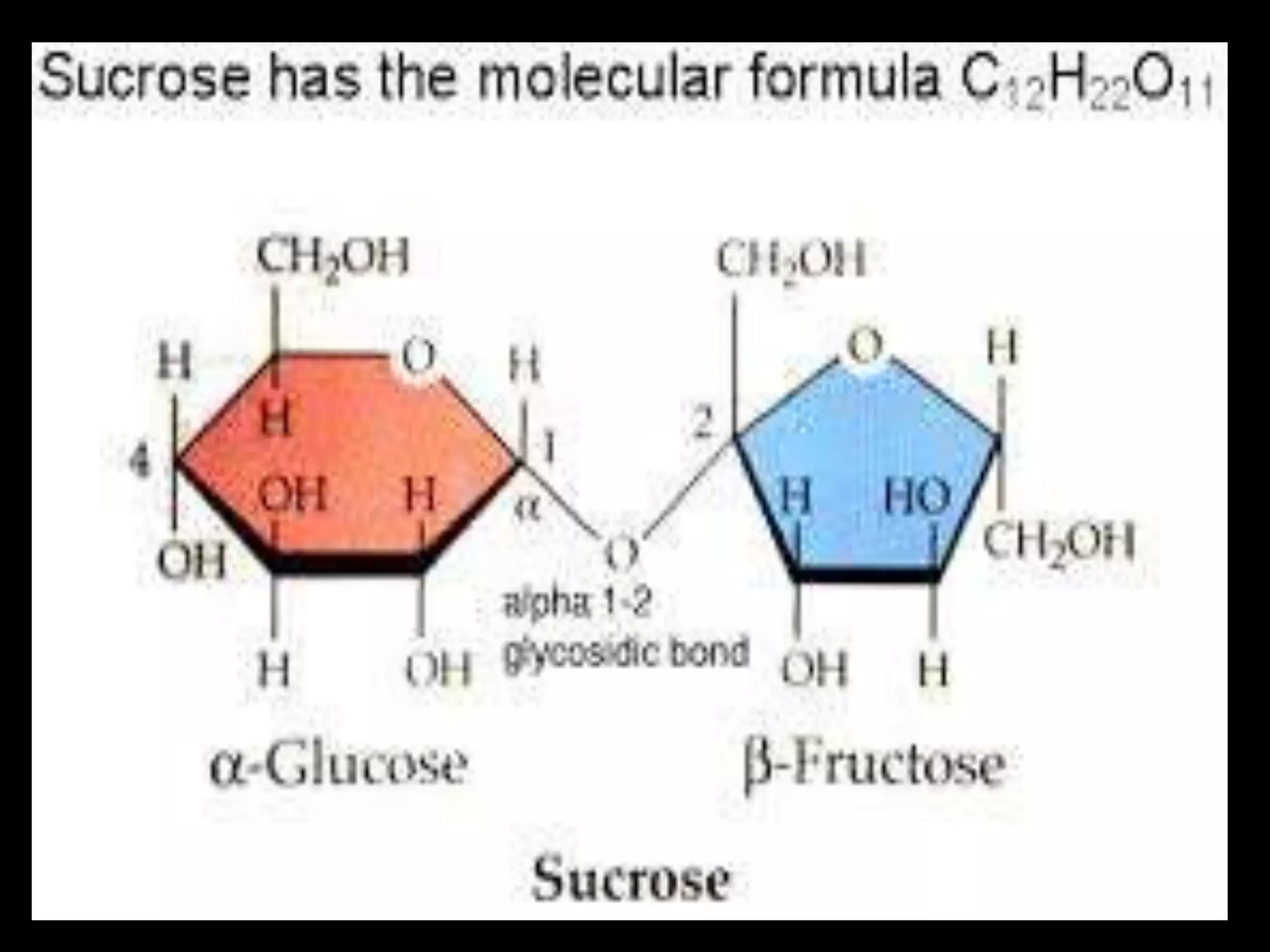

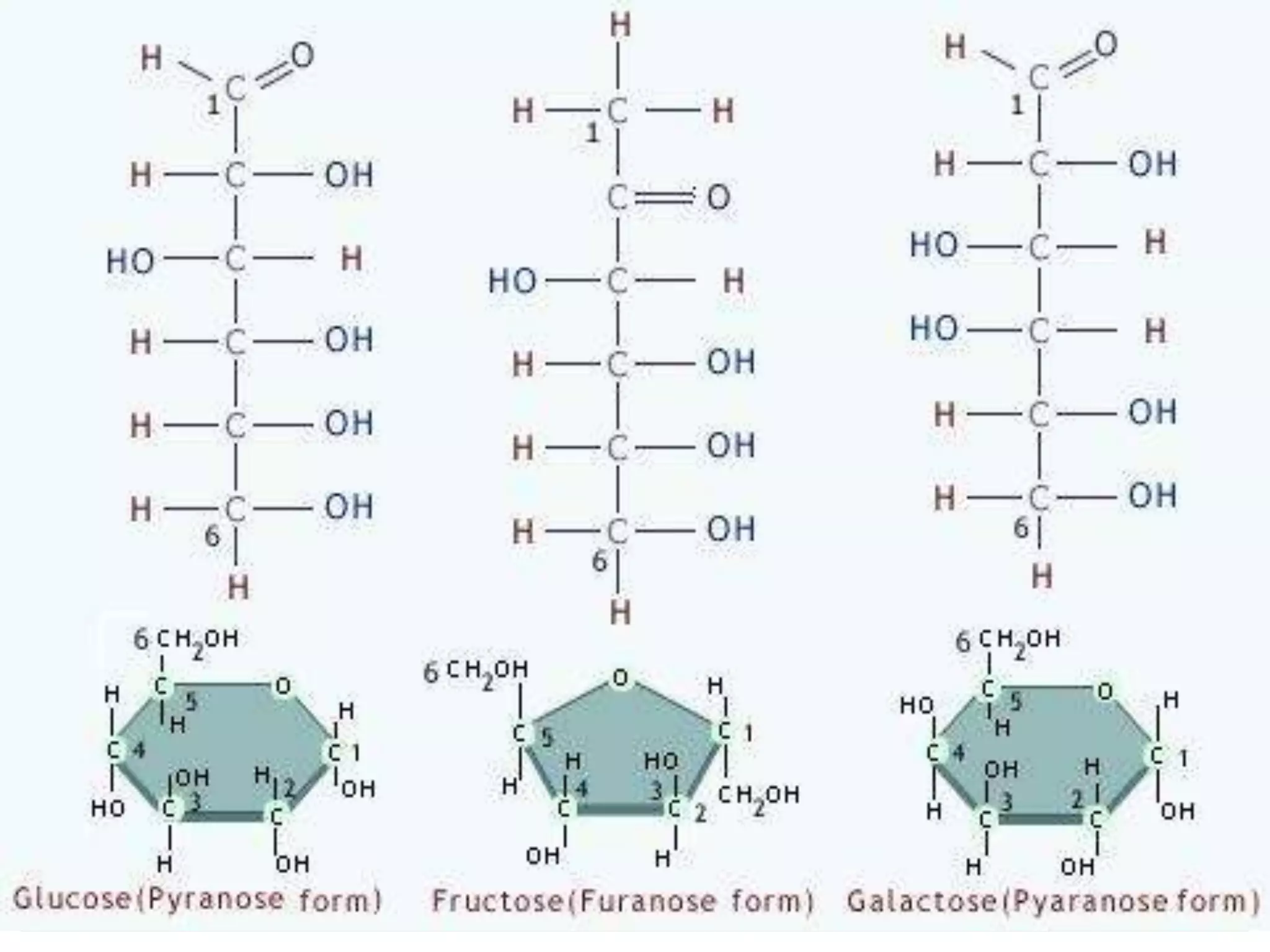


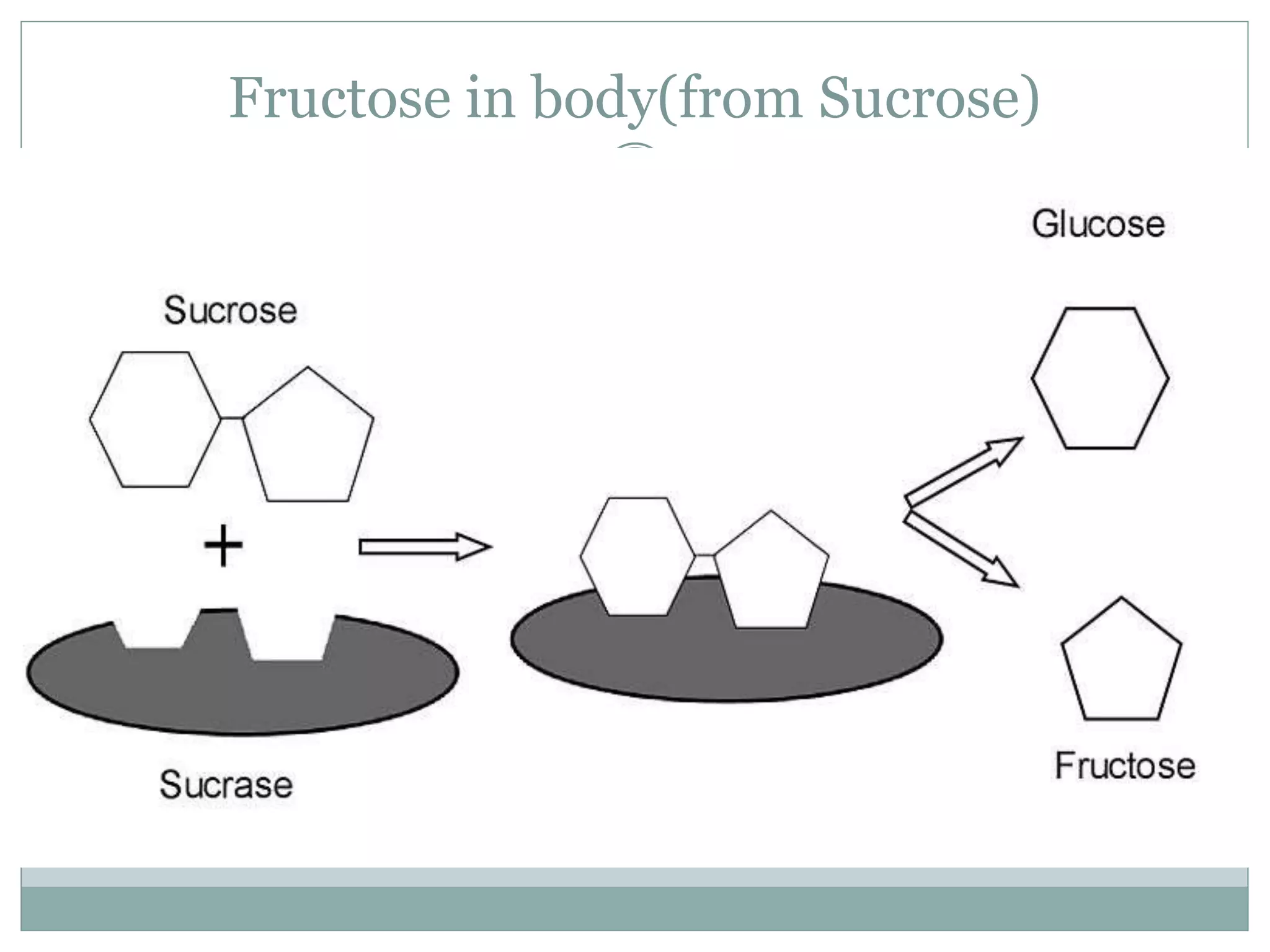
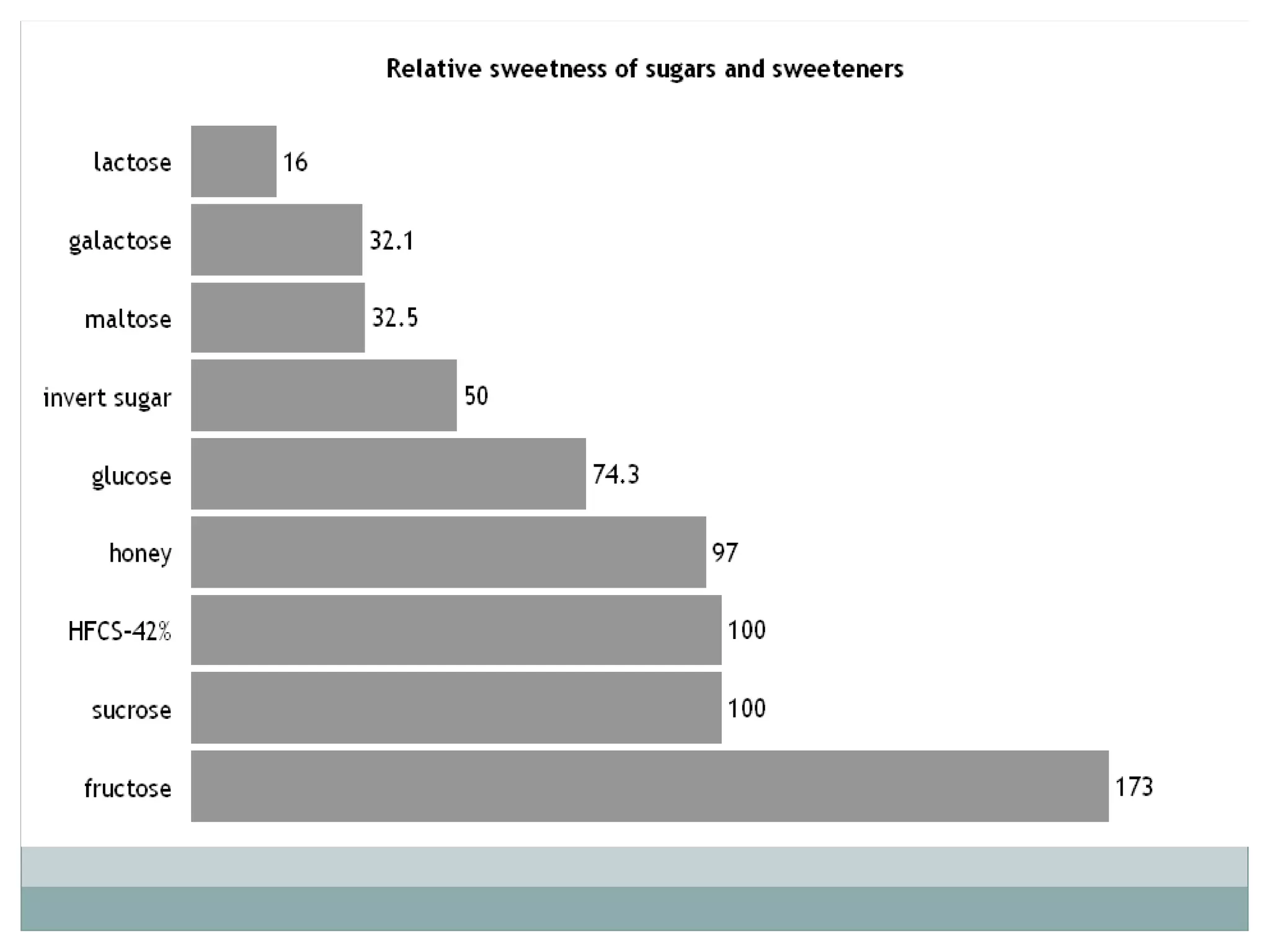

Monosaccharides are simple sugars with 3 to 7 carbons that are sweet in taste and cannot be further broken down. They include trioses like glyceraldehyde, pentoses that form the backbone of nucleic acids and polysaccharides, and hexoses such as glucose and fructose. Glucose is an important energy source for the body and precursor to cellulose, glycogen and starch. Fructose is sweeter than glucose and found naturally in fruits.
















